🎧 Real entrepreneurs. Real stories.
Subscribe to The Hurdle podcast today!

How to Create an Expense Budget

4 min. read
Updated October 27, 2023

One of the fundamentals of your financial plan and the start of good business management is managing expenses. That starts with an expense budget. Set your budget as a goal, then review and revise often to stay on track. Being right on budget is usually good, but good management takes the regular review to check on the timing, efficiency, and results of what your business spends.
For the record, we could call it an expense forecast, or projected expenses. Those are the same thing. Regardless of what you call it when you combine it with projected sales and costs, you have what you need to project your profit or loss.
- The key types of expenses in business spending
Expenses make up just one of the three common types of spending in a normal business.
Expenses mostly include operating expenses, like rent, utilities, advertising, and payroll. That’s what I’m talking about in this article.
Direct costs are another type of spending—another way to say it is the costs of goods sold (COGS), or what you spend on what you sell. For example, the COGS for a bookstore are the costs of buying the books it resells to its customers. Those go in your sales forecast .
Repaying debts and purchasing assets is the third type of spending. These affect your cash flow (the amount of real cash you have on hand to pay bills) and your balance sheet, but not your profits—which are left over after you pay your bills.
- Your expense budget
It’s all about educated guessing.
Don’t expect to accurately guess the future. Do use your experience, educated guessing, a bit of research, and common sense to estimate expenses in line with sales and costs and your planned activities.
The math is simple
The illustration here shows a sample expense budget from a soup delivery subscription plan we use as an example.
The math and the logic is simple. Make the rows match your accounting as much as possible. Set timeframes and estimate what expenses will be for each of the next 12 months, and then for the following two years as estimated annual totals.

In the example, the two owners know their business. As they develop their budget, they have a good idea of what they pay for kitchen time, Facebook ads, commissions, office equipment, and so on.
And if you don’t know these numbers for your business, find out. If you don’t know rents, talk to a broker, see some locations, and estimate what you’ll end up paying.
Do the same for utilities, insurance, and leased equipment: Make a good list, call people, and take a good educated guess.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Payroll and payroll taxes are operating expenses
Expenses also include payroll, wages and salaries, or compensation. They are worth a list of their own. In the case of the soup business in the example above, for payroll, they do a separate list so they can keep track. Payroll is a serious fixed cost and an obligation. Here is the payroll budget associated with the sample plan above.

Notice that the totals from the personnel plan show up in the expense budget. And you can see the estimated expense for benefits over and above the gross salary. Employee-related expenses include payroll taxes along with what they budget for health insurance and other benefits.
Don’t worry too much about depreciation
Depreciation is a special case. Traditionally, it counts as an operating expense, but a lot of businesses budget for it separately because it doesn’t actually cost money.
It’s a concept the tax code allows us to deduct as a business expense, in theory, to allow for the gradual decline in the value of an asset, or—depending on which expert you follow—to allow money to buy new assets when existing assets become obsolete.
The argument for including it in the expenses is that it gives a more accurate picture of profits. And many people separate depreciation from the other expenses so they can calculate EBITDA, which is earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (which is like depreciation, but for intangible assets).
Bottom line: Include it or not; it’s your choice.
Yes, interest expense is an expense
Because interest is also excluded from EBITDA, many people also exclude it from operating expenses. They list it separately, along with depreciation, to make the EBITDA calculation easier. I say you can do that either way, it doesn’t matter, as long as you include the interest expense in your budget. Because, unlike depreciation, interest does cost money.
- Remember the underlying goal
The purpose of the budget is to help you make good decisions.
Set expenses to align with your strategy and tactics, so you do what works best for your long-term progress. Match your accounting categories as much as possible, so you can track later. Keep track of assumptions so when things come out different from the plan —and they always do—you can adjust quickly.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.
Table of Contents
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
How to Create a Profit and Loss Forecast

7 Min. Read
7 Financial Terms Small Business Owners Need to Know

11 Min. Read
How to Create a Sales Forecast

10 Min. Read
What Is a Balance Sheet? Definition, Formulas, and Example
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Accounting Services
Bench simplifies your small business accounting by combining intuitive software that automates the busywork with real, professional human support. Less stress for you, more time to grow your business.
Ongoing online bookkeeping service for small business owners
Catch up bookkeeping services for small businesses, no matter how far behind they are
All-in-one small business tax preparation, filing and year-round income tax advisory
Expert support for small businesses to resolve IRS issues and reduce back tax liabilities
Book a demo with our friendly team of experts
Not sure where to start or which accounting service fits your needs? We’re just a call away. Our team is ready to learn about your business and guide you to the right solution.
Easy-To-Use Platform
Our intuitive software automates the busywork with powerful tools and features designed to help you simplify your financial management and make informed business decisions.
Effortless messaging with your Bench team for unlimited support or advice, anytime, anywhere
Upload, manage and access your financial documents swiftly with just a few clicks
Connect all your financial accounts to automate data entry, speed up your books, reduce errors and save time
Accurate transaction categorization, powered by smart automation with instant guidance
Real-time reporting. Access or download your updated income statement or balance sheet at all times
Get timely reminders to stay on top of your financial tasks and deadlines
See Bench’s features in action
The magic happens when our intuitive software and real, human support come together. Book a demo today to see what running your business is like with Bench.
Get free guides, articles, tools and calculators to help you navigate the financial side of your business with ease. Empower yourself with knowledge and practical tips.
Tips for understanding business finances Accounting · Bookkeeping Operations · Tax Tips
Live and on-demand recordings of webinars covering everything from bookkeeping to taxes
Free downloadable bookkeeping and tax guides, checklists, and expert-tested accounting templates
Tools and calculators to help you stay on top of your small business taxes and evaluate your financials
Info about small business tax deadlines, deductions, IRS forms and tax filing support - all in one, easy-to-access place
See what’s new at Bench and learn more about our company
Free Course: Understanding Financial Statements
Learn how to build, read, and use financial statements for your business so you can make more informed decisions. Easy-to-use templates and financial ratios provided.
Learn more about Bench, our mission, and the dedicated team behind your financial success. We’re committed to helping you thrive.
Learn about what we do, how we got here and why our hearts are in it
Learn how we’re committed to building a more just and inclusive society through our work
Hear straight from our customers why thousands of small business owners trust Bench with their finances
Answers to the common questions we get about our services and our software
The latest news, updates, and happenings from Bench
We partner with businesses that help other small businesses scale—see who’s on the list

“Working with Bench has saved me so many times. I could have made decisions for my business that would not have turned out well, should they have not been made based on the numbers.”

