- Python Basics
- Interview Questions
- Python Quiz
- Popular Packages
- Python Projects
- Practice Python
- AI With Python
- Learn Python3
- Python Automation
- Python Web Dev
- DSA with Python
- Python OOPs
- Dictionaries

How to Fix - UnboundLocalError: Local variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python
Developers often encounter the UnboundLocalError Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment error in Python. In this article, we will see what is local variable referenced before assignment error in Python and how to fix it by using different approaches.
What is UnboundLocalError: Local variable Referenced Before Assignment?
This error occurs when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value within a function or method. This error typically surfaces when utilizing try-except blocks to handle exceptions, creating a puzzle for developers trying to comprehend its origins and find a solution.
Below, are the reasons by which UnboundLocalError: Local variable Referenced Before Assignment error occurs in Python :
Nested Function Variable Access
Global variable modification.
In this code, the outer_function defines a variable 'x' and a nested inner_function attempts to access it, but encounters an UnboundLocalError due to a local 'x' being defined later in the inner_function.
In this code, the function example_function tries to increment the global variable 'x', but encounters an UnboundLocalError since it's treated as a local variable due to the assignment operation within the function.
Solution for Local variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python
Below, are the approaches to solve “Local variable Referenced Before Assignment”.
In this code, example_function successfully modifies the global variable 'x' by declaring it as global within the function, incrementing its value by 1, and then printing the updated value.
In this code, the outer_function defines a local variable 'x', and the inner_function accesses and modifies it as a nonlocal variable, allowing changes to the outer function's scope from within the inner function.
Similar Reads
- How to Fix - UnboundLocalError: Local variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python Developers often encounter the UnboundLocalError Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment error in Python. In this article, we will see what is local variable referenced before assignment error in Python and how to fix it by using different approaches. What is UnboundLocalError: Local variable Re 3 min read
- UnboundLocalError Local variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python Handling errors is an integral part of writing robust and reliable Python code. One common stumbling block that developers often encounter is the "UnboundLocalError" raised within a try-except block. This error can be perplexing for those unfamiliar with its nuances but fear not – in this article, w 4 min read
- How to Access Dictionary Values in Python Using For Loop A dictionary is a built-in data type in Python designed to store key-value pairs of data. The most common method to access values in Python is through the use of a for loop. This article explores various approaches to accessing values in a dictionary using a for loop. Access Dictionary Values in Pyt 2 min read
- How to fix "SyntaxError: invalid character" in Python In this article, we will understand the SyntaxError: invalid character in Python through examples, and we will also explore potential approaches to resolve this issue. What is "SyntaxError: invalid character" in Python?Python SyntaxError: Invalid Character occurs when the interpreter encounters a ch 3 min read
- Python | Accessing variable value from code scope Sometimes, we just need to access a variable other than the usual way of accessing by it's name. There are many method by which a variable can be accessed from the code scope. These are by default dictionaries that are created and which keep the variable values as dictionary key-value pair. Let's ta 3 min read
- How To Fix - Python RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in scalar One such error that developers may encounter is the "Python RuntimeWarning: Overflow Encountered In Scalars". In Python, numeric operations can sometimes trigger a "RuntimeWarning: overflow encountered in a scalar." In this article, we will see what is Python "Python Runtimewarning: Overflow Encount 3 min read
- Different Forms of Assignment Statements in Python We use Python assignment statements to assign objects to names. The target of an assignment statement is written on the left side of the equal sign (=), and the object on the right can be an arbitrary expression that computes an object. There are some important properties of assignment in Python :- 3 min read
- Python Program to Find and Print Address of Variable In this article, we are going to see how to find and print the address of the Python variable. It can be done in these ways: Using id() functionUsing addressof() functionUsing hex() functionMethod 1: Find and Print Address of Variable using id()We can get an address using id() function, id() functio 2 min read
- Accessing Python Function Variable Outside the Function In Python, variables defined within a function have local scope by default. But to Access function variables outside the function usually requires the use of the global keyword, but can we do it without using Global. In this article, we will see how to access a function variable outside the function 4 min read
- Variables under the hood in Python In simple terms, variables are names attached to particular objects in Python. To create a variable, you just need to assign a value and then start using it. The assignment is done with a single equals sign (=): C/C++ Code # Variable named age age = 20 print(age) # Variable named id_number id_no = 4 3 min read
- How to Change Class Attributes By Reference in Python We have the problem of how to change class attributes by reference in Python, we will see in this article how can we change the class attributes by reference in Python. What is Class Attributes?Class attributes are typically defined outside of any method within a class and are shared among all insta 3 min read
- Python program to find number of local variables in a function Given a Python program, task is to find the number of local variables present in a function. Examples: Input : a = 1 b = 2.1 str = 'GeeksForGeeks' Output : 3 We can use the co_nlocals() function which returns the number of local variables used by the function to get the desired result. Code #1: # Im 1 min read
- Python program to create dynamically named variables from user input Given a string input, our task is to write a Python program to create a variable from that input (as a variable name) and assign it to some value. Below are the methods to create dynamically named variables from user input. Using globals() method to create dynamically named variables Here we are usi 2 min read
- Python TabError: Inconsistent Use of Tabs and Spaces in Indentation Python, known for its readability and simplicity, enforces strict indentation rules to structure code. However, encountering a TabError can be frustrating, especially when the code appears to be properly aligned. In this article, we'll explore what a TabError is, and how to resolve TabError in Pytho 2 min read
- Insert a Variable into a String - Python In Python, inserting a variable inside a string is a common task. There are different ways to do this depending on which method you find easiest. Let’s look at some simple methods to insert variables into strings. Using + OperatorThe simplest way to insert a variable into a string is by using the + 1 min read
- Python | Using variable outside and inside the class and method In Python, we can define the variable outside the class, inside the class, and even inside the methods. Let's see, how to use and access these variables throughout the program. Variable defined outside the class: The variables that are defined outside the class can be accessed by any class or any me 3 min read
- SyntaxError: ‘return’ outside function in Python We are given a problem of how to solve the 'Return Outside Function' Error in Python. In this article, we will see how to solve the 'Return Outside Function' Error in Python with reasons for it's occurring and also approaches to solve SyntaxError: ‘return’ outside function” in Python. What is Syntax 4 min read
- Run One Python Script From Another in Python In Python, we can run one file from another using the import statement for integrating functions or modules, exec() function for dynamic code execution, subprocess module for running a script as a separate process, or os.system() function for executing a command to run another Python file within the 5 min read
- Python | Scope resolution when a function is called or defined Python resolves the scope of the parameters of a function in two ways: When the function is definedWhen the function is called When the function is defined Consider this sample program which has a function adder(a, b) which adds an element a to the list b and returns the list b. The default value of 3 min read
- Python Programs
- Python Errors
- Python How-to-fix
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
[SOLVED] Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment

