- Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans

How to Write the Operations Plan Section of a Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
How to Write the Operations Plan Section of the Business Plan
Stage of development section, production process section, the bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
The operations plan is the section of your business plan that gives an overview of your workflow, supply chains, and similar aspects of your business. Any key details of how your business physically produces goods or services will be included in this section.
You need an operations plan to help others understand how you'll deliver on your promise to turn a profit. Keep reading to learn what to include in your operations plan.
Key Takeaways
- The operations plan section should include general operational details that help investors understand the physical details of your vision.
- Details in the operations plan include information about any physical plants, equipment, assets, and more.
- The operations plan can also serve as a checklist for startups; it includes a list of everything that must be done to start turning a profit.
In your business plan , the operations plan section describes the physical necessities of your business's operation, such as your physical location, facilities, and equipment. Depending on what kind of business you'll be operating, it may also include information about inventory requirements, suppliers, and a description of the manufacturing process.
Staying focused on the bottom line will help you organize this part of the business plan.
Think of the operating plan as an outline of the capital and expense requirements your business will need to operate from day to day.
You need to do two things for the reader of your business plan in the operations section: show what you've done so far to get your business off the ground and demonstrate that you understand the manufacturing or delivery process of producing your product or service.
When you're writing this section of the operations plan, start by explaining what you've done to date to get the business operational, then follow up with an explanation of what still needs to be done. The following should be included:
Production Workflow
A high-level, step-by-step description of how your product or service will be made, identifying the problems that may occur in the production process. Follow this with a subsection titled "Risks," which outlines the potential problems that may interfere with the production process and what you're going to do to negate these risks. If any part of the production process can expose employees to hazards, describe how employees will be trained in dealing with safety issues. If hazardous materials will be used, describe how these will be safely stored, handled, and discarded.
Industry Association Memberships
Show your awareness of your industry's local, regional, or national standards and regulations by telling which industry organizations you are already a member of and which ones you plan to join. This is also an opportunity to outline what steps you've taken to comply with the laws and regulations that apply to your industry.
Supply Chains
An explanation of who your suppliers are and their prices, terms, and conditions. Describe what alternative arrangements you have made or will make if these suppliers let you down.
Quality Control
An explanation of the quality control measures that you've set up or are going to establish. For example, if you intend to pursue some form of quality control certification such as ISO 9000, describe how you will accomplish this.
While you can think of the stage of the development part of the operations plan as an overview, the production process section lays out the details of your business's day-to-day operations. Remember, your goal for writing this business plan section is to demonstrate your understanding of your product or service's manufacturing or delivery process.
When writing this section, you can use the headings below as subheadings and then provide the details in paragraph format. Leave out any topic that does not apply to your particular business.
Do an outline of your business's day-to-day operations, including your hours of operation and the days the business will be open. If the business is seasonal, be sure to say so.
The Physical Plant
Describe the type, size, and location of premises for your business. If applicable, include drawings of the building, copies of lease agreements, and recent real estate appraisals. You need to show how much the land or buildings required for your business operations are worth and tell why they're important to your proposed business.
The same goes for equipment. Besides describing the equipment necessary and how much of it you need, you also need to include its worth and cost and explain any financing arrangements.
Make a list of your assets , such as land, buildings, inventory, furniture, equipment, and vehicles. Include legal descriptions and the worth of each asset.
Special Requirements
If your business has any special requirements, such as water or power needs, ventilation, drainage, etc., provide the details in your operating plan, as well as what you've done to secure the necessary permissions.
State where you're going to get the materials you need to produce your product or service and explain what terms you've negotiated with suppliers.
Explain how long it takes to produce a unit and when you'll be able to start producing your product or service. Include factors that may affect the time frame of production and describe how you'll deal with potential challenges such as rush orders.
Explain how you'll keep track of inventory.
Feasibility
Describe any product testing, price testing, or prototype testing that you've done on your product or service.
Give details of product cost estimates.
Once you've worked through this business plan section, you'll not only have a detailed operations plan to show your readers, but you'll also have a convenient list of what needs to be done next to make your business a reality. Writing this document gives you a chance to crystallize your business ideas into a clear checklist that you can reference. As you check items off the list, use it to explain your vision to investors, partners, and others within your organization.
What is an operations plan?
An operations plan is one section of a company's business plan. This section conveys the physical requirements for your business's operations, including supply chains, workflow , and quality control processes.
What is the main difference between the operations plan and the financial plan?
The operations plan and financial plan tackle similar issues, in that they seek to explain how the business will turn a profit. The operations plan approaches this issue from a physical perspective, such as property, routes, and locations. The financial plan explains how revenue and expenses will ultimately lead to the business's success.
Related Articles

