Robotics PPT: Definition, Types, Components, Future
Robotics is the field of technology focused on designing, building, and programming robots to perform tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention. Robots are used in various industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to space exploration and agriculture. In factories, they assemble products with speed and precision, while in healthcare, robotic arms assist in surgeries.
Also See: Artificial Intelligence In Robotics PPT
Advanced robots can perform complex tasks, such as exploring distant planets or delivering packages. Robotics combines engineering, computer science, and artificial intelligence to create machines that can sense, act, and learn. As the field evolves, robots are becoming more intelligent, adaptable, and integrated into everyday life.
Also See: Artificial Intelligence PPT

Table of Content for Robotics PPT
- Introduction
- What Is Robotics
- The Three Laws Of Robotics
- Why Robotics ?
- Types Of Robots
- Components Of Robots
- Future Prospects
Free Download Link
Robotics PPT
Related posts:

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- YouTube Thumbnail Downloader
- Image Compressor
- QR Code Generator
- Environment
- Submit An Article
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Basics of Robotics PowerPoint Presentation
- by Refresh Science
- July 10, 2020 January 6, 2022
What is robotics?
- Robotics is the combination of engineering, science and technology that produces a machine called robot.
- Robotics is a domain where people work with the development and use of robots.
- It is mostly used as an alternative of human beings in various works.
- Robotics mainly deals with the design construction and operation of a robot and the computer systems for their control, feedback and information processing.
- It is a machine that is programmed to perform the given tasks and gather information from its surroundings.
- It works from a central microprocessor that helps to control the movements and they have sensors to sense the environment .
Why robotics ?
The main purpose of robotics is to automate operations that humans do and replace them with machines that can do the work with better accuracy. As we know robotics is fully automated, it can process the dangerous and mundane jobs from humans with high productivity.
While a human be able to do a piece of work at some speed we can definitely design a robot to do the same piece of work better, faster, economical and environmentally friendly . Because of its long run it can free humans from dangerous, repetitive and annoying jobs.
Robotics PPT:
Laws of robotics:.
Asimov proposed three laws of robotics, they are:
Law 1: A robot may not injure a human being or through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm
Law 2: A robot must obey orders given to it by human beings, except where such orders would conflict with the first law
Law 3: A robot must protect its own existence as long as such protection does not conflict with the first law.
Types of robots ?
Robots are used in various sectors. some of the important sectors and the types used there are as follows

1. Industrial Robots
Various works such as Welding, material Handling, Improving Productivity, Inspection are carried out by robots.
There are various types of industrial robots as below:
- Articulated
- Cylindrical
2. Mobile Robots
Robots that move around legs, tracks or wheels. There are types of robots that can even handle radio active material. Types of mobile robots are
- Land based wheeled, tracked, legged robots
- Air based robots –plane, Helicopter
- Water based – Submarines
- Combinational robots
3. Educational Robots
Robots that are used in education. They are abled to bring schools to students who cannot be able to present Physically.
Types of educational robots are:
- Dash and dot
- Mbot
4. Domestic Robots
There are two types one is to perform household tasks and the other one is modern toy that performs tasks like talking, walking etc .
Components of robots:
Manipulator.
The arm of the robot is called as manipulator. It resemble the human hand. It has several joints and links.
End effectors
End effectors are used by robots to interact with the environment. They vary according to the task given to the robot. It performs the tasks that are performed by palm and fingers of human hand
Sensors are used to gather information from the surroundings. If camera is present Visual representation of the surroundings can be seen. Microphones allows to detect the surrounding sounds. If the robot is equipped with thermometer and barometer temperature and pressure can be found out. These informations are used to guide the robotics behaviour.
Inside the body of a robot small motor is present known as actuators. Robot moves in reaction to feedback from sensors with the help of actuators.
The controller is the brain of a robot. Both the hardware and software are the controllers of the robot. The controller controls the movement of the manipulator and end effector.
Power supply
The main source of power supply for robots are batteries and photovoltaic cells. Lead acid and silver cadmium batteries are mostly preferred. Industrial and manufacturing robots are consuming an average of 21000 kWh annually. In future it may be designed such as a robot may charge by itself when the power is low.

Components of robots
Advantages of Robotics:
- No human intervention.
- Faster, precise and accurate.
- They can work 24*7 , so productivity increases.
- They can perform multitasking. So manpower gets reduced.
- They work in dangerous tasks, the risk of human health and safety is reduced.
- There is minimal risk if any failure occurs.
Disadvantages of Robotics:
- There are replacing human beings in many places which leads to widespread unemployment.
- They are costly to built.
- There is lack of emotions and conscience.
- They don’t have on the spot decision making capability, they act only as they programmed. When an unexpected situation arises it would be difficult for a robot to go through it.
Future prospects of robotics:
Many industries have started using robotic technology such as automotive, defence, pharmaceuticals , textiles, atomic energy etc. experts says that a moment may come when robots becomes smarter than humans.
At present robots can rotate base of arm, bend elbow, rotate wrist etc. In future it may look, feel and act like humans. Realistic looking skins and hair can be fitted which allows the robot to react naturally in the environment.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
PPT Bundles
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories


Autonomous Mobile Robots Types Powerpoint Presentation Slides
Autonomous mobile robots AMRs have become increasingly important in recent years due to their ability to automate various tasks in various industries. Grab our insightfully designed Autonomous Mobile Robots Types template. It provides a brief overview of autonomous mobile robots, including their advantages and disadvantages. Our Types of Autonomous Robotic Systems deck covers various topics related to AMRs, like reasons for adoption, architecture, functional and operational software, and operating systems. Additionally, it delves into the multiple types of AMRs, including goods-to-person, collaborative, autonomous forklifts, enhanced sortation solutions, and automated storage and retrieval systems. Further, our Autonomous Mobile Robots Architecture PPT explores different types of autonomous robotic systems, like programmable, non-programmable, adaptive, and intelligent systems. It also discusses the applications of AMRs in various industries, the differences between AMRs and AGVs, and pricing for building AMRs. Lastly, the module features a timeline, a roadmap for AMR development, and a dashboard to track performance. Get instant access.

