FREE shipping on orders over $89

- Microscopes
- Experiment Kits
This section doesn’t currently include any content. Add content to this section using the sidebar.
Add description and links to your promotion
Your headline
Image caption appears here
Your product's name
Add your deal, information or promotional text

Helping Kids with Homework: 11 Easy & Do-Able Tips for Parents
Tips for Smart Parenting 09/21/2021 11 minute read
Homework is the bane of every student, as it is for the parents.
As a matter of fact, homework is not even necessary in the first place.
Before you react, there are countless studies to validate this claim. But even if we go on a hard-fought, well-thought, debate on whether homework is important or not, homework is here to stay.
That said, helping kids with their take-home assignments is a duty we have to fulfill. But how exactly do we do it?
Below are actionable parenting tips to help your kids with their homework without doing it for them!
You might be interested: How to Support Kids Learning Science and Why it Matters?
Parenting Tips on How to Do Homework with Kids
We used to believe that parental availability and support while kids do their assignments is key for their class success. "The more involved parents are, the better off they would be," so to speak.
But that is a misconception and sometimes may even be counterproductive. As Kathleen Reilly said:
“When parents are overly immersed in homework, they deny kids the chance to become more independent and confident. Worse, it can breed anxiety along the way.”
Helping kids with homework means that you offer your support but never treat the assignment like it's your responsibility. It's challenging, but kids need to do homework on their own because the assignments deal with lessons already discussed in class. Plus, answering homework by themselves is a good way to teach independent learning .
With that in mind, here are the homework tips for parents:
1. Work Out a Working Routine
Believe it or not, children love routines because they create structure .
This helps children feel more secure because they know what to do and what's expected of them.
Face it, nobody likes homeworks. But make it easier for your kids to do their's by doing routines such as below:
What time should they start? Set a definite time when they should do their homeworks. Will it be right after they arrive from school? Should they play for an hour first? Would they do it after shower time or after dinner?
Where is their homework place? The place they choose is likely the area they feel most comfy working in. That element adds extra help when doing homework. Find a place and stick with it.
If you have multiple kids, distinct routines for each are fine. What matters is that you enforce discipline and commitment to the schedule. Write the details on a sheet of paper and post their routines on the wall!
2. Make a Homework Plan
The routine simply tackles the when and where kids do their assignments. A homework plan focuses on how they do it.
Doing homework needs to be systematic , both for you and the child. Approach homework from a systematic point of view and you save yourselves time and whine.
The example below is the system I found most suited for my children. You can follow it or fashion your own process, whichever works best. Here's what my kids do:
Read the directions of the homework, twice.
Determine the goal and the steps needed to achieve it.
Divide the assignment into several chunks (if logically possible).
Set time limits for each portion and mark each as complete when finished.
Helping kids with homework is not about giving them all the answers. It's about strategizing on how to finish the homework effectively and efficiently.
3. Monitor, Don't Correct
Let's get back to basics .
What is the purpose of homework?
Homework allows teachers to gauge what the students understood in class. That said, mistakes are welcomed.
But since most parents dread the idea of making mistakes, they try to correct each flaw too often all for a perfect remark.
Word of advice: Teachers are well-aware of how your kids perform in class, so they know the truth.
My point is, remove the notion of absolute perfection from your kids.
It's okay to make mistakes, as long as they learn how to correct them on their own ! There should be no pressure on them to avoid mistakes at all costs. Encourage an atmosphere of growth. But, make it clear to your kids they should resolve their mistakes the next time around, once they understand the correct answer.
Do this instead:
Allow your kids to ask you up to 3 questions on their homework. But, be stingy on answering their questions right away.
When they ask, reply to them something like "I can help you once I finish my chores" or "Read it again, I'll be back in a sec."
You might not realize it, but this is one subtle way to help kids with homework. When you delay your aid, you gently force them to reread the directions and rework the problem on their own.
Monitor and ask them probing questions on the reason behind their homework answers.
4. Set an Example to Imitate
Helping kids how to do homework can also mean modeling the behavior to them. This is a parenting hack that most parents fail to practice.
It can be a good motivating factor for the kids if you do chores like budgeting or computing household expenses at the same time they do their assignments.
This is one indirect way to teach kids how to do homework. Set a good example and you'll find them following your footsteps.
5. Don't Sit Beside Them
Sitting and closely monitoring your kids as they answer homework is not at all helpful.
Behind the scenes, it sends a message to their brains that you might think they can't do the work without direct supervision.
Would you like that? Of course not!
Helping kids with their homework should also tap into the emotional aspect of learning. Show them that you trust their brains by letting them do their assignment on their own. Otherwise, you shatter their self-confidence leading to feelings of inferiority.
Here are my suggestions:
Stay nearby, do chores, balance your checks, wash dishes. Basically, just be there for them, without literally sitting beside them.
