- Create new account
- Reset your password
Register and get FREE resources and activities
Ready to unlock all our resources?

The Vikings

Who were the Vikings?
The Vikings came from all around Scandinavia (where Norway, Sweden and Denmark are today). They sent armies to Britain about the year 700 AD to take over some of the land, and they lived here until around 1050.
Even though the Vikings didn’t stay in Britain, they left a strong mark on society – we’ve even kept some of the same names of towns. They had a large settlement around York and the Midlands, and you can see some of the artefacts from Viking settlements today.
Top 10 facts
- The Vikings are also called Norsemen, and came from Scandinavia.
- They spoke Norse , which had an alphabet made up of characters called runes.
- They travelled over the sea in longships, which are long, narrow wooden boats that could be sailed in both deep and shallow water.
- The Vikings left their homeland because they were looking for better places to farm than the kind of terrain that Scandinavia had.
- The Vikings first attacked Britain in 787 AD, but didn’t start to invade and settle in the British Isles until 793 .
- In 878, King Alfred the Great defeated the Vikings in battle and had them sign a treaty saying they had to keep to their own land in England – this section of land was called Danelaw.
- Jorvik was a large Viking kingdom around York ; the last king of Jorvik was Eric Bloodaxe in 954.
- Viking warriors believed that when they died in battle, they went to Valhalla – this is where the king of the gods lived, named Odin.
- England once had a Viking king: King Canute ruled from 1016-1035, and his descendants ruled until 1042.
- A few weeks before the Anglo-Saxons were defeated in the Battle of Hastings in 1066 , they defeated Viking warriors near York, led by Harald Hardrada at the Battle of Stamford Bridge.

- 793 The Vikings attacked a monastery at Lindisfarne in Northumbria and started to settle in England
- 866 The Vikings raided and conquered York, and established the Viking Kingdom of Jorvik

- 878 Alfred the Great defeated the Vikings at the Battle of Ethandun
- 886 The boundary between Anglo-Saxon and Viking territories was established, called Danelaw
- 950 Viking armies raided Wales
- 954 The Viking Kingdom of Jorvik became part of England again
- 994 Viking armies from Denmark and Norway attempted to raid London, but were defeated

- 25 September 1066 The Battle of Stamford Bridge took place near York, between the Anglo-Saxons and Viking invaders led by Harald Hardrada
- 14 October 1066 William from Normandy, "William the Conqueror", won the Battle of Hastings and the Normans began to rule England