Operational Plan for Business Plan

It is important for a business plan to have an operational plan. Your business functions will not be complete if you will not set action plans and strategies that will be used for your operations.
- 19+ Hotel Operational Business Plan Examples
- 11+ Operational Plan For Cleaning Services Examples
Business Operational Plan Template

- Google Docs
Size: US, A4
Operational Plan Template

Startup Operational Plan Template

Having an operational plan can help you look into the quality standards and metrics that you need to consider to attain operational successes and other business goals and objectives. May it be a monthly, quarterly, or annual operational plan that you would like to develop or update as a part of your business plan, you always have to ensure that you are fully aware of the purposes of the document and how its usage can affect the actual operations of your business.
We have listed a number of operational plan for business plan examples that you can browse through and download in this post. Refer to these downloadable examples if you want to be more specific with the formatting and content development of your own operational plan.
Operational Plan and Budget for Business Plan Example

Size: 871 KB
Operational Plan for Business Plan Elements Example

Size: 172 KB
Operational Business Plan Example

Size: 91 KB
What Is an Operational Plan for Business Plan?
Just like a project operational plan , an operational plan for business plan promotes organization within all the processes that concerned stakeholders will be involved in. Every business should have an operational plan as this document can help point out operational goals, the gap that is needed to be filled during business operations, and the business condition that is needed to be achieved with the help of a proactive and productive workforce.
Here are some ways on how an operational plan for business plan can be defined:
1. An operational plan for simple business plan deals with the daily activities of the business. It helps prepare specific action plans that can be used to support the requirements, needs, and demands of the operations. This can help the workplace become more organized, functional, and appropriate for all the work processes that are needed to be done on a day-to-day basis.
2. An operational plan for business plan is an extremely detailed document that presents the tactics and strategies necessary to be implemented for operational growth and development.
For an operational plan to be highly usable, it needs to present the entities who will be responsible for the execution of particular call-to-actions, the details of the operational plan activities, the location where specific work functions will be implemented, and the time frames that are necessary to be considered when executing general action plans .
3. An operational plan for business plan ensures that the lower management is fully aware of the desired and demands of the upper management. With this document, there will be clarity with the direction where the operations will be brought which should be relevant and aligned with the objectives of the business. You may also see operational plan for restaurant examples .
4. An operational plan for business plan adheres to low-level management. This means that this document is helpful for single-area units like specific departments. As an example, a sales operational plan can help the sales team associate its professional goals , work processes, and action plans with the objectives of the business.
Annual Operational Plan for a Business Example

Size: 310 KB
Farm Operational Plan for Business Plan Example

Size: 350 KB
Bank Group Operational Plan for Business Plan Example

Size: 565 KB
Key Elements of an Operational Plan for Business Plan Example
Using an operational plan for business plan can help you define all the factors, elements, and components that you need to consider to ensure that all the objectives and goals of the upper management for its operations can be achieved. The same goes with how event management teams use an event operational plan to ensure that the workforce is well aware of what is expected from them.
Especially when dealing with potential operational successes, it is important for you to know how strategies and tactics can help business processes, operational workloads, and stakeholders’ relationships to be better. Here are the key elements that you should not forget to include in your own operational plan for general business plan :
- The desired output of the upper management and the operational guidelines that the workforce can refer to so that they can provide all their deliverable needed during operations.
- The strategies and tactics that you will incorporate in your business operations for you to yield better results and return of investments.
- The tasks, obligations, and responsibilities that are needed to be done in a timely manner to ensure that specific operational goals and objectives will be realized.
- The particular entities who will be assigned to take ownership of the incorporation of strategies or the execution of call-to-actions.
- The timeline that will serve as guide within the entire execution of the operational plan for business plan.
- The time frames or duration where particular operational activities are expected to be done, completed, and/or provided.
- The amount that will be used for the implementation of the operational plan for business plan and the financial resources where the required budget will be coming from. You may also see event operational plan examples .
- The performance indicators that can assess the quality of the results given by the workforce and other stakeholders with the help of the operational plan.
Operations and Maintenance Business Plan Draft Example