6. Establish the No-Nonsense Responsibility
Make the duties of each member in the family clear.
Of course, both you and your partner have work responsibilities, and so do the kids! They're expected to be diligent with their responsibilities:
Attend classes
Work with their teachers
And of course... do their homeworks
Once they agreed to a working routine and a homework plan , then there is no turning back. Tell them to buckle their seats until they finish their tasks. Discipline matters just as much as intellect and system when dealing with homework.
7. Teach Them Time Management
Time management is the one of the most important tools for productivity.
Once your kids learn the benefits of being in control of their time, they position themselves to a life of success. Time management is not only relevant for homework. Instilling this behavior is a must from the get-go.
One tip is using an old analog wall clock and coloring in the hour when they should do answer their homework. Once the short arm reaches it, teach them to take initiative to do their tasks.
Help them in sorting the time out too, especially, if there are multiple homework in one seating.
8. Positive Reinforcement is a Great Hack
They say the best way to man's heart is through their stomach. Well, the best way to a child's heart is through snacks and treats . (I made that up)
Instead of threatening them to limit their TV watching time or call their teachers, why not compensate their efforts with some good ol' sweets?
Reinforcing their diligence pushes them more to do it. Scare tactics are not as good as rewards to encourage a behavior. Although, do the positive reinforcement practice sparingly.
Appreciating their efforts is another way to help kids with homework as this motivates them. You can do this by:
Posting their aced assignments or exams
Displaying their art projects on the fridge
It showcases how much you value their efforts and how proud you are of them.
9. Walk Away Once the Whine Fest Starts
How does walking away help kids on how to do homework? Well, it doesn't. It's more for your benefit than them.
Having a rough day at work is physically and mentally exhausting . Add another layer of whining because kids don't want to do their assignments, and you enter a whole new level of stress .
If they keep on complaining, check their homework progress.
If they are only being grumpy even when they can do it, then try to motivate them. Tell them that the sooner they finish, the more time they'd have to watch their favorite TV shows .
If the homework is indeed truly difficult, then lend them a hand.
Ask their teacher about it, especially if the homework is beyond the kid's level of understanding. Inquire if it's appropriate to give kids complex problems. Their teachers would love to hear feedback from parents, on top of that, to aid the pupils with their homework!
10. Let Them Take the Lead
Their Homework is not only a test of one's learning but also of a kid's sense of responsibility .
Their answers should be theirs and they must own up if they fail to do it. If they left their homework at home, then parents shouldn't bail their kids out by bringing their assignments to class.
Matt Vaccaro, a first-grade teacher, says that he makes students do their assignment during recess if they forget to do it at home.
According to him "Once she starts missing playtime, she gets the message."
This seemingly harsh yet rightful way to deal with their negligence actually motivates the kids to be responsible in the succeeding homework.
Helping them how to do homework is as necessary as teaching them to be responsible for it.
11. Keep Your Composure and Carry On
Homework meltdowns do occur, so be ready!
These are children's ways of saying they're overwhelmed . And sometimes these kids are indeed struggling so bad.
Parents, please keep your composure. Breathe and stay calm . You risk compromising their progress if you too burst out in frustration. Remember that homework is an opportunity to cultivate better parent-child relationships .
Here are ways to address homework meltdowns:
A simple hug might do
Speak words of affirmation like "we'll figure it out"
Let them vent out to you while you listen calmly
Sometimes, kids just need to blow off some steam. Catering to these needs are subtle ways of helping kids with homework. See the mood change after they've burst the bubble.
If ever you did lash out (although we hope not). Apologize immediately and tell your child that you both need a timeout for 10 minutes. They can play for within that period and resume working on the homework once the time is up.
Helping kids with homework is a dual purpose. You make homework accomplishment more manageable for them and you make life easier for you. Consider the above homework tips next time your kids have assignments.
The How-to-do-Homework Hack!
Some kids might still see learning as a chore, and that's okay. I mean, who likes to wake up early and be in class when they can play at home all day?
Making the most out of their curiosity helps transform their perception of learning — from a tedious and boring chore to a fun and interactive learning experience. We believe that the way to encourage kids to do their homework is by making them see the fun in learning.
The best way to do this is using educational toys!
The STEMscope portable microscope is a good tool to cultivate your child's curiosity. This handheld science gadget is an all-around partner for your kid's best learning!
Once they activate their curiosity, they develop the insatiable desire to learn, after that, they will see homework as fun learning opportunity!
Check out our complete catalog of science toys to find the best toy for your kid!
« Back to Blog
30 Day Science Kid Guarantee
Easy returns
24/7 support
Free shipping over $89
Internet Explorer is no longer supported
Please upgrade to Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Firefox .
Lo sentimos, la página que usted busca no se ha podido encontrar. Puede intentar su búsqueda de nuevo o visitar la lista de temas populares.
Get this as a PDF