Python treats variables referenced only inside a function as global variables. Any variable assigned to a function’s body is assumed to be a local variable unless explicitly declared as global.
Why Does This Error Occur?
Unboundlocalerror: local variable referenced before assignment occurs when a variable is used before its created. Python does not have the concept of variable declarations. Hence it searches for the variable whenever used. When not found, it throws the error.
Before we hop into the solutions, let’s have a look at what is the global and local variables.
Local Variable Declarations vs. Global Variable Declarations
![unboundlocalerror local variable 'sum' referenced before assignment [Fixed] typeerror can’t compare datetime.datetime to datetime.date](https://www.pythonpool.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/typeerror-cant-compare-datetime.datetime-to-datetime.date_-300x157.webp)
Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment Error with Explanation
Try these examples yourself using our Online Compiler.
Let’s look at the following function:
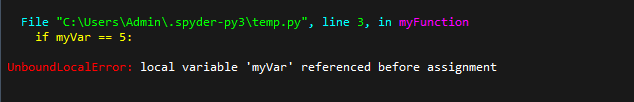
Explanation
The variable myVar has been assigned a value twice. Once before the declaration of myFunction and within myFunction itself.
Using Global Variables
Passing the variable as global allows the function to recognize the variable outside the function.
Create Functions that Take in Parameters
Instead of initializing myVar as a global or local variable, it can be passed to the function as a parameter. This removes the need to create a variable in memory.
UnboundLocalError: local variable ‘DISTRO_NAME’
This error may occur when trying to launch the Anaconda Navigator in Linux Systems.
Upon launching Anaconda Navigator, the opening screen freezes and doesn’t proceed to load.
Try and update your Anaconda Navigator with the following command.
If solution one doesn’t work, you have to edit a file located at
After finding and opening the Python file, make the following changes:
In the function on line 159, simply add the line:
DISTRO_NAME = None
Save the file and re-launch Anaconda Navigator.
DJANGO – Local Variable Referenced Before Assignment [Form]
The program takes information from a form filled out by a user. Accordingly, an email is sent using the information.
Upon running you get the following error:
We have created a class myForm that creates instances of Django forms. It extracts the user’s name, email, and message to be sent.
A function GetContact is created to use the information from the Django form and produce an email. It takes one request parameter. Prior to sending the email, the function verifies the validity of the form. Upon True , .get() function is passed to fetch the name, email, and message. Finally, the email sent via the send_mail function
Why does the error occur?
We are initializing form under the if request.method == “POST” condition statement. Using the GET request, our variable form doesn’t get defined.
Local variable Referenced before assignment but it is global
This is a common error that happens when we don’t provide a value to a variable and reference it. This can happen with local variables. Global variables can’t be assigned.
This error message is raised when a variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value within the local scope of a function, even though it is a global variable.
Here’s an example to help illustrate the problem:
In this example, x is a global variable that is defined outside of the function my_func(). However, when we try to print the value of x inside the function, we get a UnboundLocalError with the message “local variable ‘x’ referenced before assignment”.
This is because the += operator implicitly creates a local variable within the function’s scope, which shadows the global variable of the same name. Since we’re trying to access the value of x before it’s been assigned a value within the local scope, the interpreter raises an error.
To fix this, you can use the global keyword to explicitly refer to the global variable within the function’s scope:
However, in the above example, the global keyword tells Python that we want to modify the value of the global variable x, rather than creating a new local variable. This allows us to access and modify the global variable within the function’s scope, without causing any errors.
Local variable ‘version’ referenced before assignment ubuntu-drivers
This error occurs with Ubuntu version drivers. To solve this error, you can re-specify the version information and give a split as 2 –
Here, p_name means package name.
With the help of the threading module, you can avoid using global variables in multi-threading. Make sure you lock and release your threads correctly to avoid the race condition.
When a variable that is created locally is called before assigning, it results in Unbound Local Error in Python. The interpreter can’t track the variable.
Therefore, we have examined the local variable referenced before the assignment Exception in Python. The differences between a local and global variable declaration have been explained, and multiple solutions regarding the issue have been provided.
Trending Python Articles
![unboundlocalerror local variable 'sum' referenced before assignment [Fixed] nameerror: name Unicode is not defined](https://www.pythonpool.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/Fixed-nameerror-name-Unicode-is-not-defined-300x157.webp)
How to fix UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment in Python
by Nathan Sebhastian
Posted on May 26, 2023
Reading time: 2 minutes