Business Plan Outline with a Thorough Operational Plan Example

Size: 12 KB
Things That You Need to Focus on When Developing an Operational Plan for Business Plan
It is essential for you to know the phases of the business management planning processes where you will incorporate the operational plan. You have to consider the different setups within various business areas so you can develop an operational plan that works for every department and division while still considering the overall corporate goal of the company. With this, you have to be keen with the development of your own operational plan for business plan.
Here are some of the things that you always need to look into when drafting the specified document:
1. Ensure that there is clarity with your objectives. You have to be aware of what it is that you truly want to achieve. If you can present the better goals that you have in mind for the operations of the business, then it will be easier for you to come up with strategies and process guides that can help your objectives be a reality.
2. Particularly and specifically present all the activities and functions that the operations team is expected to be delivered. The people that you will be working with must be knowledgeable of what you expect from them so that they can execute work processes accordingly. Having an operational plan for a business plan can also help the operations become more sensitive with the quality standards that they need to meet.
3. Speaking about quality standards, you have to set the measures and metrics that you will use for assessment and evaluation. It is essential for you to have a thorough process of identifying whether the operational plan is working for the benefit of the business, and not against the direction where the upper management would like the business to be at. You may also see annual operational plan examples .
4. List down all your desired outcomes. This should be based on your long-term and short-term goals . Specify the things that you would like to achieve in different time frames and periods. Through this, you can be aware of whether there is growth and development that is happening to the business and its operations with the usage of the operational plan that you have created.
5. It is important for you to consider the staffing needs of the operational plan for business plan that you will develop. You have to look into the current workforce pool of the company so that you can identify whether the plans that you have are realistic and attainable based on the number of people that you can work with. You may also like IT operational plan examples .
6. Present all the resource requirements, needs, and demands that are essential to be supplied within the actual implementation of the operational plan for business plan. You have to be aware of the resources that you will be needing, from the budget that you need up to the equipment and materials that are expected to be at hand and readily available, so that there will be a smooth execution of all your simple action plans for the business operations.
7. Develop an implementation timetable that can ensure the timeliness of all your work processes. You have to keep in mind that the daily operations of the business have particular requirements.
Hence, you have to make sure that all your listed work functions are time-sensitive. If you can present all the time frames for every operational action plan, then it will be easier for all point persons to execute their responsibilities in a timely manner. You may also checkout project operational plan examples .
8. Include all the processes, activities, programs, and efforts that are relevant to the operations of the business. You have to incorporate a particular success measure for monitoring the progress and growth of the business operations. Your b usiness operational plan should be evaluated and updated from time to time so you can ensure that the usage of the document is still effective.
Food Truck Operational Plan for Business Plan Example
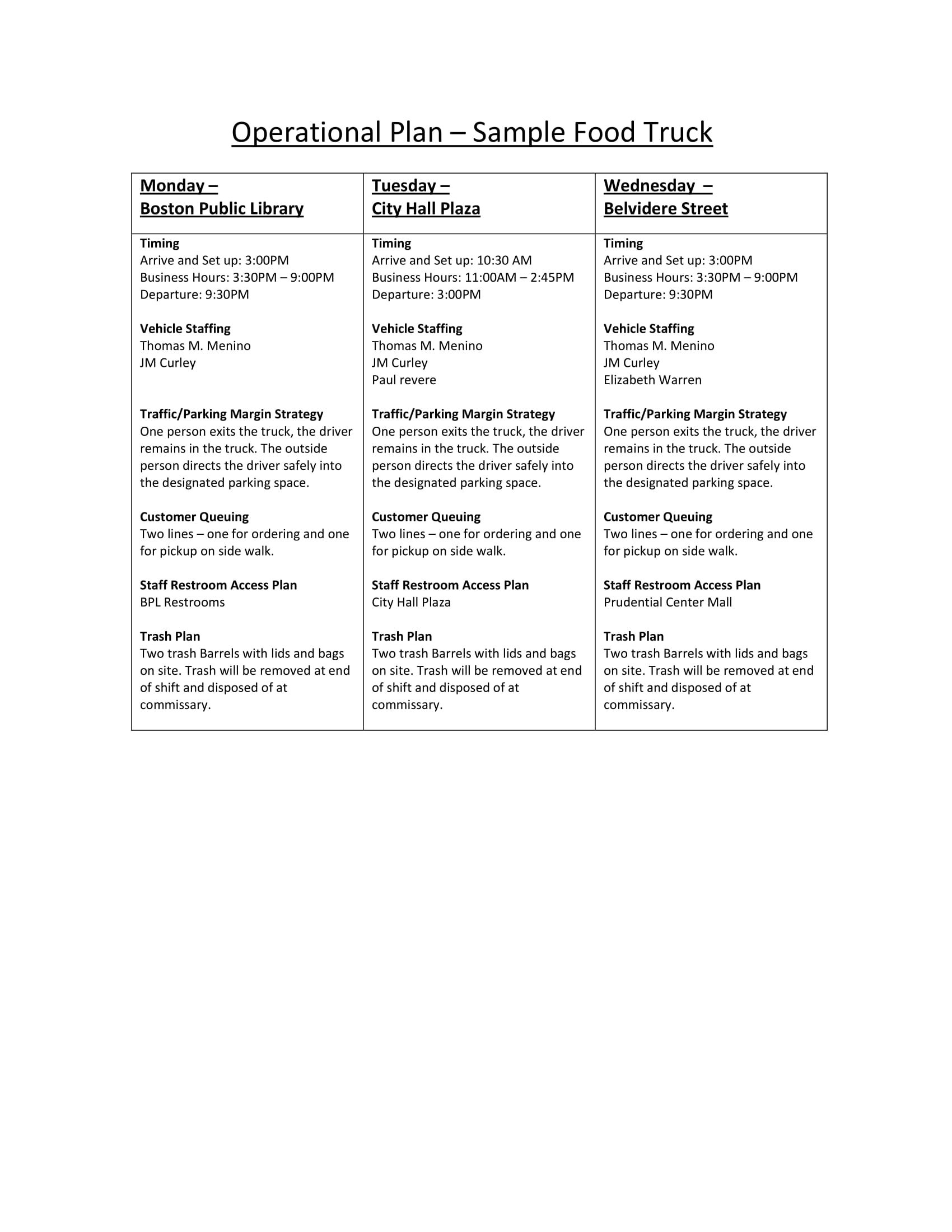
Size: 45 KB
Business Planning: Operating Plan or Operations and Maintenance Plan