Boost Your Child's Learning Today!
- We'll created a tailored plan for your child...
- ...and add English & maths activities to it each week...
- ...so you can watch your child grow in skills & confidence
Did you know?
- The word ‘Viking’ means ‘a pirate raid’ in the Norse language, which is what the Vikings spoke.
- ‘-by’, as in Corby or Whitby, means ‘farm’ or ‘town’
- ‘-thorpe’, as in Scunthorpe, means ‘village’
- The Viking alphabet, ‘Futhark’, was made up of 24 characters called runes. Each one stood for entire words or gods, as well as sounds.
- There was a large Viking community around York called Jorvik. Archaeologists have found out a lot about the Vikings thanks to the artefacts they found there.
- The Vikings kept long benches in their homes that they’d use to sit on during the day, and then to sleep on at night. Only rich people had beds.
- In Viking times, people usually just took baths once a week! This was often on Saturdays.
- The Normans from France who defeated the Anglo-Saxons in the Battle of Hastings were actually descendants of Vikings! Vikings settled around more places than just Britain – they went to Ireland , Iceland, Greenland, France and Spain too.
Can you find the following in the gallery below?
- A map showing where the Vikings originally lived, and where they settled in Britain and Ireland
- A map showing the Danelaw
- A replica of a Viking longboat
- What a Viking warrior would have looked like
- A Viking warrior’s helmet
- What a Viking man would have worn
- What a Viking woman would have worn
- The names of clothing that the Vikings wore
- Weapons that the Vikings used
- A Viking ship reconstruction
- A Viking village reconstructed in Ukranenland, an archeological village-museum in Germany
- Viking gold bracelets
- A Viking boat sculpture in Iceland
- An illustration of a Viking boat
- A re-enactment of Viking life
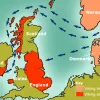
The Vikings wanted new land because the places where they came from in Scandinavia – Norway, Sweden and Denmark – weren’t very easy to live in. It was hard to grow crops, which meant there wasn’t a lot of food as the population got bigger. Britain and Europe had plenty of good farmland , so the Vikings tried to claim some of that land for themselves.
Even though the Anglo-Saxons were pretty well established in England, the Vikings would turn up every now and then to raid towns and take a bit of land. Sometimes, instead of fighting the Vikings, the Anglo-Saxons decided it was better to pay them money so they’d stay away. This payment was called Danegeld.
The first Viking attack on England was in 787 on the Isle of Portland. The Vikings went home straight afterwards, but they came back to England in 793 and raided a monastery at Lindisfarne. Monastaries made easy targets because the monks who lived there didn’t have any weapons, and they did have money and food.
The Vikings believed in many different gods , and they thought making sacrifices to the gods kept them all happy. They also told stories about the gods, called Norse mythology . Some of the gods included:
- Thor , the god of thunder
- Idun , the goddess of spring
- Odin , the king of gods and the god of war
The Vikings believed that if a warrior died while fighting in battle, he’d go to Valhalla , which is where Odin was. Other heroes who had died would also be there. Odin would send his warrior maidens, called Valkyries, across the sky to ferry dead warriors to Valhalla.
Viking warriors were very good fighters. They’d wear helmets and carry shields to defend themselves, and they’d also have one of these weapons:
- spear – a leaf shape or spike at the end of a wooden shaft
- sword – these were expensive to make and usually double-edged, and warriors would decorate the hilts
- battle axe – an axe with a long handle, and cheaper to make than a sword
Boats that the Vikings built are called longships – they are long, narrow boats that can be used in both deep and shallow water, making them perfect for travelling over the ocean and carrying lots of warriors onto the shore. Longships were symmetrical, meaning they looked the same at the front as they did at the back. They’d often have dragon heads carved at either end.
VIkings sailed all the way across the Atlantic Ocean to Newfoundland in North America in their longships!
Viking homes were long too – they were called longhouses ! They were rectangular, made from wood and were usually just one big room without any inside walls. There would be one big fire pit in the centre for cooking and keeping the house warm. The roof was covered in thatch, and there was a hole in the middle for smoke from the fire to go through. Benches around the house would be used both to sit on and to sleep on.
Most clothes that the Vikings had were made from wool, but they also had some clothes made from linen. They used dyes made from plants and minerals to make red, green, brown, yellow and blue, so their clothes were very colourful.
Viking men wore a long shirt, trousers with a drawstring tie and a coat with a belt around the waist. Viking women wore long dresses with a tunic over the top that was held up by two brooches pinned at the shoulders. Both men and women wore woollen socks and leather shoes.
Alfred the Great defeated the Vikings at the Battle of Ethandun (in modern day Wiltshire). After this, he and the Vikings agreed to set boundaries for their kingdoms. The area that the Vikings lived in was called Danelaw, and it meant that the land south of the diagonal line between London and Chester belonged to King Alfred (Wessex). Danelaw eventually became smaller and smaller as the Anglo-Saxons took more and more control.
Jorvik was a large Viking kingdom around York. The last king of Jorvik was Eric Bloodaxe, who was driven out in 954. The Vikings in England then agreed to be ruled by the king of England rather than having their own king.
But, that doesn’t mean that the king of England couldn’t be a Viking! The first Viking king of England was King Canute in 1016. He ruled until 1035, and then his sons were kings after that – but only for a total of seven years. Harold Harefoot was king until 1040, then Hardicanute was king until 1042.

Names to know:
King Canute (ruled as king of England from 1016-1035) – Canute was the first Viking king of England. He won a battle against Edmund II that divided their kingdoms, but when Edmund died Canute ruled both kingdoms. His sons, Harold Harefoot and then Hardicanute, ruled until 1042.
Harald Hardrada (c.1015-1066) – Harald Hardrada was the king of Norway. He led Viking armies into England, but was defeated at the Battle of Stamford Bridge in York by King Harold II.
Leif Erikson (c.970-1020) – Leif Erikson was a famous Viking explorer who sailed all the way to North America.
Eric Bloodaxe (died in 954) – Eric Bloodaxe was king of the Viking kingdom of Jorvik between 947-948 and 952-954. He was the last king of Jorvik before it became part of England.
Related Videos
Just for fun...
- Type your name into the box and see how it looks written in Viking runes!
- Have Mum or Dad help you make some porridge in the way that the Vikings would have had it
- Watch Horrible Histories songs about the Vikings, the Vikings & Garkunkel Song and The Vikings - Literally
- Print some Viking colouring sheets and a Viking Age boat to colour in
- Make your own Viking tortoise brooches and try Viking cord winding
- You'll find amazing artefacts from the Viking Age on the Jorvik Discover from Home webpage, as well as Viking colouring, puzzles, crafts, stories and videos
- Quiz yourself on the Vikings
- Make your own Viking name
- Bake your own Viking flatbread
- The Cbeebies television show Gudrun the Viking Princess offers a glimpse of what life might have been like for the Vikings a thousand years ago
- Listen to a collection of Viking sagas told by Loki, Viking god of fire, on BBC Schools Radio
- Read a National Geographic kids comic set on a Viking longboat
- Make your own Viking shield , Viking longboat and Viking helmet with step-by-step instructions and videos from Hobbycraft
- Try some Viking puzzles from the Yorvik Centre
- Step back to 876AD and make your own Viking longship, Viking longship figurehead and Viking helmet
Children's books about the Vikings