Enter email to download and get news and resources in your inbox.
Share this on social
Strategies to make homework go more smoothly.
Routines and incentive systems to help kids succeed
Writer: Peg Dawson, EdD, NCSP
Clinical Experts: Peg Dawson, EdD, NCSP , Karol Espejo, LCSW
Here is the best guide to helping kids do homework successfully that we’ve seen, published by the National Association of School Psychologists on their website, NASPonline.org . Our thanks to NASP for sharing it with us.
There are two key strategies parents can draw on to reduce homework hassles. The first is to establish clear routines around homework, including when and where homework gets done and setting up daily schedules for homework. The second is to build in rewards or incentives to use with children for whom “good grades” is not a sufficient reward for doing homework.
Homework Routines
Tasks are easiest to accomplish when tied to specific routines. By establishing daily routines for homework completion, you will not only make homework go more smoothly, but you will also be fostering a sense of order your child can apply to later life, including college and work.
Step 1. Find a location in the house where homework will be done. The right location will depend on your child and the culture of your family. Some children do best at a desk in their bedroom. It is a quiet location, away from the hubbub of family noise. Other children become too distracted by the things they keep in their bedroom and do better at a place removed from those distractions, like the dining room table. Some children need to work by themselves. Others need to have parents nearby to help keep them on task and to answer questions when problems arise. Ask your child where the best place is to work. Both you and your child need to discuss pros and cons of different settings to arrive at a mutually agreed upon location.
Step 2. Set up a homework center. Once you and your child have identified a location, fix it up as a home office/homework center. Make sure there is a clear workspace large enough to set out all the materials necessary for completing assignments. Outfit the homework center with the kinds of supplies your child is most likely to need, such as pencils, pens, colored markers, rulers, scissors, a dictionary and thesaurus, graph paper, construction paper, glue and cellophane tape, lined paper, a calculator, spell checker, and, depending on the age and needs of your child, a computer or laptop. If the homework center is a place that will be used for other things (such as the dining room table), then your child can keep the supplies in a portable crate or bin. If possible, the homework center should include a bulletin board that can hold a monthly calendar on which your child can keep track of longterm assignments. Allowing children some leeway in decorating the homework center can help them feel at home there, but you should be careful that it does not become too cluttered with distracting materials.
Step 3. Establish a homework time. Your child should get in the habit of doing homework at the same time every day. The time may vary depending on the individual child. Some children need a break right after school to get some exercise and have a snack. Others need to start homework while they are still in a school mode (i.e., right after school when there is still some momentum left from getting through the day). In general, it may be best to get homework done either before dinner or as early in the evening as the child can tolerate. The later it gets, the more tired the child becomes and the more slowly the homework gets done.
Step 4. Establish a daily homework schedule. In general, at least into middle school, the homework session should begin with your sitting down with your child and drawing up a homework schedule. You should review all the assignments and make sure your child understands them and has all the necessary materials. Ask your child to estimate how long it will take to complete each assignment. Then ask when each assignment will get started. If your child needs help with any assignment , then this should be determined at the beginning so that the start times can take into account parent availability. A Daily Homework Planner is included at the end of this handout and contains a place for identifying when breaks may be taken and what rewards may be earned.
Incentive Systems
Many children who are not motivated by the enjoyment of doing homework are motivated by the high grade they hope to earn as a result of doing a quality job. Thus, the grade is an incentive, motivating the child to do homework with care and in a timely manner. For children who are not motivated by grades, parents will need to look for other rewards to help them get through their nightly chores. Incentive systems fall into two categories: simple and elaborate.
Simple incentive systems. The simplest incentive system is reminding the child of a fun activity to do when homework is done. It may be a favorite television show, a chance to spend some time with a video or computer game, talking on the telephone or instant messaging, or playing a game with a parent. This system of withholding fun things until the drudgery is over is sometimes called Grandma’s Law because grandmothers often use it quite effectively (“First take out the trash, then you can have chocolate chip cookies.”). Having something to look forward to can be a powerful incentive to get the hard work done. When parents remind children of this as they sit down at their desks they may be able to spark the engine that drives the child to stick with the work until it is done.
Elaborate incentive systems. These involve more planning and more work on the part of parents but in some cases are necessary to address more significant homework problems. More complex incentives systems might include a structure for earning points that could be used to “purchase” privileges or rewards or a system that provides greater reward for accomplishing more difficult homework tasks. These systems work best when parents and children together develop them. Giving children input gives them a sense of control and ownership, making the system more likely to succeed. We have found that children are generally realistic in setting goals and deciding on rewards and penalties when they are involved in the decision-making process.