Size: 54 KB
Operational Plan for Business Plan Example

Size: 116 KB
Guidelines and Instructions for an Operational Plan for a Business Plan Example

Tips and Guidelines for the Creation of an Operational Plan for Business Plan
Whether you are making an operational plan for a restaurant or any other kinds of businesses, you always have to ensure that the document that you will come up with is understandable, specific, direct to the point, and complete with all the details that you would like to disseminate to your target audience. A few of the useful tips and guidelines that you can refer to if you want to start drafting your own operational plan for business plan are as follows:
1. Ensure that the discussion in the operational plan for formal business plan are divided into clauses or segments. You have to present key points and areas of consideration in an organized manner so that it will be easier for the document to be understood and interpreted accordingly.
2. Know the nature of your business operations and how your performance as a corporate entity pars up with your competition. Having the knowledge about your current operational conditions can give you an idea on how you can develop formal action plans that can bridge the gap between the state of the business right now and the condition that you would like to experience, business operations wise.
3. Browse through a selection of operational plan for business plan examples especially those that have been used by successful businesses in the same industry. Being able to see the trends or common denominators in the development of this document can help you come up with an effective operational plan of your own. You may also see importance of business plan .
4. Be specific with your plan discussion. Limit the content of the document to its bare minimum ensuring that your operational plan only contains relevant and necessary information.
With the help and guidance of the operational plan for business plan examples that we have compiled just for you, we hope that you can have an easier and faster time in developing your operational plan for sample business plan . You can always go back to the discussion specified above if you need to refresh your mind about the proper and efficient creation of an operational plan.
Download any of our examples and try to create a well-formatted and comprehensive operational plan for business plan now.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.
How to Write an Operations Plan Section of your Business Plan
Free Operations Plan Template
- June 26, 2024

An operational plan bridges the gap between high ambitions and actual achievements. This essential integral section helps businesses thrive, achieve their goals, and handle challenges with accuracy and purpose.
But is it challenging for you to write one in a manner that shows a clear picture of your business operations? Drafting the operations plan section can be tricky due to the uncertainties of the business environment and the risks associated with it.
Well, worry not you’re at the right place! Here, we will see how to write an engaging operational plan in a business plan with an example. So let’s get going.
What is an operations plan?
An operations plan of a business plan is an in-depth description of your daily business activities centered on achieving the goals and objectives described in the previous sections of the plan. It outlines various departments’ processes, activities, responsibilities, and execution time frame.
The operations section explains in detail the role of a team or department in the collective accomplishment of your goals. In other words, it’s a strategic allocation of physical, financial, and human resources toward reaching milestones within a specific timeframe.
Key questions your operational plan should address

A successful operational plan section of your business plan should be able to answer the following questions:
- Who is responsible for a specific task or department?
- What are the tasks that need to be completed?
- Where will these operations take place?
- When should the tasks be completed? What are the deadlines?
- How will the tasks be performed? Is there a standard procedure?
- How much is it going to cost to complete these tasks?
Let’s see how to write the operations section that answers all the above questions:
Create winning business plans with our
AI Business Plan Generator
Plans starting from $7/month

How do you write an operations plan section?
Writing an operations plan within a business plan involves summarizing the day-to-day tasks necessary to run the business efficiently and meet its goals in both the development and manufacturing phases of the business.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:

1. Development phase
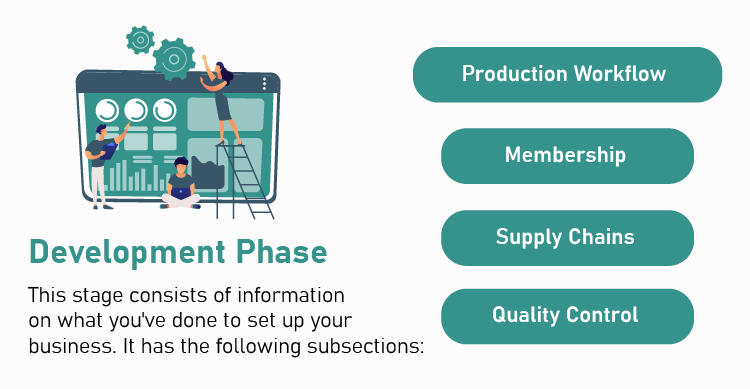
In this stage, you mention what you’ve done to get your business operations up and running. Explain what you aim to change and improvise in the process. These are the elements your development section will contain:
Production workflow
Explain all the steps involved in creating your product. Provide a detailed description of each step, including any inefficiencies and the actions needed to address them. Here, you also mention any inefficiencies that exist and talk about the actions that need to be taken to tackle them.
Write down the risks involved in the production and potential problems you may face later down the line. State the safety measures employees take to avoid any misfortune while working. Explain how you store hazardous material and discard waste.
Mention any industry organizations and associations you’re a part of or plan to join. It’s essential to include this information to convey to the reader that you’re aware of the organizations and associations in your industry.
Supply chains
Here, you mention the vendors you work with to sell your products. Give a quick rundown of the agreements you signed with them. Mention the terms and conditions, prices, and timeframe of the contract. You can also mention if you have any backup suppliers if the existing ones fail to fulfill the requirements.
Quality control
Describe the measures you’re taking to assure and verify the quality of the end product. If you’re working towards getting a product certification, explain the steps you take to meet the set standards.
2. Manufacturing phase
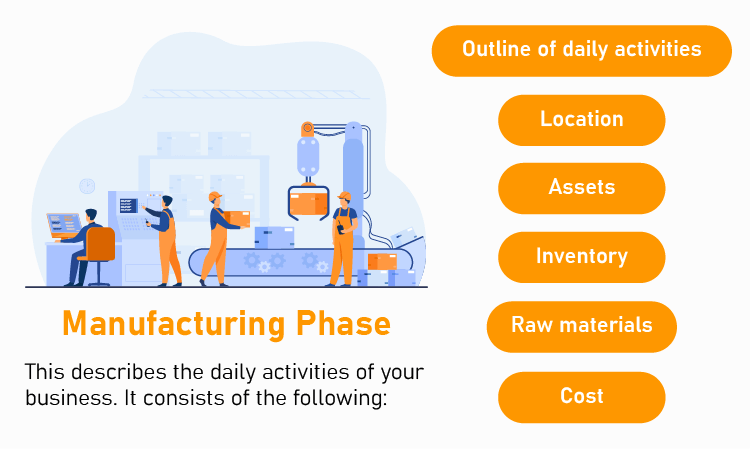
The development stage acquaints the reader with the functioning of your business, while the manufacturing stage describes the day-to-day operation. This includes the following elements:
Outline of daily activities
Create an outline of the day-to-day activities of the production process. This includes the hours of operation, days the business will be open, and whether the business is seasonal or not.
Mention the location of your business , other branches you have, and their locations. If available, include images or drawings of the buildings, lease documents, real estate agreements, and other relevant documents. If you include these in your plan, mention why they’re crucial.
Tools and equipment
Describe the tools and machinery you use. You should also include the cost of the equipment; these will be important to predict financial requirements.
List down all your assets. These include land, buildings, tools, machinery, vehicles, and furniture. Include a legal description and the value of these assets.
Special requirements
If you require any additional facilities like water supply or power requirements, you mention them here. Specify what you need to do or have already done to acquire permissions for these requirements.
Raw materials
Mention your raw material suppliers. If you need any extra materials, you can also include them in your operations plan. Here, you also mention the contracts and agreements with your suppliers.
Productions
Explain the production process and the time required to produce one unit. Include the factors that may disrupt the production flow. Further, mention your strategies to tackle these inefficiencies to avoid delays in manufacturing.
Here, you state the process of storing manufactured products, managing the stock, and the costs of the storage spaces. Stringent management of inventory is essential to maintain product quality and assure customer satisfaction.
Feasibility
To ensure the viability and effectiveness of your product, detail any tests it has undergone. This includes prototype testing to evaluate the design and functionality.
Additionally, highlight product or service testing, such as performance, safety, and user experience assessments. These tests validate your product’s readiness for the market, ensuring it meets customers’ needs and regulatory standards.
Include the pricing strategy for your products or services. You can also include the final prices of your products.
Outline your pricing strategy including which approach you used, for example—cost-plus, value-based, or competitive pricing. Include the final prices of your products or services, providing a breakdown if there are different tiers or packages.
Why do you need an operations plan?
An operations plan is like an instruction manual for your business. It helps investors assess your credibility and understand the structure of your operations.
Internally, an operations plan works as a guide, which helps your employees and managers to know their responsibilities. It also helps them understand how to execute their tasks in the desired manner—all while keeping account of deadlines.