- Add a user to your subscription for free
You must be logged in to download this presentation.
PowerPoint presentation slides
Enthrall your audience with this Autonomous Mobile Robots Types Powerpoint Presentation Slides. Increase your presentation threshold by deploying this well-crafted template. It acts as a great communication tool due to its well-researched content. It also contains stylized icons, graphics, visuals etc, which make it an immediate attention-grabber. Comprising seventy one slides, this complete deck is all you need to get noticed. All the slides and their content can be altered to suit your unique business setting. Not only that, other components and graphics can also be modified to add personal touches to this prefabricated set.

People who downloaded this PowerPoint presentation also viewed the following :
- IT , Robotic Process Automation
- Autonomous Mobile Robots Types ,
- Types Of Autonomous Robotic Systems ,
- Autonomous Mobile Robots Architecture
Content of this Powerpoint Presentation
Slide 1 : This slide introduces Autonomous Mobile Robots Types. Commence by stating Your Company Name. Slide 2 : This slide depicts the Agenda of the presentation. Slide 3 : This slide includes the Table of contents. Slide 4 : This is yet another slide continuing the Table of contents. Slide 5 : This slide highlights the Title for the Topics to be covered further. Slide 6 : This slide represents the introduction of autonomous mobile robots. Slide 7 : This slide depicts why AMRs are called mobile robots by explaining their various features. Slide 8 : This slide describes why AMR is called an autonomous robot. Slide 9 : This slide exhibits the Benefits of working with autonomous mobile robots. Slide 10 : This slide reveals the Disadvantages of autonomous mobile robots. Slide 11 : This slide mentions about the Heading for the Contents to be discussed in the following template. Slide 12 : This slide depicts why organizations should adopt autonomous mobile robots. Slide 13 : This slide states the Title for the Ideas to be covered next. Slide 14 : This slide shows the autonomous mobile robot's architecture. Slide 15 : This slide states the Key considerations while choosing the right hardware. Slide 16 : This slide indicates the Functional software of autonomous mobile robots. Slide 17 : This slide talks about the operational software of autonomous mobile robots. Slide 18 : This slide reevals the Operating systems of autonomous mobile robots. Slide 19 : This slide mentions about the Heading for the Ideas to be discussed further. Slide 20 : This slide discusses the Crucial components of autonomous mobile robot. Slide 21 : This slide represents how system components work together to enable autonomous mobile robots. Slide 22 : This slide displays the Title for the Contents to be covered next. Slide 23 : This slide talks about the Goods-to-person autonomous mobile robots. Slide 24 : This slide depicts the Overview of collaborative mobile robots. Slide 25 : This slide outlines the overview of autonomous forklifts and their types. Slide 26 : This slide deals with Enhanced sortation AMR solutions overview. Slide 27 : This slide talks about the Automated storage and retrieval system. Slide 28 : This slide shows the overview of autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles to provide real-time inventory information. Slide 29 : This slide displays the Overview of autonomous inventory robots. Slide 30 : This slide highlights the Heading for the Topics to be discussed further. Slide 31 : This slide presents the Programmable automatic robot overview. Slide 32 : This slide portrays the Non-programmable automatic robot overview. Slide 33 : This slide outlines the overview of adaptive robots that are used for spraying and welding systems. Slide 34 : This slide explains the overview of intelligent robots equipped with sensors and microprocessors. Slide 35 : This slide contains the Title for the Ideas to be coveerd in the following template. Slide 36 : This slide represents the hardware technological advances impacting autonomous mobile robots. Slide 37 : This slide depicts the software technological advances impacting the autonomous mobile robots. Slide 38 : This slide mentions about the Heading for the Ideas to be discussed in the next template. Slide 39 : This slide depicts the national and international safety standards and sensors installed for the safety of AMRs. Slide 40 : This slide represents the overview of the AMR fleet manager that manages the autonomous mobile robots. Slide 41 : This slide reveals the Title for the Contents to be covered further. Slide 42 : This slide talks about the Autonomous mobile robots in distribution centres. Slide 43 : This slide focuses on the Autonomous mobile robots for cleaning and disinfection. Slide 44 : This slide depicts the Autonomous robots in hospitals & healthcare. Slide 45 : This slide outlines the application of robots to provide hospitality services in hotels and restaurants. Slide 46 : This slide emphasizes on Autonomous robots in grocery stores. Slide 47 : This slide talks about using autonomous robots in last-mile delivery to deliver consumer products faster. Slide 48 : This slide indicates the AMRs in autonomous security robots (ASRs). Slide 49 : This slide deals with AMRs in smart cities and public sector. Slide 50 : This slide reveals the Heading for the Topics to be discussed next. Slide 51 : This slide represents the difference between autonomous mobile robots and automated guided vehicles. Slide 52 : This slide contains the Title for the Topics to be covered in the following template. Slide 53 : This slide depicts the pricing for autonomous mobile robot development and installation. Slide 54 : This slide incorporates the Heading for the Contents to be discussed further. Slide 55 : This slide represents the timeline for autonomous mobile robot development. Slide 56 : This slide reveals the Title for the Ideas to be covered in the following template. Slide 57 : This slide describes the roadmap for autonomous mobile robot development. Slide 58 : This slide exhibits the Heading for the Ideas to be discussed further. Slide 59 : This slide represents the dashboard to track the AMR’s performance in the warehouse. Slide 60 : This is the Icons slide containing all the Icons used in the plan. Slide 61 : This slide displays Additional information. Slide 62 : This is the Column chart slide. Slide 63 : This is the 30 60 90 days plan slide for effective planning. Slide 64 : This is Our goal slide. State your company-goals here. Slide 65 : This slide contains the Post it notes for reminders and deadlines. Slide 66 : This is the Puzzle slide with related imagery. Slide 67 : This slide showcases the Venn diagram. Slide 68 : This slide elucidates the firm's Timeline. Slide 69 : This is the Idea generation slide for encouraging fresh ideas. Slide 70 : This slide is used for the purpose of Comparison. Slide 71 : This is the Thank you slide for acknowledgement.
Autonomous Mobile Robots Types Powerpoint Presentation Slides with all 76 slides:
Use our Autonomous Mobile Robots Types Powerpoint Presentation Slides to effectively help you save your valuable time. They are readymade to fit into any presentation structure.