A How-To Guide for Creating a Business Budget
Amanda Smith
Reviewed by
September 23, 2022
This article is Tax Professional approved
Most business owners know how important a business budget is when it comes to managing expenses and planning for the future—but in a challenging economic environment like the one we’ve been experiencing, your business budget takes on even greater significance.
With inflation running rampant and the possibility of a recession looming, business owners need to be able to forecast their cash flow, manage their expenses, and plan for the future. Creating a detailed business budget is the first step.
Whether you want to revamp your budgeting method, or you’ve never created a business budget before, this guide will walk you through the process.
I am the text that will be copied.
What is a business budget?
A budget is a detailed plan that outlines where you’ll spend your money monthly or annually.
You give every dollar a “job,” based on what you think is the best use of your business funds, and then go back and compare your plan with reality to see how you did.
A budget will help you:
- Forecast what money you expect to earn
- Plan where to spend that revenue
- See the difference between your plan and reality
What makes a good budget?
The best budgets are simple and flexible. If circumstances change (as they do), your budget can flex to give you a clear picture of where you stand at all times.
Every good budget should include seven components:
1. Your estimated revenue
This is the amount you expect to make from the sale of goods or services. It’s all of the cash you bring in the door, regardless of what you spent to get there. This is the first line on your budget. It can be based on last year’s numbers or (if you’re a startup ), based on industry averages.
2. Your fixed costs
These are all your regular, consistent costs that don’t change according to how much you make—things like rent, insurance, utilities, bank fees, accounting and legal services, and equipment leasing.
Further reading: Fixed Costs (Everything You Need to Know)
3. Your variable costs
These change according to production or sales volume and are closely related to “ costs of goods sold ,” i.e., anything related to the production or purchase of the product your business sells. Variable costs might include raw materials, inventory, production costs, packaging, or shipping. Other variable costs can include sales commission, credit card fees, and travel. A clear budget plan outlines what you expect to spend on all these costs.
The cost of salaries can fall under both fixed and variable costs. For example, your core in-house team is usually associated with fixed costs, while production or manufacturing teams—anything related to the production of goods—are treated as variable costs. Make sure you file your different salary costs in the correct area of your budget.
Further reading: Variable Costs (A Simple Guide)
4. Your one-off costs
One-off costs fall outside the usual work your business does. These are startup costs like moving offices, equipment, furniture, and software, as well as other costs related to launch and research.
5. Your cash flow
Cash flow is all money traveling into and out of a business. You have positive cash flow if there is more money coming into your business over a set period of time than going out. This is most easily calculated by subtracting the amount of money available at the beginning of a set period of time and at the end.
Since cash flow is the oxygen of every business, make sure you monitor this weekly, or at least monthly. You could be raking it in and still not have enough money on hand to pay your suppliers.
6. Your profit
Profit is what you take home after deducting your expenses from your revenue. Growing profits mean a growing business. Here you’ll plan out how much profit you plan to make based on your projected revenue, expenses, and cost of goods sold. If the difference between revenue and expenses (aka “ profit margins ”) aren’t where you’d like them to be, you need to rethink your cost of goods sold and consider raising prices .
Or, if you think you can’t squeeze any more profit margin out of your business, consider boosting the Advertising and Promotions line in your budget to increase total sales.
7. A budget calculator
A budget calculator can help you see exactly where you stand when it comes to your business budget planning. It might sound obvious, but getting all the numbers in your budget in one easy-to-read summary is really helpful.
In your spreadsheet, create a summary page with a row for each of the budget categories above. This is the framework of your basic budget. Then, next to each category, list the total amount you’ve budgeted. Finally, create another column to the right—when the time period ends, use it to record the actual amounts spent in each category. This gives you a snapshot of your budget that’s easy to find without diving into layers of crowded spreadsheets.
See the sample below.
Pro tip: link the totals on the summary page to the original sums in your other budget tabs . That way when you update any figures, your budget summary gets updated at the same time. The result: your very own budget calculator.
You can also check out this simple Startup Cost Calculator from CardConnect. It lays out some of the most common expenses that you might not have considered. From there, you can customize a rough budget for your own industry.
Small business budgets for different types of company
While every good budget has the same framework, you’ll need to think about the unique budgeting quirks of your industry and business type.
Seasonal businesses
If your business has a busy season and a slow season, budgeting is doubly important.
Because your business isn’t consistent each month, a budget gives you a good view of past and present data to predict future cash flow . Forecasting in this way helps you spot annual trends, see how much money you need to get you through the slow months, and look for opportunities to cut costs to offset the low season. You can use your slow season to plan for the next year, negotiate with vendors, and build customer loyalty through engagement.
Don’t assume the same thing will happen every year, though. Just like any budget, forecasting is a process that evolves. So start with what you know, and if you don’t know something—like what kind of unexpected costs might pop up next quarter— just give it your best guess . Better to set aside money for an emergency that doesn’t happen than to be blindsided.
Ecommerce businesses
The main budgeting factor for ecommerce is shipping. Shipping costs (and potential import duties) can have a huge impact.
Do you have space in your budget to cover shipping to customers? If not, do you have an alternative strategy that’s in line with your budget—like flat rate shipping or real-time shipping quotes for customers? Packaging can affect shipping rates, so factor that into your cost of goods sold too. While you’re at it, consider any international warehousing costs and duties.
You’ll also want to create the best online shopping experience for your customers, so make sure you include a good web hosting service, web design, product photography, advertising, blogging, and social media in your budget.
Inventory businesses
If you need to stock up on inventory to meet demand, factor this into your cost of goods sold. Use the previous year’s sales or industry benchmarks to take a best guess at the amount of inventory you need. A little upfront research will help ensure you’re getting the best prices from your vendors and shipping the right amount to satisfy need, mitigate shipping costs, and fit within your budget.
The volume of inventory might affect your pricing. For example, if you order more stock, your cost per unit will be lower, but your overall spend will be higher. Make sure this is factored into your budget and pricing, and that the volume ordered isn’t greater than actual product demand.
You may also need to include the cost of storage solutions or disposal of leftover stock.
Custom order businesses
When creating custom ordered goods, factor in labor time and cost of operations and materials. These vary from order to order, so make an average estimate.
Budgeting is tricky for startups—you rarely have an existing model to use. Do your due diligence by researching industry benchmarks for salaries, rent, and marketing costs. Ask your network what you can expect to pay for professional fees, benefits, and equipment. Set aside a portion of your budget for advisors—accountants, lawyers, that kind of thing. A few thousand dollars upfront could save you thousands more in legal fees and inefficiencies later on.
This is just scratching the surface, and there’s plenty more to consider when creating a budget for a startup. This business startup budget guide from The Balance is a great start.
Service businesses
If you don’t have a physical product, focus on projected sales, revenue, salaries, and consultant costs. Figures in these industries—whether accounting, legal services, creative, or insurance—can vary greatly, which means budgets need flexibility. These figures are reliant on the number of people required to provide the service, the cost of their time, and fluctuating customer demand.
Small business budgeting templates
A business budget template can be as simple as a table or as complex as a multi-page spreadsheet. Just make sure you’re creating something that you’ll actually use.
Create your budget yearly—a 12-month budget is standard fare—with quarterly or monthly updates and check-ins to ensure you’re on track.
Here are some of our favorite templates for you to plug into and get rolling.
- The Balance has a clear table template that lists every budget item, the budgeted amount, the actual amount, and the difference between the two. Use this one if you’re looking to keep it simple.
- Capterra has both monthly and annual breakdowns in their Excel download. It’s straightforward, thorough, and fairly foolproof.
- Google Sheets has plenty of budget templates hiding right under your nose. They’re easy to use, and they translate your figures into clear tables and charts on a concise, visual summary page.
- Smartsheet has multiple resources for small businesses, including 12-month budget spreadsheets, department budget templates, projection templates, project-by-project templates, and startup templates. These templates are ideal if you’re looking for a little more detail.
- Scott’s Marketplace is a blog for small businesses. Their budget template comes with step-by-step instructions that make it dead simple for anyone.
- Vertex42 focuses on Excel spreadsheets and offers templates for both product-based and service-based businesses, as well as a business startup costs template for anyone launching a new business.
Budgeting + bookkeeping = a match made in heaven
Making a budget is kind of like dreaming: it’s mostly pretend. But when you can start pulling on accurate historical financials to plan the upcoming year, and when you can check your budget against real numbers, that’s when budgets start to become useful.
The only way to get accurate financial data is through consistent bookkeeping.
Don’t have a regular bookkeeping process down pat? Check out our free guide, Bookkeeping Basics for Entrepreneurs . We’ll walk you through everything you need to know to get going yourself, for free.
If you need a bit more help, get in touch with us. Bookkeeping isn’t for everyone, especially when you’re also trying to stay on top of a growing business—but at Bench, bookkeeping is what we do best.
Related Posts

Understanding an Income Statement (Definition and Examples)
How profitable is your business? Your income statement will tell you.

Gross Profit: What Is It and What It Means For Your Business
If you want to have a profitable business, you must first turn a gross profit. But what exactly is it, how do you calculate it, and how do you make more of it?

Top 12 Questions to Ask an Accountant When You Want to Grow Your Business
Accountants aren’t just numbers people—they’re business advisors.
Join over 140,000 fellow entrepreneurs who receive expert advice for their small business finances
Get a regular dose of educational guides and resources curated from the experts at Bench to help you confidently make the right decisions to grow your business. No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.


- Testimonials
- Case Studies
- Auditing Process
- FAQ’s
- Telecom Auditing
- Utility Auditing
- Waste and Recycling Services Auditing
- Merchant Processing Auditing
- Property Tax Consulting
- Managed Print Auditing
- Uniform & Linen Services Auditing
- Economic Incentives
- Small Parcel Auditing
- Vendor Payment Solutions
- Maintenance Contracts
- Auto Dealerships
- City and County Government
- Commercial Property Management
- Hospitals and Healthcare
- Hotels and Hotel Groups
- Manufacturing
- Multi-Location Businesses
- Private Equity Firms
- Restaurant Groups
- Schools and Universities
- All Other Businesses or Organizations
- Cost Reduction
- Franchising
- Learning Hub
- Our Offices
- Join Our Team
1-877-843-7579