The operations plan helps identify and cut the variances between planned & actual performance and makes necessary changes.
It helps you visualize how your operations affect revenue and gives you an idea of when you need to implement new strategies to maximize profits. Some of the advantages of preparing an operations plan include:
Offers clarity
Operational planning makes sure that everyone in the audience and team is aware of the daily, weekly, and monthly work. It improves concentration and productivity.
Contains a roadmap
Operational planning makes it much easier to reach long-term objectives. When members have a clear business strategy to follow—productivity rises, and accountability is maintained.
Set a benchmark
It sets a clear goal for everyone about what is the destination of the company and how to reach it.
Manages resources
It supports you in allocating resources, such as human resources, equipment, and materials, ensuring that nothing is wasted and everything is used optimally.
Helps in decision making
An operations plan helps make smart decisions by showing how the business runs day-to-day. It provides details on resources, wise investments, and effective risk management, ensuring that decisions improve overall business operations.
Operations plan essentials
Now that you have understood the importance of the operations plan, let’s go through the essentials of an operations plan:
Strategic plan
Your operations plan is fundamentally a medium for implementing your strategic plan . Hence, it’s crucial to have a solid plan to write an effective operations plan.
Having clear goals is one of the most important things for an operations plan. For clear goals, you need to think SMART:
- Specific: Clearly define what employees should achieve
- Measurable: Quantify the goal to track progress
- Attainable: Set ambitious but achievable goals
- Timely: Provide a deadline
Different departments will have their objectives, all supporting the main goal. All these strategic objectives are flexible and should align with the company’s long-term goals.
Key performance indicators
It’s essential to choose the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). It’s a good practice to involve all your teams while you decide your KPIs. Some of the important KPIs can be revenue growth, customer acquisition cost (CAC), net profit margin, churn rate, etc.
Creating a timeline with milestones is necessary for any business. It keeps everyone focused and helps track efficiency. If some milestones aren’t met in a certain period, then it’s time to re-evaluate them.
Examples of some milestones are:
- Hiring key team members in six months
- Setting checkpoints for different production phases like design, prototype, development, testing, etc.
- Acquiring the first 50 clients in a year
Now you’re all set to write an operations plan section for your business plan. To give you a headstart, we have created an operations plan example.
Operations Plan Example
We know this guide has been helpful for you in drafting a comprehensive operational plan section for your business plan.
If you’re still unsure or need help getting started, consider using business plan software like Upmetrics . It offers step-by-step guidance, so you won’t have to worry about what comes next.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a strategic plan and an operational plan.
A strategic plan outlines the long-term vision, mission, and goals of an organization, focusing on growth and direction over several years.
In contrast, an operational plan details the short-term tasks, processes, and resource allocation needed to achieve those strategic goals, emphasizing day-to-day efficiency and productivity.
What role does the operations plan play in securing funding for a business?
The operations plan defines the clear goals of your business and what actions will be taken daily to reach them. So, investors need to know where your business stands and it will prove the viability of the goals helping you in getting funded.
What are the factors affecting the operations plan?
Some of the factors that affect the operations plan are:
- The mission of the company
- Goals to be achieved
- Finance and resources your company will need
Can an operations plan be created for both start-up and established businesses?
Yes, both a startup and a small business need an operations plan to get a better idea of the roadmap they want for their business.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Get started with Upmetrics Al
- 400+ sample business plans
- Al-powered financial planning
- Collaborative workspace
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
How to Write the Operations Plan Section of Your Business Plan