Ratings and Reviews
by Edgar George
April 13, 2023
by Danilo Woods

- Preferences

Types Of Robots PowerPoint PPT Presentations

ROBOT CLASSIFICATION
Apr 13, 2012
1.07k likes | 3.96k Views
ROBOT CLASSIFICATION. OBJECTIVES: BE AWARE OF ROBOT CLASSIFICATION. BE ACQUAINTED WITH MANIPULATOR ARM GEOMETRY. UNDERSTAND THE DEGREES OF FREEDOM OF A ROBOTIC SYSTEM. RECOGNIZE THE TYPE OF POWER SOURCES USED IN CURRENT ROBOTS. BE FAMILIAR WITH TYPE OF MOTION. KNOW A ROBOT’S PATH CONTROL.
Share Presentation
- motion configurations
- extreme limits
- commercially available industrial robots
- continuous path
- automated loading cnc lathe

Presentation Transcript
ROBOT CLASSIFICATION OBJECTIVES: • BE AWARE OF ROBOT CLASSIFICATION. • BE ACQUAINTED WITH MANIPULATOR ARM GEOMETRY. • UNDERSTAND THE DEGREES OF FREEDOM OF A ROBOTIC SYSTEM. • RECOGNIZE THE TYPE OF POWER SOURCES USED IN CURRENT ROBOTS. • BE FAMILIAR WITH TYPE OF MOTION. • KNOW A ROBOT’S PATH CONTROL. • UNDERSTAND THE INTELLIGENCE LEVEL OF ROBOTS.
CLASSIFICATION: CLASSIFIED INTO SIX CATEGORIES • ARM GEOMETRY: RECTANGULAR;CYLINDIRICAL;SPHERICAL; JOINTED-ARM(VERTICAL);JOINED-ARM(HORIZONTAL). • DEGREES OF FREEDOM: ROBOT ARM; ROBOT WRIST. • POWER SOURCES: ELECTRICAL;PNEUMATIC;HYDRAULIC;ANY COMBINATION. • TYPE OF MOTION: SLEW MOTION; JOINT-INTERPOLATION; STRAIGHT-LINE INTERPOLATION; CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION. • PATH CONTROL: LIMITED SEQUENCE; POINT-TO-POINT; CONTINOUS PATH; CONTROLLED PATH. • INTELLLIGENCE LEVEL: LOW-TECHNOLOGY(NONSERVO); HIGH-TECHONOLOGY(SERVO).
ARM GEOMETRY • ROBOT MUST BE ABLE TO REACH A POINT IN SPACE WITHIN THREE AXES BY MOVING FORWARD AND BACKWARD, TO THE LEFT AND RIGHT, AND UP AND DOWN. • ROBOT MANIPULATOR MAY BE CLASSIFIED ACCORDING TO THE TYPE OF MOVEMENT NEEDED TO COMPLETE THE TASK. • RECTANGULAR-COORDINATED: - HAS THREE LINEAR AXES OF MOTION. - X REPRESENTSD LEFT AND RIGHT MOTION - Y DESCRIBES FORWARD AND BACKWARD MOTION. - Z IS USED TO DEPICT UP-AND-DOWN MOTION. THE WORK ENVELOPE OF A RECTANGULAR ROBOT IS A CUBE OR RECTANGLE, SO THAT ANY WORK PERFORMED BY ROBOT MUST ONLY INVOLVE MOTIONS INSIDE THE SPACE.
RECTANGULAR COORDINATES • ADVANTAGES: • THEY CAN OBTAIN LARGE WORK ENVELOPE BECAUSE RAVELLING ALONG THE X-AXIS, THE VOLUME REGION CAN BE INCREASED EASILY. • THEIR LINEAR MOVEMENT ALLOWS FOR SIMPLER CONTROLS. • THEY HAVE HIGH DEGREE OF MECHANICAL RIGIDITY, ACCURACY, AND REPEATABILITY DUE O THEIR STRUCTURE. • THEY CAN CARRY HEAVY LOADS BECAUSE THE WEIGHT-LIFTING CAPACITY DOES NOT VARY AT DIFFERENT LOCATIONS WITHING THE WORK ENVELOPE. • DISADVANTAGES: • THEY MAKES MAINTENANCE MORE DIFFICULT FOR SOME MODELS WITH OVERHEAD DRIVE MECHANISMS AND CONTROL EQUIPMENT. • ACCESS TO THE VOLUME REGION BY OVERHEAD CRANE OR OTHER MATERIAL-HANDLING EQUIPMENT MAY BE IMPAIRED BY THE ROBOT-SUPPORTING STRUCTURE. • THEIR MOVEMENT IS LIMITED TO ONE DIRECTION AT A TIME.
APPLICATION: • PICK-AND-PLACE OPERATIONS. • ADHESIVE APPLICATIONS(MOSTLY LONG AND STRAIGHT). • ADVANCED MUNITION HANDLING. • ASSEMBLY AND SUBASSEMBLY(MOSTLY STRAINGHT). • AUTOMATED LOADING CNC LATHE AND MILLING OPERATIONS. • NUCLEAR MATERIAL HANDLING. • WELDING.