Building in breaks. These are good for the child who cannot quite make it to the end without a small reward en route. When creating the daily homework schedule, it may be useful with these children to identify when they will take their breaks. Some children prefer to take breaks at specific time intervals (every 15 minutes), while others do better when the breaks occur after they finish an activity. If you use this approach, you should discuss with your child how long the breaks will last and what will be done during the breaks (get a snack, call a friend, play one level on a video game). The Daily Homework Planner includes sections where breaks and end-of-homework rewards can be identified.
Building in choice. This can be an effective strategy for parents to use with children who resist homework. Choice can be incorporated into both the order in which the child agrees to complete assignments and the schedule they will follow to get the work done. Building in choice not only helps motivate children but can also reduce power struggles between parents and children.
Developing Incentive Systems
Step 1. Describe the problem behaviors. Parents and children decide which behaviors are causing problems at homework time. For some children putting homework off to the last minute is the problem; for others, it is forgetting materials or neglecting to write down assignments. Still others rush through their work and make careless mistakes, while others dawdle over assignments, taking hours to complete what should take only a few minutes. It is important to be as specific as possible when describing the problem behaviors. The problem behavior should be described as behaviors that can be seen or heard; for instance, complains about h omework or rushes through homework, making many mistakes are better descriptors than has a bad attitude or is lazy.
Step 2. Set a goal. Usually the goal relates directly to the problem behavior. For instance, if not writing down assignments is the problem, the goal might be: “Joe will write down his assignments in his assignment book for every class.”
Step 3. Decide on possible rewards and penalties. Homework incentive systems work best when children have a menu of rewards to choose from, since no single reward will be attractive for long. We recommend a point system in which points can be earned for the goal behaviors and traded in for the reward the child wants to earn. The bigger the reward, the more points the child will need to earn it. The menu should include both larger, more expensive rewards that may take a week or a month to earn and smaller, inexpensive rewards that can be earned daily. It may also be necessary to build penalties into the system. This is usually the loss of a privilege (such as the chance to watch a favorite TV show or the chance to talk on the telephone to a friend).
Once the system is up and running, and if you find your child is earning more penalties than rewards, then the program needs to be revised so that your child can be more successful. Usually when this kind of system fails, we think of it as a design failure rather than the failure of the child to respond to rewards. It may be a good idea if you are having difficulty designing a system that works to consult a specialist, such as a school psychologist or counselor, for assistance.
Step 4. Write a homework contract. The contract should say exactly what the child agrees to do and exactly what the parents’ roles and responsibilities will be. When the contract is in place, it should reduce some of the tension parents and kids often experience around homework. For instance, if part of the contract is that the child will earn a point for not complaining about homework, then if the child does complain, this should not be cause for a battle between parent and child: the child simply does not earn that point. Parents should also be sure to praise their children for following the contract. It will be important for parents to agree to a contract they can live with; that is, avoiding penalties they are either unable or unwilling to impose (e.g., if both parents work and are not at home, they cannot monitor whether a child is beginning homework right after school, so an alternative contract may need to be written).
We have found that it is a rare incentive system that works the first time. Parents should expect to try it out and redesign it to work the kinks out. Eventually, once the child is used to doing the behaviors specified in the contract, the contract can be rewritten to work on another problem behavior. Your child over time may be willing to drop the use of an incentive system altogether. This is often a long-term goal, however, and you should be ready to write a new contract if your child slips back to bad habits once a system is dropped.
Click here to download the homework planner and incentive sheet .
Frequently Asked Questions
To help homework go more smoothly, e stablish a routine that includes a time and place where it will be done, a planner that lists each assignment, scheduled breaks when some of the work is done, and a reward system for kids who are not motivated by good grades alone.
Set a good homework routine following these steps: Find a location in the house where homework will be done. Set up a homework center stocked with needed materials . Establish a homework time. Use a daily homework planner so that your child has everything in writing.
One tool that can make homework go more smoothly i s a Daily Homework Planner , which lists each assignment, how long it should take to complete, and what rewards may be earned for completing each assignment.
Was this article helpful?
Explore popular topics, subscribe to our newsletters.
" * " indicates required fields
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Change Lives this Holiday Season
Your donation provides vital care and resources for children in need. Give now to make a difference.