One error you might encounter when running Python code is:
This error commonly occurs when you reference a variable inside a function without first assigning it a value.
You could also see this error when you forget to pass the variable as an argument to your function.
Let me show you an example that causes this error and how I fix it in practice.
How to reproduce this error
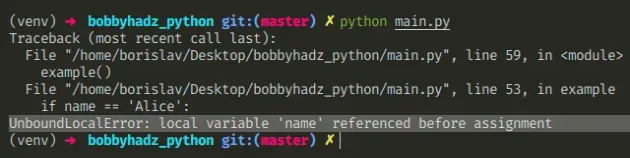
Suppose you have a variable called name declared in your Python code as follows:
Next, you created a function that uses the name variable as shown below:
When you execute the code above, you’ll get this error:
This error occurs because you both assign and reference a variable called name inside the function.
Python thinks you’re trying to assign the local variable name to name , which is not the case here because the original name variable we declared is a global variable.
How to fix this error
To resolve this error, you can change the variable’s name inside the function to something else. For example, name_with_title should work:
As an alternative, you can specify a name parameter in the greet() function to indicate that you require a variable to be passed to the function.
When calling the function, you need to pass a variable as follows:
This code allows Python to know that you intend to use the name variable which is passed as an argument to the function as part of the newly declared name variable.
Still, I would say that you need to use a different name when declaring a variable inside the function. Using the same name might confuse you in the future.
Here’s the best solution to the error:
Now it’s clear that we’re using the name variable given to the function as part of the value assigned to name_with_title . Way to go!
The UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment occurs when you reference a variable inside a function before declaring that variable.
To resolve this error, you need to use a different variable name when referencing the existing variable, or you can also specify a parameter for the function.
I hope this tutorial is useful. See you in other tutorials.
Take your skills to the next level ⚡️
I'm sending out an occasional email with the latest tutorials on programming, web development, and statistics. Drop your email in the box below and I'll send new stuff straight into your inbox!
Hello! This website is dedicated to help you learn tech and data science skills with its step-by-step, beginner-friendly tutorials. Learn statistics, JavaScript and other programming languages using clear examples written for people.
Learn more about this website
Connect with me on Twitter
Or LinkedIn
Type the keyword below and hit enter
Click to see all tutorials tagged with:
Local variable referenced before assignment in Python
Last updated: Apr 8, 2024 Reading time · 4 min