CYLINDRICAL-COORDINATED • HAS TWO LINEAR MOTIONS AND ONE ROTARY MOTION. • ROBOTS CAN ACHIEVE VARIABLE MOTION. • THE FIRST COORDINATE DESCRIBE THE ANGLE THETA OF BASE ROTATION--- ABOUT THE UP-DOWN AXIS. • THE SECOND COORDINATE CORRESPOND TO A RADICAL OR Y--- IN OUT MOTION AT WHATEVER ANGLE THE ROBOT IS POSITIONED. • THE FINAL COORDINATE AGAIN CORRESPONDS TO THE UP-DOWN Z POSITION. • ROTATIONAL ABILITY GIVES THE ADVANTAGE OF MOVING RAPIDLY TO THE POINT IN Z PLANE OF ROTATION. • RESULTS IN A LARGER WORK ENVELOPE THAN A RECTANGULAR ROBOT MANIPULATOR. • SUITED FOR PICK-AND-PLACE OPERATIONS.
ADVANTAGE: • THEIR VERTICAL STRUCTURE CONSERVES FLOOR SPACE. • THEIR DEEP HORIZONTAL REACH IS USEFUL FOR FAR-REACHING OPERATIONS. • THEIR CAPACITY IS CAPABLE OF CARRYING LARGE PAYLOADS. • DISADVANTAGE: • THEIR OVERALL MECHANICAL RIGIDITY IS LOWER THAN THAT OF THE RECTILINEAR ROBOTS BECAUSE THEIR ROTARY AXIS MUST OVERCOME INERTIA. • THEIR REPEATABILITY AND ACCURACY ARE ALSO LOWER IN THE DIRECTION OF ROTARY MOTION. • THEIR CONFIGURATION REQUIRES A MORE SOPHISTICATED CONTROL SYSTEM THAN THE RECTANGULAR ROBOTS.
APPLICATION: • ASSEMBLY • COATING APPLICATIONS. • CONVEYOR PALLET TRANSFER. • DIE CASTING. • FOUNDARY AND FORGING APPLICATIONS. • INSPECTION MOULDING. • INVESTMENT CASTING. • MACHINE LOADING AND UNLOADING.
SPHERICAL COORDINATED • HAS ONE LINEAR MOTION AND TWO ROTARY MOTIONS. • THE WORK VOLUME IS LIKE A SECTION OF SPHERE. • THE FIRST MOTION CORRESPONDS TO A BASE ROTATION ABOUT A VERTICAL AXIS. • THE SECOND MOTION CORRESPONDS TO AN ELBOW ROTATION. • THE THIRD MOTION CORRESPONDS TO A RADIAL, OR IN-OUT, TRANSLATION. • A SPHERICAL-COORDINATED ROBOTS PROVIDES A LARGER WORK ENVELOPE THAN THE RECTILINEAR OR CYLINDIRICAL ROBOT. • DESIGN GIVES WEIGHT LIFTING CAPABILITIES. • ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES SAME AS CYLINDIRICAL-COORDINATED DESIGN.
APPLICATIONS: • DIE CASTING • DIP COATING • FORGING • GLASS HANDLING • HEAT TREATING • INJECTION MOLDING • MACHINE TOOL HANDLING • MATERIAL TRANSFER • PARTS CLEANING • PRESS LOADING • STACKING AND UNSTICKING.
DEGREES OF FREEDOM • THE DEGREE OF FREEDOM OR GRIP OF A ROBOTIC SYSTEM CAN BE COMPARED TO THE WAY IN WHICH THE HUMAN BODY MOVES. • FOR EACH DEGREE OF FREEDOM A JOINT IS REQUIRED. • THE DEGREES OF FREEDOM LOCATED IN THE ARM DEFINE THE CONFIGURATION. • EACH OF THE FIVE BASIC MOTION CONFIGURATIONS DISCUSS PREVIOUSLY UTILIZES THREE DEGREES OF FREEDOM IN THE ARM. • THREE DEGREES OF FREEDOM LOCATED IN THE WRIST GIVE THE END EFFECTOR ALL THE FLEXIBILITY. • A TOTAL OF SIX DEGREES OF FREEDOM IS NEEDED TO LOCATE A ROBOT’S HAND AT ANY POINT IN ITS WORK SPACE. • ALTHOUGH SIX DEGREES OF FREEDOM ARE NEEDED FOR MAXIMUM FLEXIBILITY, MOST ROBOT EMPLOYEE ONLY THREE TO FIVE DEGREES OF FREEDOM. • THE MORE THE DEGREES OF FREEDOM, THE GREATER IS THE COMPLEXITY OF MOTIONS ENCOUNTERED.