The Operations Plan is a component of your business plan that is like the engine of your car. The operations plan holds the key parts of your business, and it shows how those parts work together to keep the business running. If you are starting a business or your business is growing, the operations plan also shows that your business is more than just a good concept. It shows why the business is running smoothly and how key milestones ahead will be met as the business grows. The operations plan is the powerhouse engine in your business plan . Let’s start that engine together.
What is the Operations Plan in a Business Plan?
The key to putting your operations plan together is choosing which processes show how your business works and what the expected outcomes will be as a result. Include the processes that you believe are most important even if they are basic or simple. And, if you think your business is too new to create an operations plan, think again. Every business has processes, no matter how large or small they may be. Your operations plan may be considered by potential investors or lenders; make it the best it can be.
Components of a Comprehensive Operations Plan
The best operations plan includes a list of key processes with short explanations that detail each process. Some explanations will also include a brief sentence explaining how the key process will help the business meet the expected key milestones. For example, “Our Marketing team will post on social media each time our product sales reach one of our sales goals. This will drive new customers to our product offering.”
Main components of an operations plan:
Product Development
Describe how the product is being developed and if it is currently offered or is on target for launch. Include the production process for testing, improvements or revisions.
Key milestone : Note the forecast for new product development to expand the product line.
Manufacturing
Describe the process of manufacturing, from the first step to the delivery of products. This may include several bullet points. Add facilities maintenance in this section. Also, include the management processes of the staff.
Key milestone : Include a brief forecast with plans to increase manufacturing capabilities.
Administration/Human Resources
Include a description of day-to-day activities that are overseen by staff members, including facilities management, safety, reports and compliance, hiring staff and training.
Key milestone : Add a sentence regarding staff training for leadership as the business grows.
List the process of purchasing parts, services, products, and raw materials. Include a sentence about financial oversight of expenditures to control costs.
Key milestone : Indicate how the staff is preparing for purchasing increases to meet higher manufacturing demands.
Customer Service
List the processes that comprise customer service, including any customer relationship management software (CRM) or other processes that interact with customers. Provide details on processes for customer retention.
Key milestone : Add a sentence describing staff training to build customer relationships.
Describe how your business conducts sales, whether through online channels, via wholesale or retail sales, or by other means. Explain why the process works for your business and how it is positioned to be successful because of the sales process.
Key milestone : Indicate how planned sales strategies will expand to meet key milestones.
Note the process of current marketing campaigns and the response of the target audience. Note how responses are scored on social media.
Key milestone : Include operational plans for building brand awareness, key selling points, and entry positions.
At this stage of business, the finance process should be clearly outlined, with current and any expected funding included. Also, include a sentence about how the business has structured a repayment plan for any loans and is making on-time payments.
Key milestone : Describe any anticipated funding options that have already been put into place.
Accounting/Payroll:
Describe in a few sentences how timely accounting is completed on a regular basis. Add a sentence about the payroll system and the software that runs it.
Key milestone : Add a note about increasing software programs in accounting to increase performance during growth.
Include a sentence about the process of oversight for the business. Add the process of documentation, filings, and oversight of any copyrights, patents, or trademarks. Include any licensing payments that add revenue to the business.
Key milestone : Include a description of the legal process already in place to accommodate expansion and long-term growth.
How to Write the Operations Plan For Your Business
Now that you’ve read about the main components in a business operations plan, it’s time to connect them in writing your own operations plan. To do this, you can follow the easy steps ahead as you construct each process.
Remember, you may not need all of the processes listed here. You will want to choose those that make sense for your business and, if needed, add some others. When completed, your operations plan will flow smoothly from start to finish.
- Consider your Business Goals . Write out each goal. Read them as you decide which processes to include in your operations plan and think about how soon you will want to meet the company goals.
- Create a Process List . Look at the list of components and decide how to make them into a list for your own business. Don’t write out full descriptions yet. We’re building the list first. How do processes start in your business?
- Finance (get funding)
- Product Development (buy a truck, provide services, equipment, tools)
- Manufacturing (maintain the garage and tow truck)
- Sales (make sales calls)
- Customer Service (answering texts, and emails)
- Marketing (getting referrals from friends)
- Accounting/Payroll (paying yourself and the bookkeeper)
- Legal (risk management assistance)
- Start filling in the Process Descriptions . Use the examples above to describe the processes of your business. A few sentences that explain each process are all you need in the operations plan.
- For example, key milestones for your tow truck business might be:
- Tow at least five vehicles daily during each week (sales/marketing)
- Buy a second tow truck within 6 months (finance)
- Add a second tow truck driver within 6 months (human resources)
- Buy a commercial truck within 12 months (finance/product development)
- Finish your Operations Plan . Re-read each Process Description and complete the Key Milestones for each operations section.
Sample Operations Plan for Badger Drains & Plumbing
Badger Drains & Plumbing, based in Milwaukee, WI, is dedicated to providing top-notch residential and commercial plumbing services. Our operations plan outlines the key processes that make our business run smoothly and how we plan to meet our key milestones as we grow.
Our services, instead of physical products, are continuously refined based on customer feedback and technological advancements in plumbing. This includes adopting newer, more efficient ways to conduct pipe repairs, installations, and maintenance services.
Key milestone : To introduce environmentally friendly and cost-effective plumbing solutions within the next year.
Our staff handle day-to-day operational tasks, prioritizing safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. This includes everything from scheduling service calls to conducting routine safety checks and equipment maintenance.
Key milestone : Implement a leadership development program for senior technicians to prepare them for managerial roles as the company expands.
We procure high-quality plumbing materials, tools, and technologies from reputable suppliers, ensuring we have the necessary inventory to meet customer demand without excessive expenditure.
Key milestone : Strengthen relationships with key suppliers to negotiate better prices and ensure priority fulfillment as service demand increases.
Customer service is a pillar of our operations, involving not just resolving issues but proactively enhancing customer satisfaction through follow-ups and feedback collection using CRM software.
Key milestone : Introduce a loyalty program by the end of the next quarter to increase customer retention rates.
Sales efforts are directed through personal client interactions and digital marketing to generate leads, with a strong focus on the benefits of choosing Badger Drains & Plumbing for reliability and professionalism.
Key milestone : Achieve a 20% increase in annual contracts by targeting commercial entities in the Milwaukee area.
Our marketing is focused on local SEO, targeted ads, and social media engagement to connect with the Milwaukee community, emphasizing our quick response times and quality service.
Key milestone : Launch a community-oriented campaign to increase brand visibility and customer engagement by participating in local events and sponsorships.
Our current financing includes business revenue and a small business loan, with a diligent approach to budgeting and a clear plan for loan repayment and future investments.
Key milestone : Secure a line of credit to fund an expansion of services within the next two years.
Accounting/Payroll
We use modern software solutions to ensure accurate and timely financial and payroll management, allowing us to focus more on serving our customers and less on back-office tasks.
Key milestone : Transition to a more comprehensive software suite that integrates CRM and finance for better overall management efficiency.
Our legal framework encompasses regular reviews of compliance, documentations, and the management of any intellectual property, ensuring all operations are above board.
Key milestone : Establish a retainer partnership with a legal firm specializing in small businesses to prepare for interstate licensing and expansion.
By following this operations plan, Badger Drains & Plumbing aims to enhance its service offerings, optimize operational efficiency, increase productivity, and achieve sustainable growth, maintaining its commitment to being Milwaukee’s trusted plumbing service provider.
If You Aren’t a Writer or Have No Time to Write…
The truth is, not all of us are writers and some of us don’t have time to spare. The good news is that we have a solution for you in the newest software designed for entrepreneurs and business owners who need a complete business plan–without having to write one.
If you would like to easily create a comprehensive business plan, you can join over 100,000 entrepreneurs and business leaders who’ve created their business plans with PlanBuildr.
Why do we offer PlanBuildr? We are business owners. We know your time is valuable. And, we know a comprehensive business plan is vital when it’s time to obtain funding or secure investors. Not all of us are writers, but we all know good value when we see it. Try PlanBuildr for free !