# Local variable referenced before assignment in Python
The Python "UnboundLocalError: Local variable referenced before assignment" occurs when we reference a local variable before assigning a value to it in a function.
To solve the error, mark the variable as global in the function definition, e.g. global my_var .
Here is an example of how the error occurs.
We assign a value to the name variable in the function.
# Mark the variable as global to solve the error
To solve the error, mark the variable as global in your function definition.
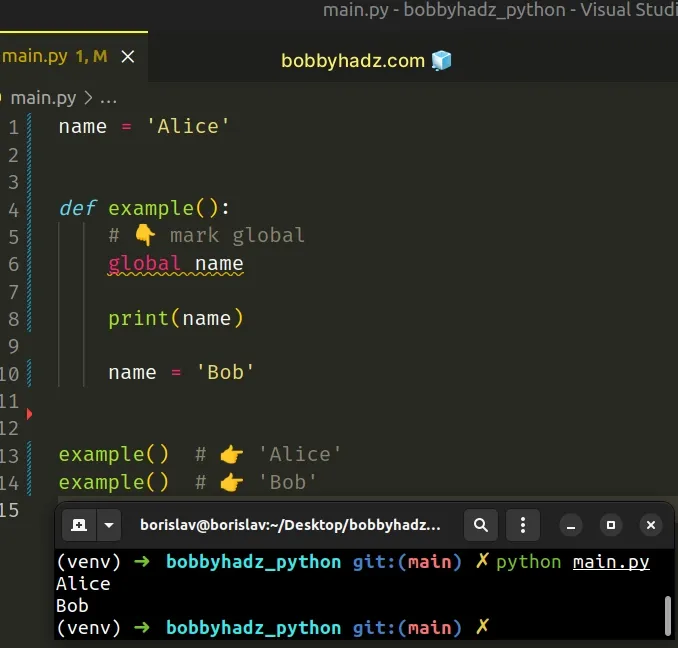
If a variable is assigned a value in a function's body, it is a local variable unless explicitly declared as global .
# Local variables shadow global ones with the same name
You could reference the global name variable from inside the function but if you assign a value to the variable in the function's body, the local variable shadows the global one.
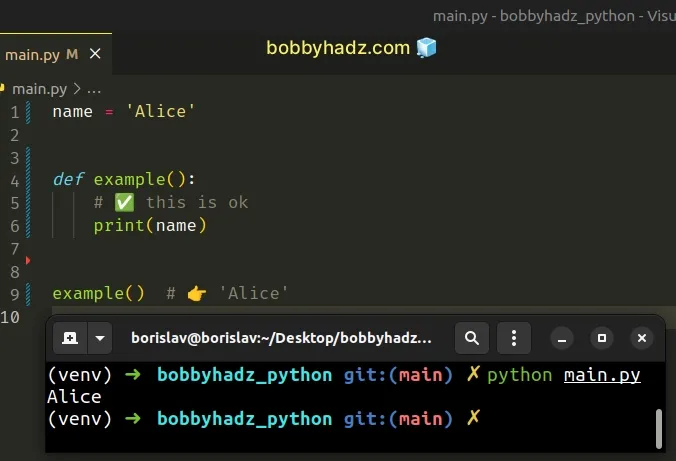
Accessing the name variable in the function is perfectly fine.
On the other hand, variables declared in a function cannot be accessed from the global scope.
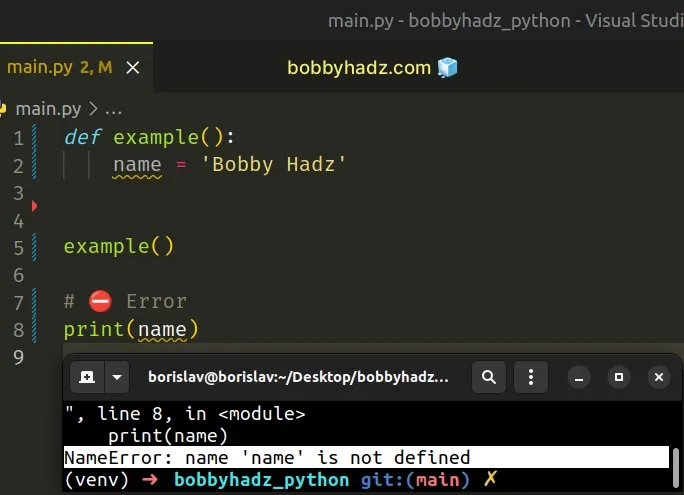
The name variable is declared in the function, so trying to access it from outside causes an error.
Make sure you don't try to access the variable before using the global keyword, otherwise, you'd get the SyntaxError: name 'X' is used prior to global declaration error.
# Returning a value from the function instead
An alternative solution to using the global keyword is to return a value from the function and use the value to reassign the global variable.
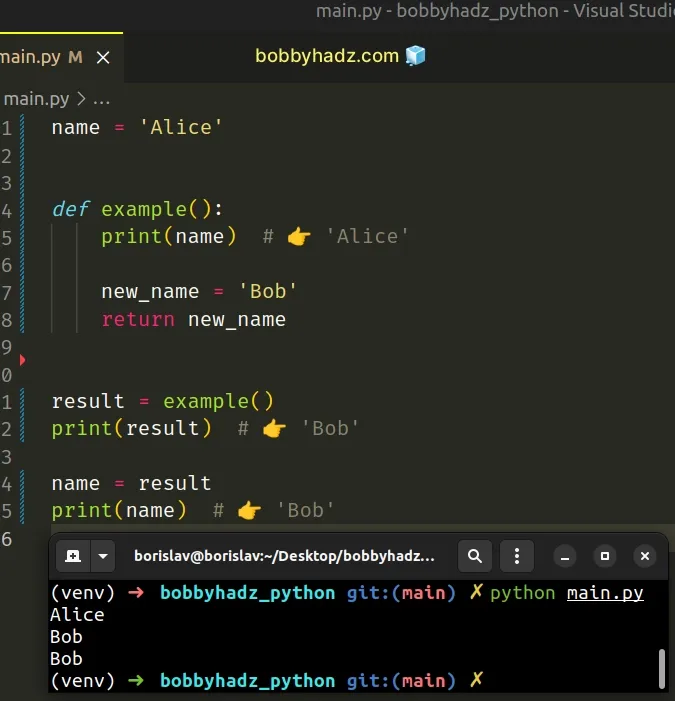
We simply return the value that we eventually use to assign to the name global variable.
# Passing the global variable as an argument to the function
You should also consider passing the global variable as an argument to the function.
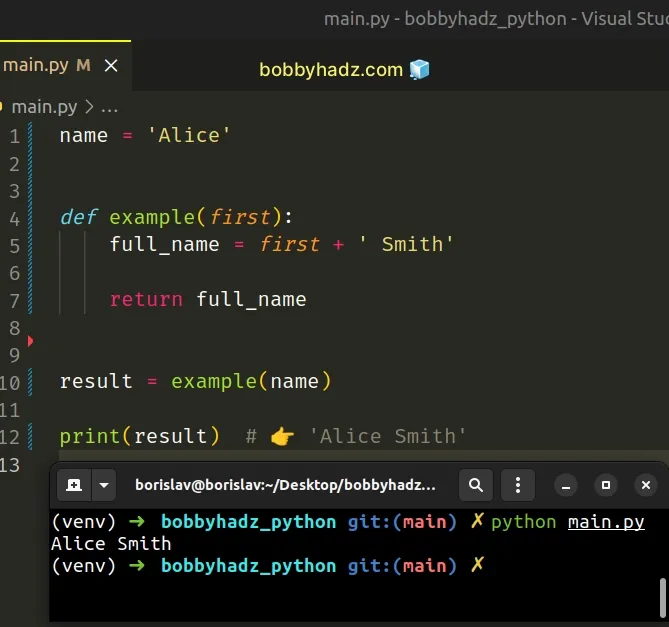
We passed the name global variable as an argument to the function.
If we assign a value to a variable in a function, the variable is assumed to be local unless explicitly declared as global .
# Assigning a value to a local variable from an outer scope
If you have a nested function and are trying to assign a value to the local variables from the outer function, use the nonlocal keyword.
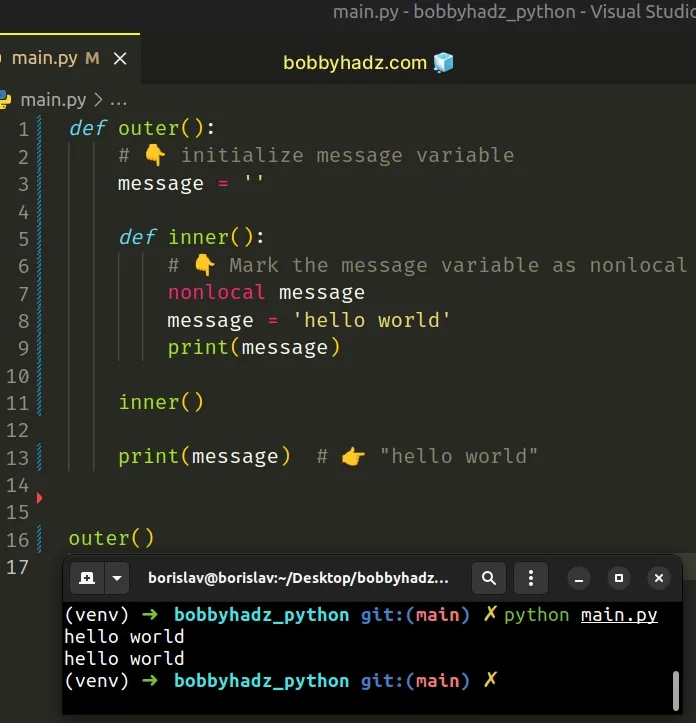
The nonlocal keyword allows us to work with the local variables of enclosing functions.
Had we not used the nonlocal statement, the call to the print() function would have returned an empty string.
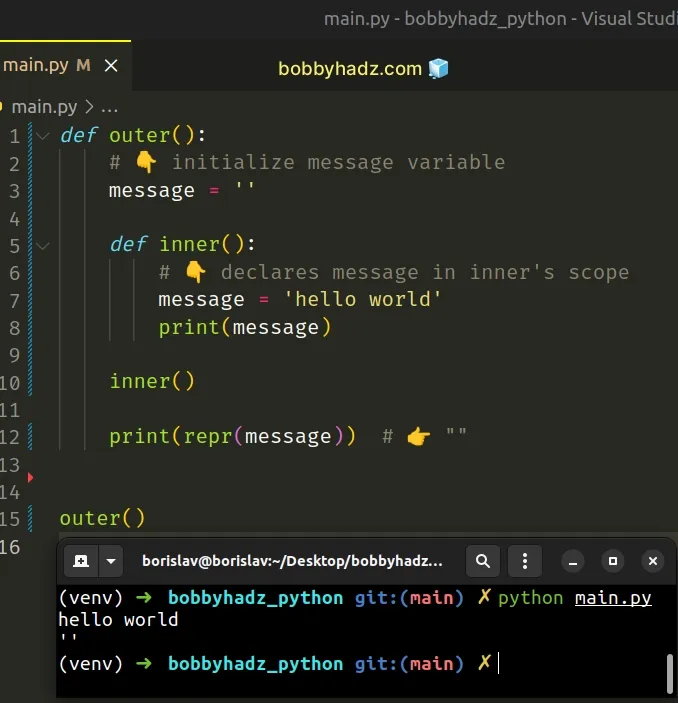
Printing the message variable on the last line of the function shows an empty string because the inner() function has its own scope.
Changing the value of the variable in the inner scope is not possible unless we use the nonlocal keyword.
Instead, the message variable in the inner function simply shadows the variable with the same name from the outer scope.
# Discussion
As shown in this section of the documentation, when you assign a value to a variable inside a function, the variable:
- Becomes local to the scope.
- Shadows any variables from the outer scope that have the same name.
The last line in the example function assigns a value to the name variable, marking it as a local variable and shadowing the name variable from the outer scope.
At the time the print(name) line runs, the name variable is not yet initialized, which causes the error.
The most intuitive way to solve the error is to use the global keyword.
The global keyword is used to indicate to Python that we are actually modifying the value of the name variable from the outer scope.
- If a variable is only referenced inside a function, it is implicitly global.
- If a variable is assigned a value inside a function's body, it is assumed to be local, unless explicitly marked as global .
If you want to read more about why this error occurs, check out [this section] ( this section ) of the docs.
# Additional Resources
You can learn more about the related topics by checking out the following tutorials:
- SyntaxError: name 'X' is used prior to global declaration