DEGREES OF FREEDOM (CONTD.) • THE THREE DEGREES OF FREEDOM LOCATED IN THE ARM OF A ROBOTIC SYSTEM ARE: • THE ROTATIONAL REVERSE: IS THE MOVEMENT OF THE ARM ASSEMBLY ABOUT A ROTARY AXIS, SUCH AS LEFT-AND-RIGHT SWIVEL OF THE ROBOT’S ARM ABOUT A BASE. • THE RADIAL TRAVERSE: IS THE EXTENSION AND RETRACTION OF THE ARM OR THE IN-AND-OUT MOTION RELATIVE TO THE BASE. • THE VERTICAL TRAVERSE: PROVIDES THE UP-AND-DOWN MOTION OF THE ARM OF THE ROBOTIC SYSTEM. • THE THREE DEGREES OF FREEDOM LOCATED IN THE WRIST, WHICH BEAR THE NAMES OF AERONAUTICAL TERMS, ARE • PITCH OR BEND: IS THE UP-AND-DOWN MOVEMENT OF THE WRIST. • YAW: IS THE RIGHT-AND-LEFT MOVEMENT OF THE WRIST. • ROLL OR SWIVEL: IS THE ROTATION OF THE HAND.
POWER SOURCES • THE FOUR POWER SOURCES USED IN CURRENT ROBOTS ARE: • ELECTRIC: ALL ROBOTS USE ELECTRICITY AS THE PRIMARY SOURCE OF ENERGY. • ELECTRICITY TURNS THE PUMPS THAT PROVIDE HYDRAULLIC AND PNEUMATIC PRESSURE. • IT ALSO POWERS THE ROBOT CONTROLLER AND ALL THE ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS AND PERIPHERAL DEVICES. • IN ALL ELECTRIC ROBOTS, THE DRIVE ACTUATORS, AS WELL AS THE CONTROLLER, ARE ELECTRICALLY POWERED. • BECAUSE ELECTRIC ROBOT DO NOT REQUIRE A HYDRAULIC POWER UNIT, THEY CONSERVE FLOOR SPACE AND DECREASE FACTORY NOISE. • NO ENERGY CONVERSION IS REQUIRED. • PNEUMATIC: THESE ARE GENERALLY FOUND IN RELATIVELY LOW-COST MANIPULATORS WITH LOW LOAD CARRYING CAPACITY. • PNEUMATIC DRIVES HAVE BEEN USED FOR MANY YEARS FOR POWERING SIMPLE STOP-TO-STOP MOTIONS. • IT IS INHERENTLY LIGHT WEIGHT, PARTICULARLY WHEN OPERATING PRESSURES ARE MODERATE.
HYDRAULIC: ARE EITHER LINEAR POSITION ACTUATORS OR A ROTARY VANE CONFIGURATION. • HYDRAULIC ACTUATORS PROVIDE A LARGE AMOUNT OF POWER FOR A GIVEN ACTUATOR. • THE HIGH POWER-TO-WEIGHT RATIO MAKES THE HYDRAULIC ACTUATOR AN ATTRACTIVE CHOICE FOR MOVING MODERATE TO HIGH LOADS AT REASONABLE SPEEDS AND MODERATE NOISE LEVEL. • HYDRAULIC MOTORS USUALLY PROVIDE A MORE EFFICIENT WAY OF ENERGY TO ACHIEVE A BETTER PERFORMANCE, BUT THEY ARE EXPENSIVE AND GENERALLY LESS ACCURATE.
TYPES OF MOTION • A ROBOT MANIPULATOR CAN MAKE FOUR TYPES OF MOTION IN TRAVELLING FROM ONE POINT TO ANOTHER IN THE WORKPLACE: • SLEW MOTION : SIMPLEST TYPE OF MOTION. ROBOT IS COMMANDED TO TRAVEL FROM ONE POINT TO ANOTHER AT DEFAULT SPEED. • JOINT-INTERPOLATED MOTION: REQUIRES THE ROBOT CONTROLLER TO CALCULATE THE TIME IT WILL TAKE EACH JOINT TO REACH ITS DESTINATION AT THE COMMANDED SPEED. • STRAIGHT-LINE INTERPOLATION MOTION: REQUIRES THE END OF THE END EFFECTOR TO TRAVEL ALONG A STRAIGHT PATH DETERMINE IN RECTANGULAR COORDINATES. • USEFUL IN APPLICATIONS SUCH AS ARC WELDING, INSERTING PINS INTO HOLES, OR LAYING MATERIAL ALONG A STRAIGHT PATH. • CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION MOTION: REQUIRES THE ROBOT CONTROLLER TO DEFINE THE POINTS OF A CIRCLE IN THE WORKPLACE BASED ON A MINIMUM OF THREE SPECIFIED POSITIONS. • CIRCULAR INTERPOLATION PRODUCES A LINEAR APPROXIMATION OF THE CIRCLE AND IS MORE READILY AVAILABLE USING A PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE RATHER THAN MANUAL OR TEACH PENDANT TECHNIQUES.