Helping kids with homework
Wondering how to help your kids with their homework this year? Psychologist Eleanor Mackey has some tips.

- Share on Facebook
- Share on WhatsApp
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share by Mail
Now that school is back in full swing, many households are dealing with how to handle homework. Helping your child be successful at homework is very important because it is a very critical part of children’s academic success. Homework helps children in several ways, including:
- continues learning after the school day
- teaches responsibility
- helps parents stay aware of what their child is learning in school
Being involved in your child’s homework is important. As with all parenting endeavors, though, there is a fine line between being too involved and not being involved enough.
So, what’s a parent to do?
Step 1: Set expectations
Set up appropriate expectations for your child and their homework responsibilities. For example, depending on the age of your child, they might be responsible for determining which homework needs to be done, doing the actual homework and putting their completed homework into their backpack.
It is very important that the child take responsibility for the actual homework, not the parent. A parent might commit to finding a quiet space for the child to do the homework, checking answers, double checking that everything has been done, as well as being on hand to answer questions.
Step 2: Set up a good study space
There must be a designated homework space in the house free of noises and distractions. If possible, try to make this fun. For instance, a colleague of mine mentioned she got her kindergarten-aged son a “homework box” that has everything he needs including pencils, erasers, scissors, etc. He puts his homework folder by the box when he comes home and then has everything he needs. I think this is a great idea to help with organization for any age.
Step 3: Schedule when homework will be done
It is important to teach kids that homework must be done on time. Set aside a certain time of the evening for homework to be completed. Put it in the calendar like any other activity so that there is always time for it. Younger kids will need the schedule made for them. Children older than 10 years of age may be able to take charge of putting homework and specific assignments into the schedule and then have a parent check it for them.
For younger grades, there is usually homework that is shorter-term and due in quick succession, which can be easier to manage and plan.
For older kids, often there is advanced planning that needs to be done, for example a term paper. Help your kids learn how to break up long-term assignments into chunks and assist in planning when each section will be completed.
Step 4: Motivate!
Your encouragement goes a long way towards motivating your child to do homework. Praise your child for steps along the way, not just successful completion of homework. For example, praise them for remembering their homework, for stopping other activities without complaint when it is homework time, for continuing a challenging task or for good grades.
It is best to build internal motivation for homework, or the desire to complete it for their feelings of pride in good work done and for caring about their academics. However, some kids may benefit from external motivators, such as earning a pass from other chores in exchange for doing homework or earning the ability to engage in preferred activities when homework is done.
Still having homework challenges?
If your child is still having difficulty with homework, there are some additional steps you can take. For more pointers, I like the book “ Homework Without Tears ” by Canter and Hausner. It may also be important to talk with your child’s teacher to strategize on how to help your child. You may also want to consult a psychologist to determine if educational testing may benefit your child.
ABOUT THE EXPERT