Borislav Hadzhiev
Web Developer

Copyright © 2024 Borislav Hadzhiev
Decode Python
Python Tutorials & Tips
Fixing ‘UnboundLocalError’ in Python: A Simple Guide with Code Samples
Python is a popular programming language that is widely used for developing various applications. However, like any other programming language, it is not free from errors. One of the common errors that Python developers encounter is the ‘UnboundLocalError’. This error occurs when a local variable is referenced before it is assigned a value. In this article, we will discuss in detail what ‘UnboundLocalError’ is, why it occurs, and how to fix it.
When a variable is defined inside a function, it is considered a local variable. If the function tries to access this variable before it is assigned a value, it results in an ‘UnboundLocalError’. This error can be frustrating for developers, especially when they are working on a large project. However, it is not difficult to fix this error. One of the ways to fix it is by using the ‘global’ keyword to declare the variable as a global variable.
In conclusion, understanding ‘UnboundLocalError’ in Python is crucial for developers who want to avoid errors in their code. By following best practices and using the right techniques, developers can easily fix this error and ensure that their code runs smoothly. In the next section, we will explore in detail how to fix ‘UnboundLocalError’ using code examples.
Understanding UnboundLocalError
UnboundLocalError is a common error in Python that occurs when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value. This error can be confusing for beginners because it is not always clear why it occurs or how to fix it. In this section, we will explore what UnboundLocalError is, why it occurs, and how to identify it.
What is UnboundLocalError?
UnboundLocalError is an exception that occurs when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value. In Python, variables can have either a local or global scope. Local variables are defined within a function and are only accessible within that function. Global variables, on the other hand, are defined outside of a function and can be accessed by any function within the module.