Business Budgeting Made Easy: A Beginner’s Guide to Success
Creating a business budget is a critical step for financial success , yet many business owners find themselves unsure where to start. Understanding how to craft an effective budget can make the difference between thriving and merely surviving in today’s competitive market.
An approach to budgeting involves examining revenue , setting realistic spending goals , and implementing practical strategies for both monthly and long-term financial planning . By utilizing helpful tools and templates , even beginners can demystify the process and gain confidence in their budgeting abilities.
With the right knowledge and approach, business owners can develop comprehensive budgets that support informed decision-making and foster sustainable growth . Mastering this essential skill empowers entrepreneurs to manage their financial future and understand the aspects of business finance with confidence.
The Importance Of Business Budgets
A well-crafted business budget is the cornerstone of financial success for any enterprise, regardless of its size or industry. It serves as a roadmap for your company’s financial future, providing clarity and direction in an often uncertain business environment.
By prioritizing the creation and maintenance of a detailed budget , you’re taking a proactive approach to keeping track of business expenses and ensuring the long-term viability of your business. With a clear understanding of your income and expenses , you can make informed decisions about investments , expansions , and reducing business expenses .
Guiding Financial Decision-Making
A well-structured budget is an invaluable tool for managing the finances of your business . It provides a framework for evaluating financial decisions, helping you determine whether a particular expenditure aligns with your overall business goals .
By referring to your budget, you can:
- Allocate resources more effectively
- Identify areas where costs can be reduced
- Make informed decisions about pricing strategies
- Plan for future growth and expansion
Facilitating Goal Setting and Performance Tracking
Your business budget serves as a benchmark for measuring your company’s financial performance . By setting clear financial goals and regularly comparing actual results to your budgeted figures, you can monitor your progress and identify areas of overperformance or underperformance.
This process allows you to:
- Make timely adjustments to your strategies
- Motivate your team by setting achievable targets
- Continuously improve your financial planning
Improving Cash Flow Management
Effective cash flow management is crucial for the survival and growth of any business. A well-planned budget helps you forecast cash inflows and outflows , identifying potential cash shortages in advance.
This foresight enables you to:
- Plan for seasonal fluctuations in revenue
- Ensure sufficient funds to cover operational expenses and investments
- Make informed decisions about timing of large purchases or investments
Enhancing Stakeholder Confidence
A detailed and realistic budget demonstrates financial responsibility and strategic planning to stakeholders such as investors , lenders , and partners . It shows that you have a clear vision for your business and are committed to its success.
This can lead to several benefits:
- Improved chances of securing funding
- Strengthened relationships with suppliers and creditors
- Increased attractiveness to potential investors or business partners
By recognizing the importance of business budgets and implementing a robust budgeting process , you’re laying the foundation for financial stability and long-term success . A well-managed budget is your key to maneuvering economic uncertainties with confidence and responding swiftly to evolving market conditions.
Preparing For Budget Creation
Establishing a solid foundation is crucial before examining the financial details for a successful budgeting process. Careful planning helps create a detailed budget that supports your business objectives .
Gathering Financial Documents
Collecting all relevant financial documents is the first step in budget preparation. These may include income statements , balance sheets , cash flow statements , bank statements , tax returns , and receipts and invoices .
Having these documents readily available provides necessary historical data for informed projections and trend identification in your business’s financial performance.
Determining Your Budgeting Period
Decide on the timeframe for your budget, considering your business cycle , seasonal fluctuations , and industry-specific factors . While most businesses create annual budgets , breaking them down into monthly or quarterly segments allows for more frequent reviews and adjustments.
Categorizing Expenses (Fixed And Variable)
An essential part of budget preparation is classifying business expenses into fixed and variable costs . This categorization helps understand spending patterns and identify potential cost reduction areas .
Fixed expenses include:
- Rent or mortgage payments
- Insurance premiums
- Salaries for full-time employees
- Loan repayments
Variable expenses include:
- Raw materials or inventory
- Shipping costs
- Commissions or bonuses
Setting Financial Goals
Establish clear, measurable financial goals to guide budgeting decisions and prioritize spending. Consider setting SMART targets for revenue growth , profit margins , debt reduction , cash reserves , and investment in new equipment or technology .
Choosing Budgeting Tools
Select the right tools to create and manage your budget effectively. Options include spreadsheet software , accounting software , and budgeting apps designed for small businesses.
Choose a tool that fits your business’s needs and financial expertise level . Many software options offer templates and guides to simplify the budgeting process.
Involving Key Stakeholders
Engage relevant team members and stakeholders in the budget preparation process. This may include department heads , financial advisors or accountants , and key investors or board members .
Their input can provide valuable insights and ensure buy-in for the final budget. Thorough preparation sets the stage for a more accurate and useful financial plan , leading to better financial management for your business.
Step-By-Step Budget Creation Process
Crafting a detailed business budget is crucial for directing financial choices and realizing objectives . Follow these steps to develop a robust financial plan that will serve as a roadmap for your business success.
Projecting Your Revenue
Estimating your revenue in business is the first crucial step in budget creation. This process involves analyzing historical data , considering market conditions , accounting for seasonality , and setting realistic growth targets .
Create monthly revenue projections for the upcoming year, breaking them down by product or service line if applicable. Be conservative in your estimates to avoid overextending your resources.
Calculating Fixed Expenses
Identify and calculate your fixed expenses , which remain relatively constant regardless of your business’s performance.
Rent And Utilities
List all operational expenses related to your physical space:
- Property taxes
- Basic utilities (electricity, water, internet)
Salaries And Benefits
Account for all regular employee costs:
- Salaries and wages for full-time staff
- Payroll taxes
- Health insurance and other benefits
- Retirement contributions
Loan Payments And Subscriptions
Include any recurring financial obligations:
- Equipment leases
- Software subscriptions
- Professional memberships
Estimating Variable Expenses
Variable expenses fluctuate based on your business activity. Estimate these costs based on your revenue projections:
- Shipping and packaging
- Sales commissions
- Credit card processing fees
- Part-time or seasonal labor
Be sure to account for potential price increases in materials or services throughout the year.
Accounting For One-Time Expenses
Budget for occasional or one-time expenses such as equipment purchases, marketing campaigns, professional development, office renovations, and legal or consulting fees. Spread these costs across the year to avoid cash flow issues.
Determining Profit Margins
Calculate your projected profit in business by subtracting your total expenses from your estimated revenue. Analyze your profit margins to ensure they align with your financial goals.
If they fall short, consider increasing prices, finding ways to reduce expenses, or focusing on higher-margin products or services.
Creating A Cash Flow Forecast
Develop a month-by-month cash flow forecast to ensure you’ll have sufficient funds to cover expenses throughout the year. This helps you identify potential cash shortages, plan for large expenses or investments, and make informed decisions about timing of purchases or hiring.
Setting Aside Contingency Funds
Allocate a portion of your budget for unexpected expenses or opportunities. A good rule of thumb is to set aside 10-20% of your revenue as a contingency fund .
Finalizing And Implementing Your Budget
Review your completed budget to ensure it’s realistic and aligns with your business goals. Once finalized, share the budget with relevant team members, set up a system for tracking actual performance against your budget, and schedule regular review sessions to monitor progress and make adjustments.
Regular Review And Adjustment
Your budget is a living document that requires ongoing attention. Plan to review it monthly and make adjustments based on actual performance vs. projections, changes in the market or your business model, and unexpected challenges or opportunities.
By following this detailed process, you’ll create a detailed business budget that serves as a helpful tool for decision-making and growth. Regular monitoring and adjustment will ensure your budget remains effective throughout the year.
Choosing The Right Budgeting Method
Selecting an appropriate budgeting method is crucial for effectively managing your business finances. Different approaches suit various business types and goals, so it’s important to explore popular budgeting methods to find the best fit for your needs.
Traditional Budgeting
Traditional budgeting involves creating a detailed budget based on historical data and future projections . This method is suitable for businesses with relatively stable operations and predictable expenses.
Pros:
- Offers a detailed financial overview
- Helps identify cost-saving opportunities
- Facilitates long-term planning
- Can be time-consuming to create and maintain
- May become outdated quickly in rapidly changing markets
Zero-Based Budgeting
Zero-based budgeting starts from scratch each budgeting period, requiring justification for every expense . This approach is ideal for businesses looking to optimize spending and eliminate unnecessary costs .
- Encourages critical evaluation of all expenses
- Helps identify and eliminate inefficiencies
- Adapts well to changing business environments
- Requires significant time and effort
- May be challenging for businesses with complex operations
Rolling Budget
A rolling budget involves continuously updating your financial plan, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis . This approach is well-suited for businesses operating in rapidly evolving markets .
- Provides up-to-date financial projections
- Allows for quick adjustments to changing conditions
- Improves accuracy of short-term forecasts
- Requires frequent attention and updates
- May make long-term planning more challenging
Incremental Budgeting
Incremental budgeting uses the previous period’s budget as a starting point, making small adjustments for the upcoming period. This approach is suitable for stable businesses with minimal year-to-year changes .
- Simple and quick to implement
- Provides consistency in budgeting
- Requires less time and resources
- May perpetuate inefficiencies
- Doesn’t encourage critical evaluation of expenses
Activity-Based Budgeting
Activity-based budgeting focuses on the relationship between activities and costs , allocating resources based on specific cost drivers . This method is beneficial for businesses looking to optimize processes and improve efficiency .
- Provides detailed insights into cost drivers
- Helps identify areas for process improvement
- Supports more accurate cost allocation
- Can be complex to implement
- Requires detailed activity tracking
Flexible Budgeting
Flexible budgeting creates multiple budget scenarios based on different levels of activity or revenue . This approach is useful for businesses with fluctuating demand or uncertain market conditions .
- Adapts to varying levels of business activity
- Helps prepare for different scenarios
- Improves decision-making in uncertain environments
- Requires more time to create multiple scenarios
- May be challenging to choose the most appropriate scenario
Value Proposition Budgeting
Value proposition budgeting aligns your budget with your company’s value proposition and strategic goals . This method is ideal for businesses focused on long-term growth and competitive advantage .
- Ensures budget aligns with strategic objectives
- Encourages investment in key value drivers
- Supports long-term business growth
- May be challenging to quantify value in some areas
- Requires a clear understanding of your value proposition
When selecting a budgeting method, consider your business size , industry , growth stage , and strategic goals . You may find that a combination of methods works best for your unique situation.
Remember, the right budgeting approach should provide clarity , support decision-making , and help propel your business to achieve its financial objectives .
Leveraging Technology For Efficient Budgeting
Technology plays a crucial role in streamlining business operations , including budgeting . By utilizing the capabilities of contemporary tools and software, you can substantially improve your budgeting process , save time , and obtain valuable insights into your financial well-being .
Budgeting Software and Apps
Numerous budgeting applications are designed specifically for businesses of all sizes. These tools often offer features such as:
- Automated data entry and categorization
- Real-time financial reporting
- Customizable budget templates Connect your bank accounts and credit cards to our platform.
- Collaboration features for team input
Popular options include QuickBooks , Xero , and FreshBooks . These platforms can dramatically reduce the time spent on manual data entry and calculations, allowing you to focus on analysis and decision-making .
Spreadsheet Templates
For those who prefer a more hands-on approach, spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets offers powerful budgeting capabilities . Many pre-designed templates are available, which you can customize to fit your business needs.
Spreadsheets provide:
- Flexibility in budget design
- Complex calculations and formulas
- Data visualization through charts and graphs
- Easy sharing and collaboration
While spreadsheets require more manual input than dedicated budgeting software, they offer unparalleled customization options .
Expense Tracking Tools
Accurate expense tracking is fundamental to effective budgeting. Using a best business expense tracker can help you:
- Automatically categorize expenses
- Capture and store receipts digitally
- Generate expense reports
- Integrate with your accounting software
These tools not only save time but also ensure that no expenses slip through the cracks, providing a more accurate picture of your business spending.
Financial Forecasting Software
Forecasting tools use historical data and advanced algorithms to predict future financial trends . This technology can help you:
- Create more accurate budget projections
- Identify potential cash flow issues in advance
- Model different scenarios and their financial impacts
- Make data-driven decisions about investments and growth
By leveraging forecasting software, you can create more robust, forward-looking budgets that account for various potential outcomes.
Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud technology has revolutionized business budgeting by offering:
- Real-time access to financial data from anywhere
- Automatic backups and data security
- Seamless updates and improvements
- Easy scalability as your business grows
Cloud-based budgeting solutions keep your financial data current and readily available, enabling improved teamwork and decision-making .
Integration with Other Business Systems
Modern budgeting tools often integrate with other business systems, such as:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems
- Point of Sale (POS) systems
- Payroll software
These integrations provide an overview of your business finances , automatically pulling in data from various sources to create a more detailed and precise budget.
Data Visualization Tools
Transforming complex financial data into easy-to-understand visuals can greatly enhance your budgeting process. Data visualization tools offer:
- Interactive dashboards
- Customizable charts and graphs
- Real-time data updates
- Drill-down capabilities for detailed analysis
By presenting your budget data visually, you can quickly identify trends, anomalies, and areas requiring attention, making it easier to communicate financial information to stakeholders.
Embracing technology in your budgeting process can lead to significant improvements in accuracy , efficiency , and insight . As you explore these tools, consider your business’s specific needs, the level of technical expertise required, and how each solution integrates with your existing systems.
With the right technological support, you can transform your budgeting process from a time-consuming task into a powerful tool for driving business success. Remember to regularly evaluate and update your chosen tools to ensure they continue to meet your evolving business needs.
Tailoring Budgets For Different Business Types
Creating an effective budget requires a customized approach for various business models. Different business types have unique financial structures, challenges, and goals that require customized budgeting strategies .
Service-Based Businesses
Service-based businesses, such as consulting firms or marketing agencies, have distinct budgeting needs compared to product-based companies. Key considerations include labor costs , project-based budgeting , fluctuating income , and limited inventory costs .
- Labor costs : Typically the largest expense, requiring careful tracking of billable hours
- Project-based budgeting : Allocating resources for specific client projects
- Fluctuating income : Planning for inconsistent revenue streams
- Limited inventory costs : Focus on operational expenses rather than stock management
Maintaining a healthy cash flow and accurately forecasting project costs and revenues are crucial for these businesses.
Retail Businesses
Retail businesses face unique budgeting challenges due to inventory management and seasonal fluctuations. Important factors to consider include:
- Inventory costs : Balancing stock levels with demand forecasts
- Seasonal variations : Budgeting for peak and off-peak periods
- Marketing expenses : Allocating funds for promotions and advertising
- Point of sale systems : Integrating sales data into the budgeting process
Retail budgets should be flexible enough to adapt to changing consumer trends and market conditions.
Manufacturing Businesses
Manufacturing businesses often deal with complex supply chains and production processes . Their budgets should account for:
- Raw material costs : Tracking price fluctuations and supplier agreements
- Equipment maintenance and upgrades : Planning for capital expenditures
- Production efficiency : Budgeting for process improvements and waste reduction
- Inventory management : Balancing raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods
Accurate cost allocation and production forecasting are essential for manufacturing budgets.
Startups and Growth-Stage Companies
Startups and quickly expanding companies encounter distinctive budgeting challenges due to their ever-changing environment. Key considerations include:
- Burn rate : Carefully monitoring cash outflow relative to available funds
- Funding rounds : Budgeting for different scenarios based on potential investments
- Scaling costs : Planning for rapid expansion of teams and resources
- Research and development : Allocating funds for product development and innovation
Flexibility and scenario planning are crucial for these businesses to adapt to changing circumstances and growth trajectories.
Nonprofit Organizations
Nonprofit organizations have distinct budgeting needs due to their mission-driven nature and reliance on donations. Important factors include:
- Grant management : Tracking restricted and unrestricted funds
- Fundraising expenses : Budgeting for donor acquisition and retention activities
- Program costs : Allocating resources to achieve mission objectives
- Transparency : Creating budgets that clearly demonstrate financial stewardship
Nonprofit budgets should align closely with the organization’s mission and demonstrate efficient use of resources to stakeholders.
Seasonal Businesses
Businesses with significant seasonal variations, such as tourism or landscaping companies, require specialized budgeting approaches . Consider the following factors:
- Cash flow management : Planning for lean periods during off-seasons
- Workforce fluctuations : Budgeting for seasonal hiring and layoffs
- Equipment utilization : Accounting for periods of high and low asset usage
- Marketing timing : Allocating promotional budgets to coincide with peak seasons
These businesses should create annual budgets that account for cyclical patterns while maintaining financial stability throughout the year.
Freelancers and Solopreneurs
Individual business owners face unique challenges in budgeting due to personal and professional financial overlap. Key considerations include:
- Income variability : Planning for inconsistent revenue streams
- Self-employment taxes : Budgeting for quarterly tax payments
- Business vs. personal expenses : Clearly delineating between the two
- Retirement and benefits : Allocating funds for personal financial security
Freelancers and solopreneurs should create budgets that balance business growth with personal financial stability .
By tailoring your budgeting approach to your specific business type, you can create a financial plan that addresses your unique challenges and opportunities . While the fundamental principles of budgeting remain consistent, the emphasis and detail may vary significantly based on your business model.
Regularly review and adjust your budget to ensure it continues to serve your business’s evolving needs and helps drive your success in your particular industry or niche.
Implementing And Maintaining Your Budget
Creating a budget is only the first step; the real challenge lies in implementing and maintaining it effectively. Let’s explore the process of putting your budget into action and ensuring its long-term success.
Rolling Out Your Budget
Implementing your budget requires careful planning and communication . Consider the following steps:
- Set a start date : Choose a specific date to begin following your new budget.
- Communicate with stakeholders : Inform all relevant parties about the new budget and their roles.
- Train staff : Ensure everyone understands how to use the budget and track expenses.
- Integrate with accounting systems : Set up your budget in your accounting software for easy tracking.
Tracking Expenses and Income
Accurate tracking is crucial for budget success. Consider these strategies:
- Use accounting software : Tools like QuickBooks can automate much of the tracking process.
- Categorize transactions : Consistently assign expenses and income to the correct budget categories.
- Reconcile accounts regularly : Match your records with bank statements to catch any discrepancies.
- Monitor cash flow : Keep a close eye on the timing of income and expenses to maintain liquidity.
Regular Budget Reviews
Periodic reviews help keep your budget on track. Consider implementing the following review schedule:
- Weekly check-ins : Quickly review income and expenses to catch any immediate issues.
- Monthly analysis : Compare actual figures to budgeted amounts and investigate variances.
- Quarterly assessments : Evaluate overall budget performance and make necessary adjustments.
- Annual review : Perform an in-depth assessment to inform the next year’s budget.
Making Adjustments
Flexibility is key to maintaining an effective budget. Consider these adjustment strategies:
- Respond to variances : Investigate and address significant differences between actual and budgeted figures.
- Adapt to changes : Modify your budget as your business evolves or market conditions shift.
- Reallocate funds : Move money between categories as needed, while staying within overall limits.
- Update forecasts : Regularly revise your projections based on actual performance and new information.