Subscribe to our newsletter and get free parenting tips delivered to your inbox every week!
Email Address *
Related Content

Packing a healthy school lunch

Reducing back-to-school anxiety in children with autism

Back-to-school vaccines

Dealing with back-to-school jitters


Enrolling your child in school

The benefits of enrolling children in early childhood education

Avoiding backpack back pain

Helping your child with autism prepare to go back to school

Addressing school-related anxiety in children

Dealing with pandemic-induced back-to-school anxiety and homesickness

Getting your student’s sleep schedule back on track for the school year

Can my child get COVID-19 from riding the school bus?

Helping your student transition back to in-person learning

Returning to school during the pandemic: Frequently asked questions

Tips for success during distance learning

Helping kids deal with back to school anxiety

Tips for homeschooling during the coronavirus outbreak

A parent’s short guide to school health forms

5 back-to-school tips from a pediatrician to parents
Posts from eleanor mackey, phd, making family new year’s resolutions, what’s the right allowance for your child, how to avoid distracted parenting, is your child’s temper more than a tantrum, helping your kids cope with a traumatic event, praising children effectively, finding special time for your kids, leave a comment, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Don’t Help Your Kids With Homework
Focus on prioritization and process, not the assignment itself.

So much of the homework advice parents are given is theory-based, and therefore not entirely helpful in the chaos of day-to-day life. People are told that students should have “ grit .” They should “ learn from failure .” But it’s hard to know how to implement these ideas when what you really need is to support a kid who has a chemistry test and two papers due in the next 48 hours but seems to be focused only on Instagram.
Some parents manage to guide their kids through these moments with relative ease. Others hire tutors. The large majority of us, however, are stuck at home alone, trying to stave off our own breakdowns in the face of our children’s.
While reprimanding your child for not having started her homework earlier may be your natural instinct, in the midst of stress, it will only make her shut down or lash out. In our experience as teachers, tutors, and parents, the students who feel terrible about procrastinating are more likely to have anxiety and negative feelings that will only fuel their continued procrastination. So instead of admonishing your procrastinator, take a deep breath and try to figure out how she’s going to manage the tasks at hand. Help her make a realistic plan to manage her time. Try to model understanding, even when you’re upset.
Having tolerance for challenges will allow her to approach future frustrations from a more positive perspective. Easier said than done, to be sure, but try to work with your child to identify not only how but why her homework habits are suffering. This understanding will be crucial to helping her transform these habits into more effective ones.
Read: The cult of homework