Why Does UnboundLocalError Occur?
UnboundLocalError occurs when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value. This can happen if the variable is defined within a function but is not assigned a value before it is referenced. It can also happen if the variable is defined as a global variable but is not explicitly declared as such using the global statement.
How to Identify UnboundLocalError
UnboundLocalError can be identified by the traceback message that is generated when the error occurs. The traceback message will indicate the line number where the error occurred and provide information about the variable that caused the error.
To fix UnboundLocalError, you need to ensure that all local variables are assigned a value before they are referenced. You can also use the global statement to explicitly declare a variable as a global variable, allowing it to be accessed by any function within the module.
In conclusion, UnboundLocalError is a common error in Python that occurs when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value. To fix this error, you need to ensure that all local variables are assigned a value before they are referenced and use the global statement to declare global variables. By understanding UnboundLocalError and how to fix it, you can write more robust and error-free Python code.
Fixing UnboundLocalError
If you are a Python developer, you may have encountered the UnboundLocalError error while working with local variables or functions. This error occurs when a local variable is referenced before it is assigned a value within a function. In this section, we will discuss how to fix UnboundLocalError in Python.
Solutions for UnboundLocalError
There are several ways to fix UnboundLocalError in Python. One solution is to explicitly declare the variable as global using the global keyword. This will make the variable a global variable instead of a local variable. Here is an example:
In this example, we declared num as a global variable inside the test() function using the global keyword. This allowed us to access and modify the value of num inside the function without raising an UnboundLocalError .
Another solution is to use the int() function to initialize the variable with a value of 0. This will ensure that the variable has a value before it is referenced. Here is an example:
In this example, we used the int() function to initialize num with a value of 0. This prevented the UnboundLocalError from being raised when we referenced num before assigning it a value.
How to Avoid UnboundLocalError
To avoid UnboundLocalError , it is important to understand the concept of local scope and local names in Python. Local scope refers to the area of a program where a variable is defined and can be accessed. Local names refer to the variables defined within a function.
To prevent UnboundLocalError , you should always make sure to assign a value to a local variable before referencing it within a function. You should also avoid using the same name for both global and local variables, as this can cause confusion and lead to errors.
Another way to avoid UnboundLocalError is to use lexical scoping. This means defining a function within another function, which allows the inner function to access the variables of the outer function. This can help prevent UnboundLocalError by ensuring that all variables are defined and assigned a value before they are referenced.
In conclusion, UnboundLocalError is a common error in Python that can be fixed by explicitly declaring variables as global or initializing them with a value using the int() function. To avoid UnboundLocalError , it is important to understand the concept of local scope and local names, and to assign values to local variables before referencing them within a function.
In conclusion, understanding the ‘UnboundLocalError’ in Python is essential for any programmer. This error occurs when a local variable is referenced before it has been assigned a value within a function. It can be frustrating to deal with, but fortunately, there are several ways to fix it.
One common solution is to use the global keyword to declare the variable as global within the function. This allows the function to access the variable outside of its scope. Another solution is to use default arguments in the function definition to initialize the variable with a default value.
It is important to note that this error is a runtime error and can only be detected when the code is executed. Therefore, it is crucial to test your code thoroughly to catch any ‘UnboundLocalError’ before deploying it.
Python is a versatile programming language that is widely used in various fields. Understanding the ‘UnboundLocalError’ and how to fix it is a crucial aspect of programming in Python. By following the tips and tricks outlined in this article, you can avoid this error and write efficient and effective code.
In summary, this guide has covered the basics of the ‘UnboundLocalError’ in Python, including its causes and solutions. We have seen how to use the global keyword and default arguments to fix this error. Hopefully, this article has been helpful in your programming journey, and you can now write better code in Python.
- Password Generator
- HTML Editor
- HTML Encoder
- JSON Beautifier
- CSS Beautifier
- Markdown Convertor
- Find the Closest Tailwind CSS Color
- Phrase encrypt / decrypt
- Browser Feature Detection
- Number convertor
- CSS Maker text shadow
- CSS Maker Text Rotation
- CSS Maker Out Line
- CSS Maker RGB Shadow
- CSS Maker Transform
- CSS Maker Font Face
- Color Picker
- Colors CMYK
- Color mixer
- Color Converter
- Color Contrast Analyzer
- Color Gradient
- String Length Calculator
- MD5 Hash Generator
- Sha256 Hash Generator
- String Reverse
- URL Encoder
- URL Decoder
- Base 64 Encoder
- Base 64 Decoder
- Extra Spaces Remover
- String to Lowercase
- String to Uppercase
- Word Count Calculator
- Empty Lines Remover
- HTML Tags Remover
- Binary to Hex
- Hex to Binary
- Rot13 Transform on a String
- String to Binary
- Duplicate Lines Remover
Python 3: UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment
This error occurs when you are trying to access a variable before it has been assigned a value. Here is an example of a code snippet that would raise this error:
Watch a video course Python - The Practical Guide
The error message will be:
In this example, the variable x is being accessed before it is assigned a value, which is causing the error. To fix this, you can either move the assignment of the variable x before the print statement, or give it an initial value before the print statement.
Both will work without any error.
Related Resources
- Using global variables in a function
- "Least Astonishment" and the Mutable Default Argument
- Why is "1000000000000000 in range(1000000000000001)" so fast in Python 3?
- HTML Basics
- Javascript Basics
- TypeScript Basics
- React Basics
- Angular Basics
- Sass Basics
- Vue.js Basics
- Python Basics
- Java Basics
- NodeJS Basics

Python UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment
by Suf | Programming , Python , Tips
If you try to reference a local variable before assigning a value to it within the body of a function, you will encounter the UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment.
The preferable way to solve this error is to pass parameters to your function, for example:
Alternatively, you can declare the variable as global to access it while inside a function. For example,
This tutorial will go through the error in detail and how to solve it with code examples .
Table of contents
What is scope in python, unboundlocalerror: local variable referenced before assignment, solution #1: passing parameters to the function, solution #2: use global keyword, solution #1: include else statement, solution #2: use global keyword.
Scope refers to a variable being only available inside the region where it was created. A variable created inside a function belongs to the local scope of that function, and we can only use that variable inside that function.
A variable created in the main body of the Python code is a global variable and belongs to the global scope. Global variables are available within any scope, global and local.
UnboundLocalError occurs when we try to modify a variable defined as local before creating it. If we only need to read a variable within a function, we can do so without using the global keyword. Consider the following example that demonstrates a variable var created with global scope and accessed from test_func :
If we try to assign a value to var within test_func , the Python interpreter will raise the UnboundLocalError:
This error occurs because when we make an assignment to a variable in a scope, that variable becomes local to that scope and overrides any variable with the same name in the global or outer scope.
var +=1 is similar to var = var + 1 , therefore the Python interpreter should first read var , perform the addition and assign the value back to var .
var is a variable local to test_func , so the variable is read or referenced before we have assigned it. As a result, the Python interpreter raises the UnboundLocalError.
Example #1: Accessing a Local Variable
Let’s look at an example where we define a global variable number. We will use the increment_func to increase the numerical value of number by 1.
Let’s run the code to see what happens:
The error occurs because we tried to read a local variable before assigning a value to it.
We can solve this error by passing a parameter to increment_func . This solution is the preferred approach. Typically Python developers avoid declaring global variables unless they are necessary. Let’s look at the revised code:
We have assigned a value to number and passed it to the increment_func , which will resolve the UnboundLocalError. Let’s run the code to see the result:
We successfully printed the value to the console.
We also can solve this error by using the global keyword. The global statement tells the Python interpreter that inside increment_func , the variable number is a global variable even if we assign to it in increment_func . Let’s look at the revised code:
Let’s run the code to see the result:
Example #2: Function with if-elif statements
Let’s look at an example where we collect a score from a player of a game to rank their level of expertise. The variable we will use is called score and the calculate_level function takes in score as a parameter and returns a string containing the player’s level .
In the above code, we have a series of if-elif statements for assigning a string to the level variable. Let’s run the code to see what happens:
The error occurs because we input a score equal to 40 . The conditional statements in the function do not account for a value below 55 , therefore when we call the calculate_level function, Python will attempt to return level without any value assigned to it.
We can solve this error by completing the set of conditions with an else statement. The else statement will provide an assignment to level for all scores lower than 55 . Let’s look at the revised code:
In the above code, all scores below 55 are given the beginner level. Let’s run the code to see what happens:
We can also create a global variable level and then use the global keyword inside calculate_level . Using the global keyword will ensure that the variable is available in the local scope of the calculate_level function. Let’s look at the revised code.
In the above code, we put the global statement inside the function and at the beginning. Note that the “default” value of level is beginner and we do not include the else statement in the function. Let’s run the code to see the result:
Congratulations on reading to the end of this tutorial! The UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment occurs when you try to reference a local variable before assigning a value to it. Preferably, you can solve this error by passing parameters to your function. Alternatively, you can use the global keyword.
If you have if-elif statements in your code where you assign a value to a local variable and do not account for all outcomes, you may encounter this error. In which case, you must include an else statement to account for the missing outcome.
For further reading on Python code blocks and structure, go to the article: How to Solve Python IndentationError: unindent does not match any outer indentation level .
Go to the online courses page on Python to learn more about Python for data science and machine learning.
Have fun and happy researching!