- Business Planning
- Venture Funding

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Jul 30, 2023 · For example, if a train manufacturer develops a plan to expand revenue by 50% that plan will include a marketing, sales and operations component. The operations component of the plan would include procurement, manufacturing and logistics strategies that enable the firm to boost production to support revenue growth.
Dec 1, 2024 · An operational plan template offers organizations a platform for creating a smooth workflow. Organizations may use an operational plan outline to get a single platform that provides goals to be followed. It brings every interested party in the business on board. A business operations plan template ensures everyone is playing their role from the ...
Aug 21, 2024 · In your business plan, the operations plan section describes the physical necessities of your business's operation, such as your physical location, facilities, and equipment. Depending on what kind of business you'll be operating, it may also include information about inventory requirements, suppliers, and a description of the manufacturing ...
May 24, 2024 · Key Elements of an Operational Plan for Business Plan Example. Using an operational plan for business plan can help you define all the factors, elements, and components that you need to consider to ensure that all the objectives and goals of the upper management for its operations can be achieved.
Jun 26, 2024 · An operations plan of a business plan is an in-depth description of your daily business activities centered on achieving the goals and objectives described in the previous sections of the plan. It outlines various departments’ processes, activities, responsibilities, and execution time frame.
If you are starting a business or your business is growing, the operations plan also shows that your business is more than just a good concept. It shows why the business is running smoothly and how key milestones ahead will be met as the business grows. The operations plan is the powerhouse engine in your business plan. Let’s start that ...