Using Budget Reports
Effective reporting helps you gain insights from your budget. Implement these reporting practices:
- Generate regular reports : Create standard reports on income, expenses, and cash flow.
- Visualize data : Use charts and graphs to make budget information more accessible.
- Share with stakeholders : Distribute relevant reports to team members, investors, or board members.
- Act on insights : Use the information from reports to make informed business decisions.
Addressing Budget Challenges
Be prepared to tackle common budgeting hurdles. Consider these strategies:
- Unexpected expenses : Maintain an emergency fund to cover unforeseen costs.
- Revenue shortfalls : Have contingency plans for periods when income doesn’t meet projections.
- Overspending : Implement approval processes for expenses exceeding budget limits.
- Seasonal fluctuations : Adjust your budget to account for predictable ups and downs in your business cycle.
Leveraging Technology
Take advantage of tools to streamline budget management. Consider these technological solutions:
- Budgeting software : Use specialized tools for creating and tracking budgets.
- Cloud-based solutions : Access your budget information from anywhere, anytime.
- Automation : Set up automatic categorization of transactions to save time.
- Connect your budgeting tools with other business systems to enable smooth data exchange.
Continuous Improvement
View budgeting as an ongoing process of refinement. Implement these improvement strategies:
- Learn from past performance : Use historical data to improve future budgets.
- Stay informed : Keep up with industry trends and economic factors that may impact your budget.
- Seek feedback : Ask team members for input on how to improve the budgeting process.
- Benchmark : Compare your financial performance against industry standards to identify areas for improvement.
Implementing and maintaining your budget requires dedication and consistency . By following these strategies, you’ll be well-equipped to transform your budget into a powerful tool that propels your business forward.
Remember, a well-maintained budget is not just about controlling costs—it’s about making informed decisions that lead to sustainable growth and success .
Common Pitfalls In Business Budgeting
Creating and maintaining a budget can be challenging for business owners. By understanding common pitfalls, you can take proactive steps to avoid them and ensure your budget remains an effective financial management tool .
Underestimating Expenses
Accurately estimating costs is crucial for effective budgeting. Consider the following strategies to avoid underestimating expenses:
- Research thoroughly : Gather accurate cost information for all expenses.
- Include hidden costs : Account for often-overlooked expenses like maintenance, taxes, and fees.
- Plan for price increases : Factor in potential inflation and supplier price hikes.
- Add a buffer : Include a contingency fund for unexpected expenses.
Overestimating Revenue
While optimism is valuable in business, it’s important to remain realistic when projecting revenue . Consider these approaches:
- Use historical data : Base projections on past performance rather than best-case scenarios.
- Consider market conditions : Factor in economic trends and industry changes.
- Account for seasonality : Adjust revenue expectations for predictable fluctuations.
- Be conservative : It’s better to exceed modest projections than fall short of ambitious ones.
Neglecting Cash Flow
Effective cash flow management is crucial for business success, even for profitable companies. Keep these points in mind:
- Track timing of payments : Consider when you’ll actually receive money, not just when it’s earned.
- Monitor accounts receivable : Implement strategies to ensure timely customer payments.
- Plan for gaps : Prepare for periods when expenses may exceed income.
- Maintain a cash reserve : Keep a buffer to cover operations during lean times.
Ignoring Fixed Costs
Fixed costs can easily be overlooked, leading to budget inaccuracies. Consider these strategies:
- List all fixed expenses : Include rent, salaries, insurance, and loan payments.
- Review regularly : Some fixed costs may change over time.
- Consider long-term commitments : Factor in multi-year contracts and leases.
- Don’t forget depreciation : Account for the declining value of assets.
Failing to Adjust the Budget
A static budget quickly becomes obsolete. Keep your budget relevant by:
- Scheduling regular reviews : Set aside time to assess and update your budget.
- Responding to changes : Adjust your budget when business circumstances shift.
- Learning from variances : Use differences between actual and budgeted figures to improve future planning.
- Staying flexible : Be prepared to reallocate resources as needed.
Lack of Detail
A vague budget is difficult to implement and track. Enhance your budget’s effectiveness by:
- Breaking down categories : Use specific line items instead of broad categories.
- Setting clear targets : Define measurable goals for income and expenses.
- Including non-financial metrics : Track key performance indicators that impact your budget.
- Documenting assumptions : Record the reasoning behind your budget figures for future reference.
Not Involving Key Stakeholders
Creating a budget in isolation can lead to unrealistic expectations. Improve your budgeting process by:
- Seeking input : Consult department heads and team leaders for their insights.
- Communicating the process : Ensure everyone understands how the budget is created and used.
- Getting buy-in : Involve key personnel in setting goals and allocating resources.
- Sharing results : Keep stakeholders informed about budget performance.
Overlooking Long-Term Goals
Focusing solely on immediate needs can hinder future growth. Balance your budget by:
- Aligning with strategy : Ensure your budget supports your long-term business objectives.
- Planning for investments : Allocate funds for future expansion or improvements.
- Considering market trends : Budget for adapting to changing industry conditions.
- Balancing short-term and long-term : Find the right mix of current operations and future planning.
Relying Too Heavily on Tools
While budgeting software is helpful, it shouldn’t replace critical thinking. Enhance your approach by:
- Understanding the numbers : Don’t blindly trust automated calculations.
- Customizing templates : Adapt generic tools to fit your specific business needs.
- Using human insight : Combine data analysis with industry knowledge and experience.
- Regularly reviewing outputs : Check that automated reports align with your business reality.
Ignoring Non-Financial Factors
A detailed budget considers more than just numbers. Strengthen your budget by:
- Factoring in industry changes : Consider how market shifts might impact your finances.
- Accounting for regulations : Budget for compliance with new laws or standards.
- Considering human factors : Think about how staffing changes or training needs might affect your budget.
- Planning for technology : Budget for necessary upgrades or new systems.
By avoiding these common pitfalls, you can create a more accurate, flexible, and effective business budget. Remember that budgeting is an ongoing process of learning and refinement, and each challenge you overcome will strengthen your financial management skills and contribute to your business’s long-term success.
Using Your Budget As A Strategic Tool
A well-crafted business budget is more than just a financial roadmap; it’s a powerful strategic tool that can guide your business to success. By using your budget effectively, you can make informed decisions , identify opportunities for growth , and address challenges with confidence .
Forecasting and Planning
Your budget serves as a crystal ball for your business’s financial future. Use it to project growth , estimate future revenue and expenses , and analyze historical data to predict seasonal fluctuations or market shifts.
- Set realistic goals based on your financial projections
- Prepare for best-case and worst-case scenarios
Resource Allocation
Strategically distribute your resources to maximize efficiency and impact. Prioritize investments by allocating funds to areas that offer the highest return on investment .
- Balance short-term and long-term needs
- Use your budget to determine when to hire, outsource, or restructure
- Manage inventory levels to meet demand without tying up excess capital
Performance Measurement
Your budget provides benchmarks to evaluate your business’s financial health. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as gross profit margin, net profit, and cash flow .
- Compare actual vs. budgeted figures regularly Investigate discrepancies to understand their causes and effects.
- Recognize when you meet or exceed budget targets to boost morale
Decision Making
Let your budget guide critical business choices . Use financial projections to assess potential new ventures or expansions.
- Determine optimal price points based on cost structures and profit margins
- Identify areas where expenses can be reduced without compromising quality
- Assess the financial impact of major purchases or upgrades
Risk Management
Your budget helps you anticipate and mitigate potential financial risks . Pinpoint areas where your business may be financially exposed.
- Build reserves by allocating funds for emergencies or unexpected downturns
- Use your budget to plan for multiple revenue sources
- Model how different economic conditions might affect your finances
Communication Tool
Use your budget to align your team and stakeholders . Clearly communicate financial goals and constraints to all departments.
- Encourage cross-functional planning and resource sharing
- Support strategic choices with solid financial data
- Regularly update stakeholders on financial performance and projections
Your budget is a living document that evolves with your business. Use discrepancies between actual and budgeted figures to refine future projections .
- Regularly review and adjust your budget to reflect new market conditions or business strategies
- Incorporate insights from team members and financial advisors
- Compare your financial metrics to industry standards to identify areas for improvement
Growth Planning
Use your budget to support sustainable expansion . Use financial analysis to spot potential areas for business development.
- Budget for the resources needed to support expansion
- Determine when and how much additional funding might be required
- Establish financial targets that signal readiness for next growth stages
Tax Planning
Use your budget to optimize your tax strategy . Estimate future tax obligations based on projected income.
- Allocate funds for tax-deductible expenses strategically Evaluate the tax effects of major investments.
- Anticipate how potential tax law changes might affect your business
Stakeholder Management
Your budget can help manage relationships with investors, lenders, and partners. Demonstrate financial acumen through well-prepared budgets and accurate projections.
- Use your budget to support loan applications or investor pitches Use financial data to discuss favorable terms with suppliers or partners
- Create clear, informative financial reports that instill confidence in your management
By viewing your budget as a strategic tool, you transform it from a mere financial document into a powerful instrument for driving business success . It serves as your guide, helping you make informed decisions , seize opportunities , and drive your company’s growth and profitability in a sustainable manner .
Frequently Asked Questions
- How often should I review and update my business budget?
Reviewing your business budget monthly and updating it quarterly is a good practice. Monthly reviews help track actual performance against projections, while quarterly updates allow for adjustments based on market changes or shifts in business strategy .
- What’s the difference between a business budget and a financial forecast?
A business budget is a detailed plan of expected income and expenses for a specific period, typically a year, broken down into monthly or quarterly segments.
A financial forecast , however, is a projection of future financial performance based on historical data , market trends , and economic factors , often covering a longer time frame and helping with long-term planning and strategic decision-making .
- Can I create an effective business budget without professional help?
Creating an effective business budget without professional help is possible, especially if you have a good understanding of your business finances and basic accounting principles .
However, for complex businesses or if you’re unsure about financial matters, consulting with a professional accountant or financial advisor can provide valuable insights and ensure accuracy in your budgeting process.
- How do I handle unexpected expenses in my business budget?
Include a contingency fund in your budget, typically 5-10% of your total expenses, to handle unexpected costs without derailing your entire budget. Regularly review and categorize unexpected expenses to identify patterns and potentially include them in future budgets.
- What are some key performance indicators (KPIs) I should track alongside my budget?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) to track alongside your budget include:
- Gross Profit Margin
- Net Profit Margin
- Accounts Receivable Turnover
- Inventory Turnover
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio
- Operating Expense Ratio
- Revenue Growth Rate
- Customer Acquisition Cost
- Customer Lifetime Value
These key performance indicators offer a detailed understanding of your financial health and performance, complementing your budget and supporting your business decision-making .
Creating a business budget is a crucial step for achieving financial stability and growth . By examining your revenue , deducting fixed and variable costs , estimating profit , and tracking cash flow , you can create a detailed financial plan for your business.
Remember that budgeting is not a one-time task but an ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustment. As you implement your budget, make use of available tools and templates to streamline the process.
Set clear spending goals and consistently track your performance against these targets. This proactive approach will help you identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions about resource allocation .
Embrace budgeting as a versatile tool that adapts to the needs of your business. Regular reviews and updates ensure that your budget remains relevant and effective in the face of changing market conditions and business needs.
By adopting a flexible yet disciplined approach to budgeting, you’ll be better positioned to address financial challenges and capitalize on growth prospects . A well-crafted and regularly maintained budget is more than just a financial document—it’s a powerful instrument for achieving your business goals and driving long-term success.
Start implementing these budgeting practices today, and watch as your business flourishes with improved financial clarity and control . Your dedication to sound financial management will undoubtedly pay dividends in the future of your enterprise.
Related Articles