PATH CONTROL • COMMERCIALLY AVAILABLE INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS CAN BE CLASSIFIED INTO FOUR CATEGORIES ACCORDING TO THE PATH CONTROL SYSTEM. • LIMITED-SEQUENCE: DO NOT USE SERVO-CONTROL TO INDICATE RELATIVE POSITIONS OF THE JOINTS. • THEY ARE CONTROLLED BY SETTING LIMIT SWITCHES AND/OR MECHANICAL STOPS TOGETHER WITH A SEQUENCER TO COORDINATE AND TIME THE ACTUATION OF THE JOINTS. • WITH THIS METHOD OF CONTROL, THE INDIVDUAL JOINTS CAN ONLY BE MOVED TO THEIR EXTREME LIMITS OF TRAVEL. • POINT-TO-POINT: THESE ROBOTS ARE MOST COMMON AND CAN MOVE FROM ONE SPECIFIED POINT TO ANOTHER BUT CANNOT STOP AT ARBITRARY POINTS NOT PREVIOUSLY DESIGNATED. • CONTROLLED PATH: IS A SPECIALIZED CONTROL METHOD THAT IS A PART OF GENERAL CATEGORY OF A POINT-TO-POINT ROBOT BUT WITH MORE PRECISE CONTROL. • THE CONTROLLED PATH ROBOT ENSURES THAT THE ROBOT WILL DESCRIBE THE RIGHT SEGMENT BETWEEN TWO TAUGHT POINTS. • CONTROLLED-PATH IS A CALCULATED METHOD AND IS DESIRED WHEN THE MANIPULATOR MUST MOVE IN THE PERFECT PATH MOTION.
CONTINUOUS PATH: IS AN EXTENSION OF THE POINT-TO-POINT METHOD. THIS INVOLVES THE UTILIZATION OF MORE POINTS AND ITS PATH CAN BE ARC, A CIRCLE, OR A STRAIGHT LINE. • BECAUSE OF THE LARGE NUMBER OF POINTS, THE ROBOT IS CAPABLE OF PRODUCING SMOOTH MOVEMENTS THAT GIVE THE APPEARANCE OF CONTINUOUS OR CONTOUR MOVEMENT.
INTELLIGENCE LEVEL • THE INTELLIGENT CONTROL ROBOT IS CAPABLE OF PERFOMING SOME OF THE FUNCTIONS AND TASKS CARRIED OUT BY HUMAN BEINGS. • IT CAN DETECT CHANGES IN THE WORK ENVIRONMENT BY MEANS OF SENSORY PERCEPTION. • INTELLIGENT ROBOT IS EQUIPPED WITH A VARIETY OF SENSORS AND SENSOR APPARATUS PROVIDING VISUAL (COMPUTER VISION) AND TACTILE (TOUCHING) CAPABILITIES TO RESPOND INSTANTLY TO VARIABLE SITUATIONS. • MUCH LIKE HUMANS, THE ROBOT OBSERVES AND EVALUATES THE IMMEDIATE ENVIRONMENT BY PERCEPTION AND PATTERN RECOGNITION. • BECAUSE ITS OPERATION IS SO COMPLEX, POWERFUL COMPUTERS ARE REQUIRED TO CONTROL ITS MOVEMENTS AND MORE- SOPHISTICATED SENSING DEVICES TO RESPOND TO ITS ACTIONS. • EXTENSIVE RESEARCH HAS BEEN AND STILL CONCERNED WITH HOW TO EQUIP ROBOTS WITH SEEING “EYES” AND TACTILE “FINGERS”. • ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) THAT WILL ENABLE THE ROBOTS TO RESPOND, ADAPT, REASON, AND MAKE DECISIONS TO REACT TO CHANGE IS ALSO AN INHERENT CAPABILITY OF THE INTELLIGENT ROBOT.
SUMMARY • INTRODUCES THE GENERAL CONCEPTS OF ROBOT CLASSIFICATION. • PROVIDED OVERVIEW OF ALL TYPES OF ROBOT ARM GEOMETRY AND STYLES, CONSIDERING DEGREES OF FREEDOM, POWER SOURCES, CONTROL SYSTEMS, AND PATH CONTROL. • THE ARM GEOMETRY IS AVAILABLE IN FIVE BASIC CONFIGURATIONS: RECTANGULAR, CYLINDRICAL, SPHERICAL, JOINTED-ARM, AND SCARA. • THE THREE DEGRESS OF FREEDOM LOCATED IN THE ARM OF ROBOT SYSTEM ARE THE ROTATIONAL TRAVERSE, THE RADIAL TRAVERSE, AND THE VERTICAL TRAVERSE. • THE THREE DEGREES OF FREEDOM LOCATED IN THE WRIST ARE PITCH, YAW, AND ROLL. • THE FOUR POWER SOURCES USED IN THE CURRENT ROBOTS ARE ELECTRIC, HYDRAULIC, PNEUMATIC, AND ELECTROMECHANICAL.
SUMMARY (CONTD.) • THERE ARE FOUR TYPES OF MOTION THAT A ROBOT MANIPULATOR CAN MAKE IN TRAVELING FROM ONE POINT TO ANOTHER IN THE WORKPLACE: SLEW, JOINT-INTEROLATED, STRAIGHT LINE INTERPOLATION, CIRCULAR. • THERE ARE FOUR TYPES OF PATH CONTROLS OF ROBOTS: LIMITED-SEQUENCE, POINT-TO-POINT, CONTROLLED-PATH, AND CONTINUOUS PATH. • ROBOT SYSTEMS ARE USUALLY CLASSIFIED AS HIGH-TECHNOLOGY AND LOW-TECHNOLOGY GROUP.
- More by User