Suf is a senior advisor in data science with deep expertise in Natural Language Processing, Complex Networks, and Anomaly Detection. Formerly a postdoctoral research fellow, he applied advanced physics techniques to tackle real-world, data-heavy industry challenges. Before that, he was a particle physicist at the ATLAS Experiment of the Large Hadron Collider. Now, he’s focused on bringing more fun and curiosity to the world of science and research online.
- Suf https://researchdatapod.com/author/soofyserial/ How to Solve Python ModuleNotFoundError: no module named ‘Crypto’
- Suf https://researchdatapod.com/author/soofyserial/ How to Solve Python NameError: name 'time' is not defined
- Suf https://researchdatapod.com/author/soofyserial/ How to Solve Python ValueError: cannot convert float nan to integer
- Suf https://researchdatapod.com/author/soofyserial/ How to Solve Python ModuleNotFoundError: no module named ‘pyautogui’
Buy Me a Coffee ✨
Fixing Python UnboundLocalError: Local Variable ‘x’ Accessed Before Assignment
Last updated: December 31, 2023
Table of Contents
Understanding unboundlocalerror, method 1: initializing the variable, method 2: using global variables, method 3: using nonlocal variables.
The UnboundLocalError in Python occurs when a function tries to access a local variable before it has been assigned a value. Variables in Python have scope that defines their level of visibility throughout the code: global scope, local scope, and nonlocal (in nested functions) scope. This error typically surfaces when using a variable that has not been initialized in the current function’s scope or when an attempt is made to modify a global variable without proper declaration.
Solutions for the Problem
To fix an UnboundLocalError, you need to identify the scope of the problematic variable and ensure it is correctly used within that scope.
Make sure to initialize the variable within the function before using it. This is often the simplest fix.
If you intend to use a global variable and modify its value within a function, you must declare it as global before you use it.
If the variable is defined in an outer function and you want to modify it within a nested function, use the nonlocal keyword.
That’s it. Happy coding!
Next Article: Fixing Python TypeError: Descriptor ‘lower’ for ‘str’ Objects Doesn’t Apply to ‘dict’ Object
Previous Article: Fixing the ValueError: Too Many Values to Unpack (Expected 2) in Python
Series: Common Errors in Python and How to Fix Them
Related Articles
Python: How to Convert a Dictionary to a Query String
February 12, 2024
Python File Modes: Explained
August 27, 2023
Python & aiohttp: How to download files using streams
August 20, 2023
Using aiohttp to make POST requests in Python (with examples)
Python asyncio.Queue class (with 3 examples)
August 18, 2023
How to Setup Python Virtual Environments (venv)
August 11, 2023
Python: Handling asyncio.exceptions.CancelledError gracefully
August 02, 2023
Python asyncio.wait_for() function (with examples)
Python Linked Lists: Explanation & Examples
July 31, 2023
Python asyncio.wait() function (with examples)
July 26, 2023
Python asyncio.gather() function (with examples)
Python match/case statement (with examples)
July 18, 2023
You May Also Like
- How to deal with Python InsecureRequestWarning
- Python Warning: Secure coding is not enabled for restorable state
- Python TypeError: write() argument must be str, not bytes
- 4 ways to install Python modules on Windows without admin rights
- Python TypeError: object of type ‘NoneType’ has no len()
- Python: How to access command-line arguments (3 approaches)
- Understanding ‘Never’ type in Python 3.11+ (5 examples)
- Python: 3 Ways to Retrieve City/Country from IP Address
- Using Type Aliases in Python: A Practical Guide (with Examples)
- Python: Defining distinct types using NewType class
- Using Optional Type in Python (explained with examples)
- Python: How to Override Methods in Classes
- Python: Define Generic Types for Lists of Nested Dictionaries
- Python: Defining type for a list that can contain both numbers and strings
- Using TypeGuard in Python (Python 3.10+)
- Python: Using ‘NoReturn’ type with functions
- Type Casting in Python: The Ultimate Guide (with Examples)
- Python: Using type hints with class methods and properties
- Python: Typing a function with default parameters
- Python: Typing a function that can return multiple types
Consultancy
- Technology Consulting
- Customer Experience Consulting
- Solution Architect Consulting
Software Development Services
- Ecommerce Development
- Web App Development
- Mobile App Development
- SAAS Product Development
- Content Management System
- System Integration & Data Migration
- Cloud Computing
- Computer Vision
Dedicated Development Team
- Full Stack Developers For Hire
- Offshore Development Center
Marketing & Creative Design
- UX/UI Design
- Customer Experience Optimization
- Digital Marketing
- Devops Services
- Service Level Management
- Security Services
- Odoo gold partner
By Industry
- Retail & Ecommerce
- Manufacturing
- Import & Distribution
- Financical & Banking
- Technology For Startups
Business Model
- MARKETPLACE ECOMMERCE
Our realized projects