No Business Income But Have Expenses? Deductions Explained
Business Expense Tracking: Best Software and Methods

No Receipts, No Problem? A Guide to Tax Deductions & What You Can Claim
Get more franchise information, franchise - quick contact form (new modal).
- Last Name *
- Phone Number *
- *Clicking the link above will take you to our Calendly page where you can select a time that works for you.
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

Helping over 30,000 client locations save money on their monthly expenses since 1991.
Auditing Services
- Waste & Recycling
- Merchant Processing
- Property Tax
- Managed Print
- Uniform & Linen
- Small Parcel Shipping
P3 Cost Analysts is proud to be a fully remote working organization since 2021. 100% of P3 employees work remotely.
© 2024 P3 Cost Analysts, All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
Schedule My Free Expense Audit
- Uniform & Linen Services Auditing
Lean Business Planning
Get what you want from your business.

How to Budget Expenses
Along with the revenue forecast, you need to plan and manage spending. Revenue is money coming in, and spending is money going out. This is how to budget expenses for your business plan.
By the way, the word budget, as I use it here, is exactly the same as forecast. The difference between the two is just custom. I could just as easily refer to revenue and spending budgets, or revenue and spending forecasts, as revenue forecast and spending budget. Most people are used to them the way I’m using them, with forecast for revenue and budget for spending.

There are three common types of spending in a normal business. These are the things you write checks for.
- The first is costs, direct costs, what you spend on what you sell. Those are the costs you have already estimated in your sales forecast.
- The second is your expenses. They are mostly operating expenses, like rent, utilities, advertising, and payroll.
- The third is what you spend to repay debts and purchase assets. I call that “other spending.” These are important financial terms that you have to use correctly; so if you have any doubt, investigate what assets are and how debt repayment is different from interest expense, not an expense, but something that absorbs cash and affects the cash available to the business.
Let’s look first at the most common kind of spending, the operating expenses.
The Expense Budget
Make sure you understand expenses as a technical financial term. Expenses are spending like payroll and rent that aren’t part of direct costs and reduce profits and taxable income. You need to understand that difference if you are going to run a business and manage cash flow. If you have any doubts, please read up on that.
Just as you did for sales forecast and direct costs, try to always project expenses in the same categories you have in your chart of accounts. If your accounting divides marketing expenses into personnel, advertising, and PR, don’t project marketing expenses in your business plan as print, online, and social media. This is important.
Summary of Operating Expenses
Forecasting your operating expenses is a matter of experience, educated guessing, a bit of research, and common sense. Let’s look at a sample expense budget from the same bicycle business plan I used in the sales forecast section above (with middle columns cut out):

All the numbers are educated guesses. Garrett, the bicycle storeowner, knows the business. As he develops his first lean plan, he has a good idea of what he pays for rent, marketing expenses, leased equipment, and so on. And if you don’t know these numbers, for your business, find out. If you don’t know rents, talk to a broker, see some locations, and estimate what you’ll end up paying. Do the same for utilities, insurance, and leased equipment: Make a good list, call people, and take a good educated guess.
Payroll and Payroll Taxes are Operating Expenses
Payroll, or wages and salaries, or compensation, are worth a list of their own. In the case of the bike shop owner, for payroll, he does a separate list so he can keep track. Payroll is a serious fixed cost and an obligation. Garrett’s summary budget (above) has the one line for payroll but it comes from a separate list. He just takes the total into the budget. Here’s the list:

Notice that the totals from the Personnel Plan show up in the expense budget. And if you look closely (it may take a calculator) at the expense row “Payroll Taxes” and compare that amount to the total payroll, you’ll see that it’s an estimate based on 25 percent of payroll. Garrett uses “Payroll Taxes” as a blanket term; it includes what he spends on health insurance and other benefits.
Restaurant Example
Since I’ve used Magda’s new restaurant as an example for the sales forecast, I’m including its operating expenses here too, as a second example.
Simple Operating Expense Budget
The illustration shows Magda’s lean plan budget for expenses:

And we can also look at Magda’s budget for payroll. As with the bicycle store, the operating expenses include the summary of payroll from two rows: Gross Salary is in the row called “Payroll,” and Benefits are in the row above titled “Payroll Taxes”. Both of these come from the payroll projection in the following illustration:

While Garrett has some other expenses along with payroll taxes in his “Benefits,” Magda’s bare-bones startup has just the payroll taxes. That’s why Garrett’s estimate of benefits compared to gross salary is 25%, and Magda’s is only 15%. And that’s why Magda labels her operating expense row as “Payroll Taxes,” while Garrett calls his “Benefits.”
Other spending
This is tricky: standard accounting and financial analysis include only sales, costs, and expenses in the calculation of Profit and Loss . However, in the real world, some of what you spend isn’t included in either costs or expenses. For example, repaying a loan takes money, but doesn’t show up anywhere in the profit and loss. And if you have a product-based business and proper accrual accounting, the money you spend buying inventory doesn’t show up in the profit and loss until that inventory sells. Buying a vehicle or production equipment isn’t tax deductible and isn’t an expense; but it costs money. The rule of thumb is that all expenses are tax deductible, but not all spending is an expense.
What to do? Plan and track your operating expenses for sure. And if you need to handle loan repayments, purchasing assets, distributing profits, owners’ draw, or other spending outside of profit and loss, keep those in your spending budget. Keep track of them. Plan for them.
Understand Starting Costs
Startup costs are a special case that applies to startup businesses only. They are the sum of the assets you need to purchase before you start, plus the expenses you incur before you start. My advice on how to estimate starting costs is waiting for you later, in Appendix A .
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply, discover more from lean business planning.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Free sample business budget templates (PDF/Excel) + instructions
By Ken Boyd
December 2, 2024
Running your own business presents unique opportunities for you to be your own boss, bring your entrepreneurial vision to life, and direct your financial future. But to avoid being among the 18% of small businesses that fail within their first year, you’ll want to take every precaution behind the scenes.
Creating a business budget is an excellent first step for any new business owner. By taking a closer look at your assets, expenses, and financial goals, you can craft a better plan for the future of your booming business. And ideally, you can reap some of the monetary benefits.