Robot Lab: Robot Path Planning
Robot Lab: Robot Path Planning William Regli Department of Computer Science (and Departments of ECE and MEM) Drexel University Introduction to Motion Planning Applications Overview of the Problem Basics – Planning for Point Robot Visibility Graphs Roadmap Cell Decomposition
1.57k views • 94 slides

Autonomous Robot
Autonomous Robot Merlin Perry Travis Shricker Ross Aten Goal Build an Autonomous robot that will navigate the R-4 parking lot using GPS tracking data. GPS The Global Position System uses a 3 segment system: Space, User, & Control segment.
701 views • 28 slides

Rescue Robot
Rescue Robot Summer 2005 Sharif University of Technology Bahador Khaleghi Amir Aminsabouri Outline Introduction Processor Specs Sensors Actuators Communications Computational power Environment model Behavioral analysis Scan time Memory allocation Software architecture
976 views • 15 slides
ROBOT TECHNOLOGY
ROBOT TECHNOLOGY OBJECTIVE REALIZE THE FUNDAMENTALS OF ROBOT TECHNOLOGY. KNOW THE GENERAL CHARACTERSITICS OF ROBOTS UNDERSTAND THE BASIC COMPONENTS OF ROBOTS RECOGNIZE ROBOT ANATOMY BE INFORMED OF ROBOT GENERATIONS BE AWARE OF ROBOT SELECTION DEFINITION
1.12k views • 19 slides
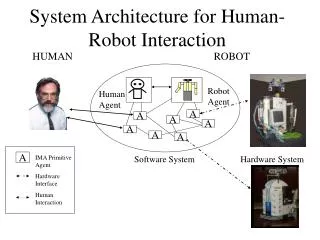
System Architecture for Human-Robot Interaction HUMAN ROBOT Robot Agent Human Agent A A A A A A A A IMA Primitive Agent Software System Hardware System Hardware Interface Human Interaction
1.19k views • 24 slides

Robot, Task. Task, Robot.
Robot, Task. Task, Robot. The morally dubious exploitation of the new slave race. Robot, Game. Game, Robot. Welcoming our creations into the playful embrace of human culture. Why Tasks are Good. General-purpose perception, action = can of worms
547 views • 16 slides

R. OS. Robot. [email protected]. R. Global Path Planning, AI Supervisory Control Marker Detection Visualization SLAM HMI. Robot. OS. R. We Need 2 x ROS. Dead Reckoning Sensor Fusion Control Position Velocity Force/Impedance Model-based
315 views • 4 slides

ROBOT CONTROL
ROBOT CONTROL. T. Bajd and M. Mihelj. Robot control. Robot control deals with computation of the forces or torques which must be generated by the actuators in order to successfully accomplish the robot task. The robot task can be
1.11k views • 31 slides
ROBOT SENSORS AND ROBOT VISON
ROBOT SENSORS AND ROBOT VISON. T. Bajd and M. Mihelj. Robot sensors. Proprioceptive sensors position velocity joint torques Exteroceptive sensors force sensors tactile sensors proximity sensors distance sensors. Robot sensors. Electric sensors potentiometers strain gauges
736 views • 18 slides

Active Sensing for Terrain Classification on an Agile Robot
Active Sensing for Terrain Classification on an Agile Robot. Richard Voyles Collaborative Systems Lab Department of Computer Science and Engineering. Outline. Motivation: Urban Search and Rescue TerminatorBot Robotic Platform NSF Center for Safety, Security, and Rescue Robots
617 views • 44 slides

Robot Lab: Robot Path Planning. William Regli Department of Computer Science (and Departments of ECE and MEM) Drexel University. Introduction to Motion Planning. Applications Overview of the Problem Basics – Planning for Point Robot Visibility Graphs Roadmap Cell Decomposition
1.24k views • 94 slides
Robot and Robot Classification
Robot and Robot Classification. Logics of presentation: Robot definition Robot classification. Robot Definition. Functional viewpoint: - automatically controlled, - reprogrammable multipurpose - reprogrammable axes Structural viewpoint: (see Fig. 2-1)
520 views • 17 slides

Robot Based 3d Printing - robot extruder
Our extruder can be connected to the printer and will produce Robot Based 3d Printing if you needed. If you want to know more about it, contact us now.https://robotextruder.com/
113 views • 5 slides

Aido Robot | Ingen Dynamics Aido Robot | Family Robot
Ingen Dynamics Aido Robot - Aido is the next generation social family robot. Smart, interactive, and uniquely mobile, Aido is the first social robot that can move around your home/office to help improve your lifestyle.
82 views • 4 slides