MB Securities - A Premier Brokerage

iONAH - A Pioneer in Consumer Electronics Industry

Emers Group - An Official Nike Distributing Agent

Academy Xi - An Australian-based EdTech Startup
- Market insight

- Ohio Digital
- Onnet Consoulting
What is UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment?
Trying to assign a value to a variable that does not have local scope can result in this error:
Python has a simple rule to determine the scope of a variable. To clarify, a variable is assigned in a function, that variable is local. Because it is assumed that when you define a variable inside a function, you only need to access it inside that function.
There are two variable scopes in Python: local and global. Global variables are accessible throughout an entire program. Whereas, local variables are only accessible within the function in which they are originally defined.
An example of Local variable referenced before assignment
We’re going to write a program that calculates the grade a student has earned in class.
Firstly, we start by declaring two variables:
These variables store the numerical and letter grades a student has earned, respectively. By default, the value of “letter” is “F”. Then, we write a function that calculates a student’s letter grade based on their numerical grade using an “if” statement:
Finally, we call our function:
This line of code prints out the value returned by the calculate_grade() function to the console. We pass through one parameter into our function: numerical. This is the numerical value of the grade a student has earned.
Let’s run our code of Local variable referenced before assignment and see what happens:
Here is an error!
The Solution of Local variable referenced before assignment
The code returns an error: Unboundlocalerror local variable referenced before assignment because we reference “letter” before we assign it.
We have set the value of “numerical” to 42. Our if statement does not set a value for any grade over 50. This means that when we call our calculate_grade() function, our return statement does not know the value to which we are referring.
Moreover, we do define “letter” at the start of our program. However, we define it in the global context. Because Python treats “return letter” as trying to return a local variable called “letter”, not a global variable.
Therefore, this problem of variable referenced before assignment could be solved in two ways. Firstly, we can add an else statement to our code. This ensures we declare “letter” before we try to return it:
Let’s try to run our code again:
Our code successfully prints out the student’s grade. This approach is good because it lets us keep “letter” in the local context. To clarify, we could even remove the “letter = “F”” statement from the top of our code because we do not use it in the global context.
Alternatively, we could use the “global” keyword to make our global keyword available in the local context in our calculate_grade() function:
We use the “global” keyword at the start of our function.
This keyword changes the scope of our variable to a global variable. This means the “return” statement will no longer treat “letter” like a local variable. Let’s run our code. Our code returns: F.
The code works successfully! Let’s try it using a different grade number by setting the value of “numerical” to a new number:
Our code returns: B.
Finally, we have fixed the local variable referenced before assignment error in the code.
To sum up, as you can see, the UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment error is raised when you try to assign a value to a local variable before it has been declared. Then, you can solve this error by ensuring that a local variable is declared before you assign it a value. Moreover, if a variable is declared globally that you want to access in a function, you can use the “global” keyword to change its value. In case you have any inquiry, let’s CONTACT US . With a lot of experience in Mobile app development services , we will surely solve it for you instantly.
>>> Read more
- Average python length: How to find it with examples
- List assignment index out of range: Python indexerror solution you should know
- Spyder vs Pycharm: The detailed comparison to get best option for Python programming
- fix python error , Local variable referenced before assignment , python , python dictionary , python error , python learning , UnboundLocalError , UnboundLocalError in Python
Our Other Services
- E-commerce Development
- Web Apps Development
- Web CMS Development
- Mobile Apps Development
- Software Consultant & Development
- System Integration & Data Migration
- Dedicated Developers & Testers For Hire
- Remote Working Team
- Saas Products Development
- Web/Mobile App Development
- Outsourcing
- Hiring Developers
- Digital Transformation
- Advanced SEO Tips

Lastest News

Challenges and Advices When Using AWS Cloud Managed Services
Comprehensive Guide about AWS Well Architected Framework
AWS Cloud Migration: Guide-to-Guide from A to Z

Uncover The Treasures Of Cloud Computing For Healthcare

A Synopsis of Cloud Computing in Financial Services

Discover Cutting-Edge Cloud Computing Applications To Optimize Business Resources
Tailor your experience
- Success Stories
Copyright ©2007 – 2021 by AHT TECH JSC. All Rights Reserved.
Thank you for your message. It has been sent.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This is because, even though Var1 exists, you're also using an assignment statement on the name Var1 inside of the function (Var1 -= 1 at the bottom line). Naturally, this creates a variable inside the function's scope called Var1 (truthfully, a -= or += will only update (reassign) an existing variable, but for reasons unknown (likely consistency in this context), Python treats it as an ...
Output. Hangup (SIGHUP) Traceback (most recent call last): File "Solution.py", line 7, in <module> example_function() File "Solution.py", line 4, in example_function x += 1 # Trying to modify global variable 'x' without declaring it as global UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment Solution for Local variable Referenced Before Assignment in Python
Unboundlocalerror: local variable referenced before assignment occurs when a variable is used before its created. Python does not have the concept of variable declarations. Python does not have the concept of variable declarations.
The UnboundLocalError: local variable 'x' referenced before assignment occurs when you reference a variable inside a function before declaring that variable. To resolve this error, you need to use a different variable name when referencing the existing variable, or you can also specify a parameter for the function. I hope this tutorial is useful.
# Local variable referenced before assignment in Python. The Python "UnboundLocalError: Local variable referenced before assignment" occurs when we reference a local variable before assigning a value to it in a function. To solve the error, mark the variable as global in the function definition, e.g. global my_var.
To avoid UnboundLocalError, it is important to understand the concept of local scope and local names, and to assign values to local variables before referencing them within a function. Conclusion In conclusion, understanding the 'UnboundLocalError' in Python is essential for any programmer.
To fix this, you can either move the assignment of the variable x before the print statement, or give it an initial value before the print statement. def example (): x = 5 print (x) example()
What is Scope in Python? Scope refers to a variable being only available inside the region where it was created. A variable created inside a function belongs to the local scope of that function, and we can only use that variable inside that function.
Method 1: Initializing the Variable. Make sure to initialize the variable within the function before using it. This is often the simplest fix. Method 2: Using Global Variables. If you intend to use a global variable and modify its value within a function, you must declare it as global before you use it. Method 3: Using Nonlocal Variables
What is UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment? Trying to assign a value to a variable that does not have local scope can result in this error: 1 UnboundLocalError: local variable referenced before assignment. Python has a simple rule to determine the scope of a variable.