Let’s take a closer look at how to create a business budget and discuss the benefits of budgeting. You will even find some helpful resources and a business budget template we hope you can leverage moving forward. With the right tools and processes, you can use business budgeting to your advantage.
• What is a business budget?
• What spreadsheets to keep for your small business
• Benefits of a budget for your business
• What’s included in a business budget?
• How to create a budget for a business
• Small business budget customization
• Budgeting best practices for business
• Free business budget templates
• How to use the Excel budget template
• Business budgeting with QuickBooks

Stay in control of your cash flow
Explore the many ways to manage your cash flow with QuickBooks
What is a business budget?
A business budget is an outline of an organization’s revenue, expenses, and profit over a period of time—generally monthly, quarterly, or annually. A good business budget assigns a purpose to every dollar your business earns. For instance, some money might go toward bills or business growth. Others will help fund daily operational expenses and take-home pay for yourself and your staff.

Solid business budget planning will provide a road map for spending and earning. It’ll create a lens into your organization’s financial future and facilitate better decisions all around. Ready to get your business idea off the ground? You’ll need to consider startup costs. Wondering if you can or should purchase new equipment this year? Refer to your business budget plan.
Maybe you’re looking for ways to cut down on expenses. Your business budget can present a view of your financial health, including where you’re spending money and where you might benefit from cutting back. With better foresight, you can cultivate stronger business performance and improve earnings from the last quarter or the last year.
Types of budgets for businesses
Here's a breakdown of the most common budgeting methods for businesses:
Master budget
This is the big-picture budget, encompassing all aspects of your business's finances. It includes projected income, expenses, and cash flow for a specific period, usually a year. It’s like your financial roadmap, which can influence and guide your overall financial strategy and decision-making.
Operating budget
This budget focuses on your day-to-day operations. An operating budget includes anticipated revenue and expenses related to your core activities, such as sales, production, and marketing. An operating budget helps you track performance, identify potential cost-saving opportunities, and ensure your daily operations are financially sustainable.
Cash flow budget
A cash-flow budget provides a detailed projection of your cash inflows and outflows over a specific period. It helps you anticipate periods of high or low cash flow, allowing you to proactively manage your finances and avoid potential shortfalls. This can be especially important for businesses with seasonal fluctuations.
Sales budget
Focused specifically on projected sales revenue, the sales budget is often broken down by product, service, or customer segment. It's a component of the overall master budget and drives many other financial projections.
Production budget
For businesses that manufacture products, this budget outlines the anticipated costs and quantities of production, including raw materials, labor, and overhead. It ensures that production aligns with projected sales and helps with inventory management .
Labor budget
This budget focuses on labor costs, including wages, salaries, benefits, and payroll taxes . It helps businesses plan for staffing needs, optimize workforce allocation, and control labor expenses.
Capital budget
A capital budget deals with long-term investments in assets like equipment, property, or technology. It helps businesses evaluate the financial viability of major projects and plan for future growth.
Financial budget
Encompassing the overall financial picture of the business, a financial budget includes projected financial statements like the balance sheet , income statement, and cash flow statement. It helps businesses assess their overall financial health and make strategic decisions.
Static budget
A static budget remains fixed, regardless of changes in sales or production volume. It's useful for planning and evaluating performance against a set target, but it may not be as flexible as other budget types.
Budgeting methods
Budgeting helps you track where your money is going and plan for future expenses. But there are different budgeting methods you can use, based on your organization’s demands and preferences. Let’s explore a few of the most common budgeting methods.
Incremental budgeting
The incremental budgeting method starts with your previous budget and adjusts it based on anticipated changes. It's a simple and easy-to-implement method, but it might not be the most accurate or flexible approach, especially for businesses with fluctuating income or expenses.
Zero-based budgeting
This detailed budgeting method starts from scratch and requires justification of every expense and fund allocation based on priority. It is not based on previous budgets or historical data. Because it is so thorough, it can be time-consuming and might not be suitable for all businesses. However, it’s a valuable method for scrutinizing expenses and where costs could be cut.
Value proposition budgeting
This budgeting option, which is also called priority-based budgeting, focuses on aligning your budget with your organization’s core values, strategic goals, and what’s most important to the customer. It’s based on allocating spending toward the activities that directly contribute to your value proposition and long-term success.
Activity-based budgeting:
Businesses with diverse operations or that rely on project-based income often use activity-based budgeting. This method links your budget to specific activities or projects, allowing you to track costs and allocate resources more effectively.
The effectiveness of a budgeting method often varies based on a business's specific industry, context, and size. Some companies may choose to combine elements from multiple budgeting strategies, creating a hybrid approach.
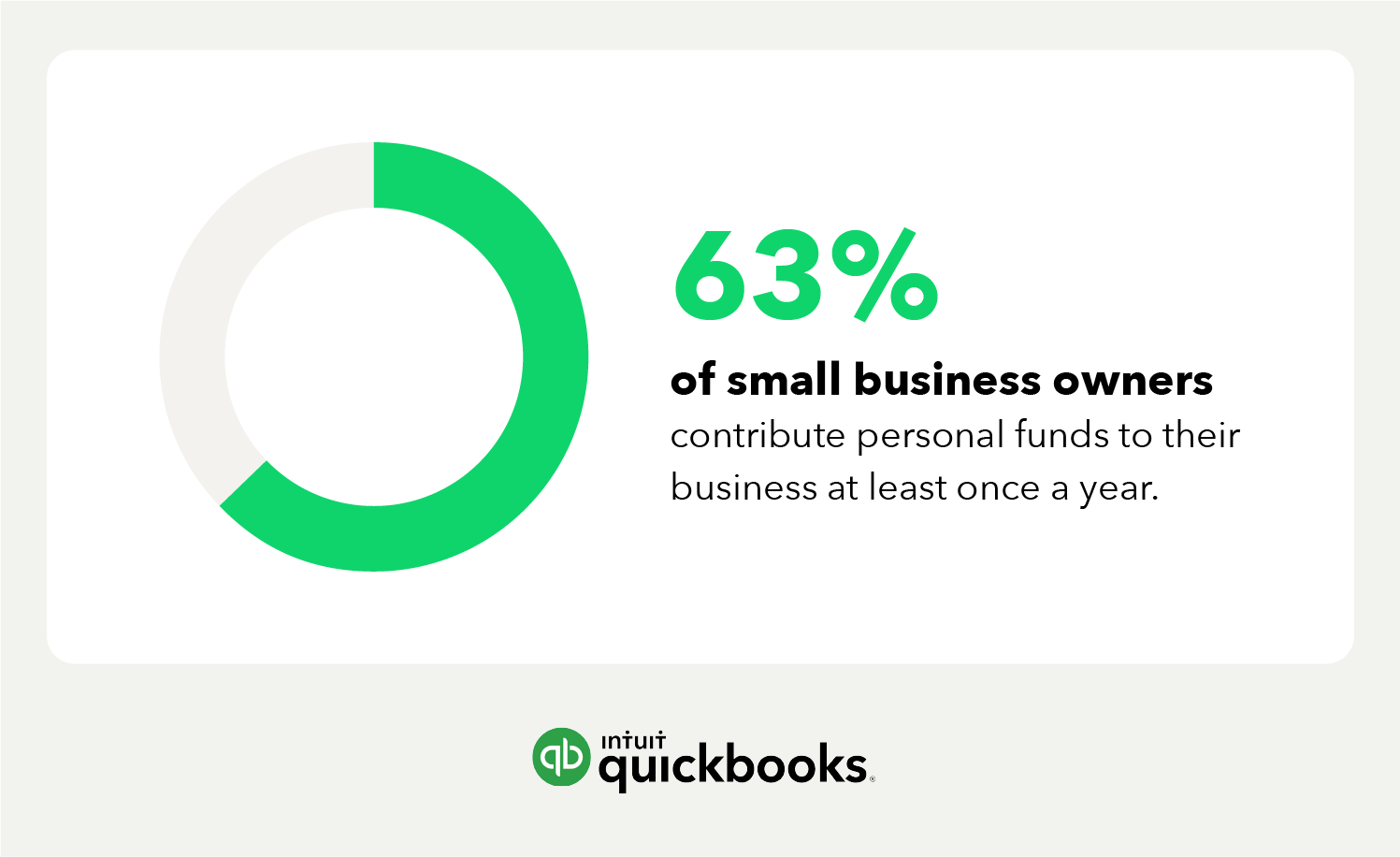
Benefits of a budget for your business
“A business budget is a financial road map to success, a vision of where you want to take your business for the upcoming 12 months,” the FDIC says . What’s more, research has suggested that business budgets offer the following benefits:
- Give business owners more freedom to run their organizations with confidence.
- Allow business owners to identify cash flow and spending problems.
- Empower business owners to have a greater sense of control and insight when dealing with financial challenges.
- Help business owners and decision-makers predict cash flow and identify trends.
- Demonstrate positive money management to lenders and investors.
- Give you the chance to identify and rectify problem areas quickly.
Bottom line: Consider a detailed budget one of your key business needs.
What’s included in a business budget?
A business budget takes into account an organization’s total revenue and expenses to reveal net profit (or loss). The FDIC says the best business budgets comprise the “nuts and bolts” of everyday revenue and expenses like:
- Average order amount
- Number of product orders per month
- Billable hours
- Average payroll costs
- Material expenses
- Rent, mortgage, and utilities
When building a business budget, business owners should bear in mind that output depends on input. Make sure you’re collecting accurate data points whenever you’re dealing with your business’s finances. A simple mathematical error or typo can lead to confusion or, worse, uninformed financial decisions.
How to create a budget for a business
Now you know what a business budget is, why it’s important, and the essential components. Let’s now take a look at the steps you need to take to create one.
1. Calculate all forms of income
Whether you’re optimizing your personal spending or building a business budget, your first step should be aggregating all of your forms of income. Your net income determines how much you can afford to spend. It also indicates your take-home pay and whether your business performance is growing or stagnating.
To find out how much money your business is bringing in, refer to your profit and loss statements. Depending on your business model, you may have several income sources, so be sure to include any and all revenue streams in this section.
2. Subtract your fixed expenses
Once you’ve added all of your business’s income together, you can subtract your fixed costs. Fixed costs are expenses that remain consistent throughout the year. Whether you pay bills monthly, weekly, or annually, you can expect to spend a set amount of dollars on each expense. These costs are easy to predict, so they’re easy to work into your budget. The one-off expenses, or variable costs ? Not so much—more on that in a minute.
Examples of fixed expenses include:
- Commercial rent or mortgage
- Operational utilities
- Loan payments
- Insurance bills
- Employee salaries
Once you’ve tallied up your fixed expenses, you can subtract that number from the total income you calculated in step 1.
3. Subtract your variable expenses
In addition to your fixed costs, you might anticipate monthly operating expenses that may not always be the same amount. These variable expenses may be harder to predict, but you can refer to old receipts and invoices to estimate them.
Examples of variable expenses include:
- Material costs
- Commissions
- Billable staff wages (freelancers, outsourced work, etc.)
After identifying your variable expenses and estimating how much they cost each month, subtract the amount from your income.
4. Prepare for emergency and one-time expenses
Life is full of unexpected circumstances. As a business owner, you’re likely familiar with unexpected expenses. New equipment, hiring expenses, and unplanned events can add up, so it’s wise to plan ahead as much as you can.
You can’t predict when you’ll need to pay for an emergency expense or how much it might cost, but you can set aside a cash reserve to lessen the burden.
5. Create a profit and loss statement
You’ve accounted for your income and fixed, variable, and emergency expenses. Now you can better understand your business finances by creating a profit and loss (P&L) statement. A P&L statement is a high-level overview that shows whether your organization is profitable or in the red.
When you add up all of your income then subtract your total expenses, you should have a positive or negative number. A positive number indicates that you’re in the black and, therefore, making money. A negative number indicates that you’re in the red and, therefore, burning a hole in your pocket.
Your P&L statement serves as a baseline for creating your business budget. You can access your profit and loss statement, track trends, monitor invoices, and more from your QuickBooks account.
Keep in mind that your profit and loss statement may not always show you the results you want. But with better business budgeting and forward thinking, you can set yourself up for a brighter and more profitable future.
6. Draft your business budget
After reviewing your P&L statement, you’ll have a better idea of where you’re spending your money—and if you’re spending responsibly. With this data in mind, you’re ready to draft your business budget for the next year, quarter, or month. Most businesses opt for quarterly budgets.
A basic budget outlines your expenditures and designates limits for each over a given period. This outline can help you determine whether you’re earning and spending within your abilities. With QuickBooks, you can easily glean insight into spending patterns and assess where your business stands financially.