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Mar 24, 2017 · The first commercial robot, Unimate, was created in 1956 and performed repetitive tasks like welding. There are several types of robots including mobile, industrial, autonomous, remote-controlled, and virtual robots. Robots are used in applications like space exploration, medical surgery, assembly lines, security, and home assistance.
Jan 21, 2012 · The document discusses the history and types of robots. It begins by explaining how early human labor led to the development of machines to perform repetitive tasks. This technological advancement eventually led to the creation of autonomous robots in 1948. The document then outlines different types of robots categorized by locomotion and ...
Feb 15, 2017 · Military robots are remote-controlled mobile robots used for military applications like capturing images in enemy territory. Space robots, called rovers, are used to explore space and analyze soil samples and take photos of planets and other celestial bodies. Read less
Sep 22, 2024 · Robotics PPT: Definition, Types, Components, Future Advanced robots can perform complex tasks, such as exploring distant planets or delivering packages. Robotics combines engineering, computer science, and artificial intelligence to create machines that can sense, act, and learn.
Dec 24, 2011 · Types of Robots. Some Literature. Motorola books not for this year. Contents about robot types in book. Topics: – Driving Robots Differential steering, synchro-drive, tracked vehicles – Omni-Directional Robots Mecanum wheels – Flying Robots Sensors, structure – Balancing Robots
Oct 1, 2010 · Types of Robots. Types of Robots. Some Literature. Motorola books not for this year. Contents about robot types in book. Topics: – Driving Robots Differential steering, synchro-drive, tracked vehicles – Omni-Directional Robots Mecanum wheels – Flying Robots Sensors, structure – Balancing Robots. 5.21k views • 61 slides
Title: Types of Robots 1 Types of Robots 2 Some Literature Motorola books not for this year 3 Contents about robot types in book. Topics ; Driving Robots ; Differential steering, synchro-drive, tracked vehicles ; Omni-Directional Robots ; Mecanum wheels ; Flying Robots ; Sensors, structure ; Balancing Robots ; Inverted pendulum ; Walking Robots
This PowerPoint presentation demonstrates different types of industrial robots, such as SCARA, cartesian, cobots, and their applications in businesses. We have also covered the reasons to implement industrial robots in different domains and how companies can use robotics to increase their productivity and revenue.
Jul 10, 2020 · Types of mobile robots are. Land based wheeled, tracked, legged robots; Air based robots –plane, Helicopter; Water based – Submarines; Combinational robots; 3. Educational Robots. Robots that are used in education. They are abled to bring schools to students who cannot be able to present Physically. Types of educational robots are: Root ...
Jan 25, 2022 · 2. CO-3 Introduction of robotics: Types of robots, Classification, usage, and the Applications of Robots. Mathematical representations of robots: Position and orientations of rigid body, Homogeneous transformations, Representation of joints, Link representation using D-H parameters, Different kinds of Actuators (Stepper, DC servo and AC motors), Sensors (internal and external sensors) Common ...
Apr 13, 2023 · Further, our Autonomous Mobile Robots Architecture PPT explores different types of autonomous robotic systems, like programmable, non-programmable, adaptive, and intelligent systems. It also discusses the applications of AMRs in various industries, the differences between AMRs and AGVs, and pricing for building AMRs.
Nov 19, 2014 · INTRODUCTION TO ROBOTICS. Presentation Objectives. Definition Types of Robot History Timeline Laws of Robotics Components Uses. Body Effectors Actuators Sensors Controller Software. Definition. Slideshow 6848342 by kim-hinton
Robotics Robotic History Robotic Technology Types of Robots. 6 First use of the word “Robotics” The word robot was introduced to the public by Czech writer Karel Capek( ) in his play R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots), published in The play begins in a factory that makes artificial people called robots .
Industrial Robotics Market Share, Growth, Trends & Forecast Report 2018-2026 - Global Industrial Robotics Market by Robot Type (Articulated Robots, Cartesian or Gantry Robots, Selective Compliant Articulated Robot for Assembly (Scara) Robots, Cylindrical Robots,delta or Parallel Robots, Polar or Spherical Robots) by End User Sectors (Automotive ...
Mar 22, 2017 · Nowadays, robots do a lot of different tasks in many fields and the number of jobs entrusted to robots is growing steadily. That's why in my opinion one of the best ways how to divide robots into types is a division by their application.
Apr 13, 2012 · ROBOT CLASSIFICATION. OBJECTIVES: BE AWARE OF ROBOT CLASSIFICATION. BE ACQUAINTED WITH MANIPULATOR ARM GEOMETRY. UNDERSTAND THE DEGREES OF FREEDOM OF A ROBOTIC SYSTEM. RECOGNIZE THE TYPE OF POWER SOURCES USED IN CURRENT ROBOTS. BE FAMILIAR WITH TYPE OF MOTION. KNOW A ROBOT’S PATH CONTROL.
Laws of Robotics • Asimov proposed three “Laws of Robotics” and later added the “zeroth law” • Law 0: A robot may not injure humanity or through inaction, allow humanity to come to harm • Law 1: A robot may not injure a human being or through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm, unless this would violate a higher order law
Agricultural robots can assess ripeness, move any branches or leaves out of the way, and pick the crop precisely and delicately to avoid causing any harm to the product. Healthcare. Various types of robots are used in the healthcare industry to enhance the patient experience.
Mar 6, 2019 · It begins with defining robots and robotics. It then covers the different types of robots categorized by their general concept, application, locomotion/kinematics. The core components of robots like manipulators, end effectors, actuators, sensors and controllers are explained. Popular robot configurations and programming languages are also ...
3 days ago · Syrebo a présenté, le 11 novembre, plusieurs types innovants de robots de rééducation, à l'occasion du salon MEDICA 2024 de Düsseldorf. Son robot de rééducation des membres supérieurs, son robot de rééducation interface cerveau-ordinateur et son nouveau robot de rééducation à domicile ont attiré l'attention.