See for yourself
- Visit Jorvik Viking Centre in York to go back in time and see what it was like to live as a Viking
- See a Viking coin made in England for a Viking ruler
- Step into a Viking Longhouse reconstruction at the Ancient Technology Outdoor Education Centre
- At the National Museum of Scotland, see the Galloway Hoard , the richest collection of rare and unique Viking-age objects ever found in the British Isles
Find out more:
- Watch BBC Bitesize animations about the Vikings
- A children's introduction to the Vikings from DKfindout!
- See an animated film about the life of a ten-year-old Viking boy
- Learn about everyday life in the Viking age
- Find out about the Vikings in Scotland with BBC Bitesize animations
- Watch a virtual tour of the British Museum's Vikings Live exhibition
- Discover the secrets of Viking ships
- "Walk" through a real Viking village
- Read stories and sagas from the Viking world – we've collected the best kids' books about the Vikings
- Find out about the Viking words we use in English place names . Did you know that words like berserk, ugly, muck, knife, die and cake come from Old Norse, the Viking language ?
- Information about Viking gods and mythology
- Did Vikings have horned helmets? Find out!
- See some images of Viking clothes and Viking jewellery and find out about Viking pets
- The Vikings were warriors of the sea. Find out more about Viking voyages and sea-faring life
- Download a Viking information booklet, packed with pictures
- Watch a video about the Vikings Eric the Red and his son Leif Ericson, who explored areas of Greenland and North America

Give your child a headstart
- FREE articles & expert information
- FREE resources & activities
- FREE homework help
©Copyright Mandy Barrow 2013 primaryhomeworkhelp.com
Follow me on Twitter @mbarrow
Woodlands Junior School, Hunt Road Tonbridge Kent TN10 4BB UK

IMAGES
COMMENTS
6 days ago · Introduction to the Vikings in Britain. The Viking Age in Britain began about 1,200 years ago in the 9th Century AD and lasted for just over 200 years. About the year 800, bands of fierce raiders began to attack our coasts. They were the Vikings (also called the Danes although they didn't just come from Denmark. See below).
The first Viking attack on England was in 787 on the Isle of Portland. The Vikings went home straight afterwards, but they came back to England in 793 and raided a monastery at Lindisfarne. Monastaries made easy targets because the monks who lived there didn’t have any weapons, and they did have money and food.
Vikings first attacked England in the late 700s. In 865 a Viking group from Denmark called the Danes conquered several English kingdoms. The English drove out the Danes in 954, but the Danes soon returned. The Danish king Canute I ruled England from 1016 to 1035 as a part of his Viking empire. England finally threw off Danish rule in 1042.
5 days ago · BBC Viking. The Vikings. The Vikings - A superb site from Snaith Primary School in East Yorkshire. 1. Who were the Vikings? Where did they come from? 2. Who were their gods and goddesses? 3. Where did the Vikings go on their travels? 4. What evidence have we that the Vikings were settlers? 5. Writing about a Viking 6. Who ruled England?
Danes capture York (which the Vikings called Jorvik) and make it their kingdon (land ruled by a king) 871: King Ethelred, the West Saxon king, and his brother Alfred, defeat the Viking army at the Battle of Ashdown (in Berkshire). 876: Vikings from Denmark, Norway and Sweden settle permanently in England.
The Vikings spoke in a language called Old Norse. 20% of modern British words came from the Viking language including happy, foot and cake! 9. Christopher Columbus is usually credited as being the European who discovered the 'New World', however it was a Viking explorer (called Leif Erikson) who beat him to it by 500 years!