QuickBooks has tools to help your business thrive
Track and manage your whole financial picture in one place - from bank transactions, expenses and beyond.
Small business budget customization
Every small business has a niche, workflow, and financial goals. So it’s important to remember that there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to business budgeting . As you learn how to build a business budget and experiment with the strategies you’ve learned, consider the following:
- Seasonality may affect customer buying behaviors, depending on your business type. Consider these fluctuations in profit and expenses as you plan your budget.
- If you run an e-commerce business, beware of hidden costs like shipping fees, website upgrades, and point-of-sale expenses.
- Budgeting for a startup can be especially challenging because they’re typically much more limited on data and performance history. But accurate accounting software and conservative estimates can help you improve your business budget year after year.
- If you run a service-based business, you’re working with more estimates than a product-focused business. Keep an eye on trends to make sure your budget has plenty of wiggle room.
Budgeting best practices for business
A great business budget creates a clear connection between your day-to-day operations and financial resources. It can help you navigate tough business decisions and even help you identify areas for growth. But an effective budget doesn’t happen overnight. As you create and reflect on your business budget, keep these small business budget best practices in mind:
Consider how changes impact your budget
Consider how every change in expenses or income will trickle down to your budget. Hiring a new employee doesn’t just mean you’re adding another salary but can also translate to changes in payroll taxes , benefits, and other expenses. Any time you adjust your business budget, consider the consequences.
Include all expense categories
Make sure that you’re budgeting for all expense categories, including fixed, variable, and emergency expenses. Anticipating these costs can help you balance your business budget and plan ahead. You can track your business expenses effortlessly and accurately using QuickBooks.
View your business budget as a living document
Financial circumstances change, and the unexpected happens. Your business should always be prepared to weather the storm. Review your financial statements regularly, reconsider your costs and spending, and refine your business budget as necessary.
Set goals but avoid wishful thinking
Use your bookkeeping records to determine what might transpire over the next month, quarter, or year. But ultimately, it’s a better idea to be conservative with your budget than to expect the best-case scenario.
Look out for ways to cut costs and create growth
As a business owner, it’s up to you to position your business for greatness. Break down your finances into areas of success and room for improvement. Spotting opportunities to improve your business finances can make your organization more profitable and sustainable in the long run.
Keep your money organized
Use categories or envelopes to organize your money. A business bank account that allows you to categorize or bucket your money makes it easier to stick to your budget plan and see at a glance where your finances stand. Use Envelopes in QuickBooks Money to organize your budget and hit your savings goals sooner.
What spreadsheets to keep for your small business
Spreadsheets are essential for budgeting and financial management. The following are some of the most important ones you’ll want for your small business.
Income statement
An income statement, also called a profit and loss statement, tracks your business's revenue and expenses over a specific period, such as a month, quarter, or year. It helps you understand your profitability and identify areas where you can improve your financial performance.
Cash flow statement
A cash flow statement tracks the movement of cash in and out of your business. This helps you understand your cash flow patterns, anticipate potential shortfalls, and make informed financial decisions.
Balance sheet
A balance sheet provides a snapshot of your business's financial health at a specific point in time. It shows your assets, liabilities, and equity, giving you a clear picture of your overall financial position.
Budget spreadsheet
A budget spreadsheet outlines your projected income and expenses for a specific period. It helps you plan your spending, monitor your progress, and make adjustments as needed to stay on track with your financial goals.
Free business budget templates
If you’re just getting started with budgeting for your business, these templates are a great medium for learning the process. We invite you to create copies, download, edit, and print these business budget templates.
Printable business budget template
Use this editable and printable template to create a quick and easy budget for your business:

Business budget template for Excel
Use our free Excel template to develop a budget for your business. The template uses an example budget from an imagined business, Widget Inc., to help guide you through the process of creating a business budget

How to use the Excel budget template
1. enter prior year information.
Input the year-end balance sheet and income statement into your Excel template.
Equity is the difference between assets and liabilities—the true value of your business. The $10,000 net income in the income statement increases equity in the year-end balance sheet.
2. Forecast future sales and costs
Next, we’ll make some assumptions for the upcoming year. In this example, Widget Inc.’s budget accounts for changes in sales, cost of sales, employee payroll costs, and other expenses.
Some accounting transactions, however, are unusual and cannot be included in a budget. For example, Widget Inc. had a $5,000 loss on the sale of equipment in the prior year.
Widget Inc.’s primary business is manufacturing and selling widgets, and the sale of equipment is not part of its annual budget. Accountants refer to these transactions as non-operating income and losses because day-to-day business operations don’t generate them.
3. Create a budget income statement
Widget Inc. produces a budget income statement using the assumptions in step 2. Note that the Widget Inc. budget has a line item for gain or loss on sale, other revenue . While the company may have an actual transaction in the category, this line has a zero budget.
4. Create a budgeted balance sheet using assumptions
The budgeted balance sheet includes assumptions that address each of the line items in the report. The budget provides percentage increases or decreases from the prior year, and 2 categories have no change.
5. Create a budgeted cash roll-forward for January
A cash roll-forward report lists your beginning cash balance, expected cash inflow and outflow , and your ending balance in cash for each month of the year.
The balance sheet and the income statement are financial statements , but the cash roll-forward is an informal internal report. The statement of cash flows is generated as part of your financial statements, but a cash roll-forward is more useful for budgeting purposes.
Business owners should create cash roll-forwards last because they need a cash projection for each month. Step 5 presents the cash roll-forward for January. You’ll see that the beginning of January cash balance ($10,000) is the year-end cash balance in the prior year’s balance sheet.
The majority of cash collections are from sales and the bulk of cash payments are for inventory. When a business sells inventory, the dollar amount transfers to the cost of sales, which is the largest expense in the budget. So it makes sense that the biggest cash outflow is for inventory.
Widget Inc. assumes that cash received for sales and the cash paid for inventory will be evenly distributed over 12 months. In reality, the payments will be uneven, but the cash inflows and outflows can be difficult to predict by month.
The budget also includes miscellaneous receivables collected in cash and other cash payments, such as payroll costs.
6. Budgeted cash roll-forward for February, other months
The beginning cash balance for February ($10,500) is the ending cash balance for January, and this connection applies to each month of the year. The February cash budget uses some of the same assumptions for sales and inventory purchases. The ending cash balance for February is also the March beginning cash balance.
Widget Inc. continues this same cash roll-forward process until the company has a cash budget for each month.
Business budgeting with QuickBooks
Building a business budget can feel like an overwhelming process, but it’s an essential one if you want to have an edge on the competition, maintain financial stability, and move your business forward.
QuickBooks features tools like business banking that automatically matches to your books , a business debit card integrated with your accounting software , and budget envelopes, making it easy to manage your business finances. Explore our product features to learn more.

Ken Boyd is a co-founder of AccountingEd.com and owns St. Louis Test Preparation (AccountingAccidentally.com). He provides blogs, videos, and speaking services on accounting and finance. Ken is the author of four Dummies books, including "Cost Accounting for Dummies."
Better accounting software is waiting
1. QuickBooks Money: QuickBooks Money is a standalone Intuit offering that includes QuickBooks Payments and QuickBooks Checking. Intuit accounts are subject to eligibility criteria, credit, and application approval. Banking services provided by and the QuickBooks Visa® Debit Card is issued by Green Dot Bank, Member FDIC, pursuant to license from Visa U.S.A., Inc. Visa is a registered trademark of Visa International Service Association. QuickBooks Checking Deposit Account Agreement applies. Banking services and debit card opening are subject to identity verification and approval by Green Dot Bank. Money movement services are provided by Intuit Payments Inc., licensed as a Money Transmitter by the New York State Department of Financial Services. For more information about Intuit Payments' money transmission licenses, please visit https://www.intuit.com/legal/licenses/payment-licenses/ . No subscription cost or monthly fees. Other fees and limits, including transaction-based fees, apply.
Envelopes: You can create up to 9 Envelopes within your primary QuickBooks Checking account. Money in Envelopes must be moved to the available balance in your primary QuickBooks Checking account before it can be used. Envelopes within your primary QuickBooks Checking account will automatically earn interest once created. At the close of each statement cycle, the interest earned on funds in your Envelopes will be credited to each Envelope in proportion to the average daily balance of each Envelope. See Deposit Account Agreement for terms and conditions. movement services are provided by Intuit Payments Inc., licensed as a Money Transmitter by the New York State Department of Financial Services. For more information about Intuit Payments' money transmission licenses, please visit https://www.intuit.com/legal/licenses/payment-licenses/ .
This content is for information purposes only and should not be considered legal, accounting, or tax advice, or a substitute for obtaining such advice specific to your business. Additional information and exceptions may apply. Applicable laws may vary by state or locality. No assurance is given that the information is comprehensive in its coverage or that it is suitable in dealing with a customer’s particular situation. Intuit Inc. does not have any responsibility for updating or revising any information presented herein. Accordingly, the information provided should not be relied upon as a substitute for independent research. Intuit Inc. does not warrant that the material contained herein will continue to be accurate nor that it is completely free of errors when published. Readers should verify statements before relying on them.
We provide third-party links as a convenience and for informational purposes only. Intuit does not endorse or approve these products and services, or the opinions of these corporations or organizations or individuals. Intuit accepts no responsibility for the accuracy, legality, or content on these sites.
- Canada (English)
- Canada (French)
- United Kingdom
- Other Countries
Call Sales: 1-800-285-4854
© 2024 Intuit Inc. All rights reserved.
Intuit, QuickBooks, QB, TurboTax, Credit Karma, and Mailchimp are registered trademarks of Intuit Inc.
By accessing and using this page you agree to the Website Terms of Service.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Create a Business Budget for Your Small Business

Many, or all, of the products featured on this page are from our advertising partners who compensate us when you take certain actions on our website or click to take an action on their website. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
How is this page expert verified?
NerdWallet's content is fact-checked for accuracy, timeliness and relevance. It undergoes a thorough review process involving writers and editors to ensure the information is as clear and complete as possible.

A business budget estimates future revenue and expenses in detail, so that you can see whether you’re on track to meet financial expectations for the month, quarter or year. Think of your budget as a point of comparison — you run your actual numbers against it to determine if you’re over or under budget.
From there, you can make informed business decisions and pivot accordingly. For example, maybe you find that your expenses are over budget for the quarter, so you may hold off on a large equipment purchase.
Here’s a step-by-step guide for creating a business budget, along with why budgets are crucial to running a successful business.
» MORE: What is accounting? Definition and basics, explained
How does a business budget work?
Budgeting uses past months’ numbers to help you make financially conservative projections for the future and wiser business decisions for the present. If you’ve had a few bad months and predict another slow one, you can prepare to minimize expenses where possible. If business has been booming and you’re bringing in new customers, maybe you invest in buying more inventory to satisfy increased demand.
Creating a business budget from scratch can feel tedious, but you might already have access to tools that can help simplify the process. Your small-business accounting software is a good place to start, since it houses your business’s financial data and may offer basic budgeting reports.
To create a budget in QuickBooks Online , for example, you break down your estimated income and expenses across each area of your business. Then, the software calculates figures like gross profit, net operating income and net income for you.
You can then compare actual versus projected figures side by side by running a Budget vs. Actuals report. Businesses that need more in-depth features, like cash flow forecasting or the ability to use different projection methods, might subscribe to business budgeting software in addition to accounting software.
If your small business doesn’t have access to these features or has simple financials, you can download free small-business budget templates to manually create and track your budget. Regardless of which option you choose, your business will likely benefit from hiring an accountant to help manage your budget, course-correct when the business gets off track, and make sure taxes are being paid correctly.
Financial and tax expertise for small business owners

Why is a business budget important?
A business budget encourages you to look beyond next week and next month to next year, or even the next five years.
Creating a budget can help your business do the following:
Maximize efficiency.
Establish a financial plan that helps your business reach its goals.
Point out leftover funds that you can reinvest.
Predict slow months and keep you out of debt.
Estimate what it will take to become profitable.
Provide a window into the future so you can prepare accordingly.
Creating a business budget will make operating your business easier and more efficient. A business budget can also help ensure you’re spending money in the right places and at the right time to stay out of debt.
How to create a business budget in 6 steps
The longer you’ve been in business, the more data you’ll have to inform your forward-looking budget. If you run a startup , however, you’ll want to do extensive research into typical costs for businesses in your industry, so that you have working estimates for revenue and expenses.
From there, here’s how to put together your business budget:
1. Examine your revenue
One of the first steps in any budgeting exercise is to look at your existing business and find all of your revenue sources. Add all those income sources together to determine how much money comes into your business monthly. It’s important to do this for multiple months and preferably for at least the previous 12 months, provided you have that much data available.
Notice how your business’s monthly income changes over time and try to look for seasonal patterns. Your business might experience a slump after the holidays, for example, or during the summer months. Understanding these seasonal changes will help you prepare for the leaner months and give you time to build a financial cushion.
Then, you can use those historic numbers and trends to make revenue projections for future months. Make sure to calculate for revenue, not profit. Your revenue is the money generated by sales before expenses are deducted. Profit is what remains after expenses are deducted.
2. Subtract fixed costs
The second step for creating a business budget involves adding up all of your historic fixed costs and using them to reliably predict future ones. Fixed costs are those that stay the same no matter how much income your business is generating. They might occur daily, weekly, monthly or yearly, so make sure to get as much data as you can.
Examples of fixed costs within your business might include:
Debt repayment.
Employee salaries.
Depreciation of assets.
Property taxes.
Insurance .
Once you’ve identified your business’s fixed costs, you’ll subtract those from your income and move to the next step.
3. Subtract variable expenses
As you compile your fixed costs, you might notice other expenses that aren’t as consistent. Unlike fixed costs, variable expenses change alongside your business’s output or production. Look at how they’ve fluctuated over time in your business, and use that information to estimate future variable costs. These expenses get subtracted from your income, too.
Some examples of variable expenses are:
Hourly employee wages.
Owner’s salary (if it fluctuates with profit).
Raw materials.
Utility costs that change depending on business activity.
During lean months, you’ll probably want to lower your business’s variable expenses. During profitable months when there’s extra income, however, you may increase your spending on variable expenses for the long-term benefit of your business.
4. Set aside a contingency fund for unexpected costs
When you’re creating a business budget, make sure you put aside extra cash and plan for contingencies.
Although you might be tempted to spend surplus income on variable expenses, it’s smart to establish an emergency fund instead, if possible. That way, you’ll be ready when equipment breaks down and needs replacing, or if you have to quickly replace inventory that's damaged unexpectedly.
5. Determine your profit
Add up all of your projected revenue and expenses for each month. Then, subtract expenses from revenue. You may also see the resulting number referred to as net income . If you end up with a positive number, you can expect to make a profit. If not, that’s a loss — and that can be OK, too. Small businesses aren’t necessarily profitable every month, let alone every year. This is especially true when your business is just starting out. Compare your projected profits to past profits to confirm whether they’re realistic.
6. Finalize your business budget
Are the resulting profits enough to work with, or is your business overspending? This is your opportunity to set spending and earning goals for each month, quarter and year. These goals should be realistic and achievable. If they don’t line up with your projections, make sure to establish a strategy for making up the difference.
As time goes on, regularly compare your actual numbers to your budget to determine whether your business is meeting those goals, and course correct if necessary.
» MORE: Ways your small business can spend smarter
A business budget projects future revenue and expenses so you can create a smart, realistic spending plan. As the year progresses, comparing your actual numbers against your budget can help you hold your business accountable and make sure it reaches its financial goals.
A business budget includes projected revenue, fixed costs, variable costs and the resulting profits. You can also factor in contingency funds for unforeseen circumstances like equipment failure.
On a similar note...
New elevated offer

American Express® Business Gold Card
Rates and Fees
on American Express' website

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Oct 27, 2023 · The key types of expenses in business spending. Expenses make up just one of the three common types of spending in a normal business. Expenses mostly include operating expenses, like rent, utilities, advertising, and payroll. That’s what I’m talking about in this article.
7. A budget calculator. A budget calculator can help you see exactly where you stand when it comes to your business budget planning. It might sound obvious, but getting all the numbers in your budget in one easy-to-read summary is really helpful. In your spreadsheet, create a summary page with a row for each of the budget categories above.
Sep 13, 2024 · A business budget is a detailed plan of expected income and expenses for a specific period, typically a year, broken down into monthly or quarterly segments. A financial forecast , however, is a projection of future financial performance based on historical data , market trends , and economic factors , often covering a longer time frame and ...
Along with the revenue forecast, you need to plan and manage spending. Revenue is money coming in, and spending is money going out. This is how to budget expenses for your business plan. By the way, the word budget, as I use it here, is exactly the same as forecast. The difference between the two is just custom.
Dec 2, 2024 · Make sure that you’re budgeting for all expense categories, including fixed, variable, and emergency expenses. Anticipating these costs can help you balance your business budget and plan ahead. You can track your business expenses effortlessly and accurately using QuickBooks. View your business budget as a living document
May 23, 2023 · Creating a budget puts your business in a better position to survive slow seasons and prepare for future expenses. It’s also an opportunity to set detailed financial goals.