Because most of us are programmed to focus on present rather than future fulfillment, it’s easy to put off something we dread. Kids who procrastinate almost always do so because they have negative associations with or feelings about a particular task. Unfortunately, avoiding assignments usually lowers students’ self-esteem and makes them dislike the topic that much more, resulting in a vicious cycle of procrastination. Therefore, it’s important both to address why students are procrastinating—what’s upsetting them about the work at hand—and to give them practical tools to manage their time and set priorities.
If you’re worried that your child is the only one in her class who takes ages to get started on her homework, fear not. Students in our classes—and our own kids too, just like many of us adults—have found every which way to put off sitting down to tackle the one thing they know they need to get done. There are all kinds of reasons kids avoid doing their homework. Maybe they’re concerned about what a teacher will think, or that their work won’t measure up to a friend’s. Maybe they’re distracted by something that happened in school that day.
Whatever the case may be, the first step here is determining out what’s stressing your child out in the first place.
If your child fears what her teacher will think if she makes mistakes: She should start off by independently reviewing the material that she feels unsure of, and then reach out to her teacher for further help if she needs it. Assure her that asking questions and making an effort are important to her teacher. Take it from us: Teachers see questions as a sign of an engaged, conscientious, and curious student. No matter the teacher’s temperament or reputation, she will respond positively to your child coming to her with sincere questions and hard work.
If your child fears parental judgment due to bad grades: Remember that although high marks may be important to you, focusing on process and effort is key to your child’s success, not to mention that putting too much pressure on her can lead to resentment. Help your child create a process she can rely on for her work. Better effort will help your child engage with the material and yield better results in the long run.
If your child fears her best friend’s judgment: Start by encouraging your child not to discuss grades with her friends. Middle schoolers in particular tend to share their marks with one another, and it usually just makes kids feel lousy. The “What did you get?” question is tough for all students, especially in the middle grades, when they are looking for affirmation from their peers. Your child’s grades are no one else’s business. While her best friend may do well in history, he may have more trouble with math than your child does. Or maybe he seems great at everything now, but he actually struggles in art class, and in the future he’ll be a terrible driver or have an awkward first date. In other words, we all have subjects—or areas of our lives—that come more or less easily than others. Challenges are inevitable. What matters most is how we approach them.
If your child fears she isn’t capable: First acknowledge how painful this feeling must be. Then reassure her that she is capable and give concrete anecdotes so she doesn’t roll her eyes. Share with her a moment when you thought you couldn’t do something, but you learned to conquer the task. And be honest! Your kid will know that you didn’t really wrestle that champion alligator. Emphasize the importance of determination, effort, and persistence in whichever example of your successes you choose to share.
If your child is exhausted: Prioritize only what’s really essential. Try to help your child go to bed earlier. She can always wake up early to complete smaller assignments if need be. Getting major work done while exhausted is a losing battle for everyone. Help her plan ahead. Create a schedule for completing small portions of a larger assignment over the course of several days or weeks to make overwhelming work seem more manageable.
Read: My daughter’s homework is killing me
Once you figure out what’s driving your child’s procrastination, you can strategize with her about logistics. Start by removing temptation when possible. Of course she’d rather see where her friends went this afternoon than stare at a blinking cursor, and if all it takes is a simple click or swipe for your child to access social media, it’s going to take her eons to finish an assignment. It will be almost impossible for her to develop an argument that flows if she’s tempted by her phone. So all possible impediments to success should be removed. Disabling social-media and messaging apps and having a conversation about the purpose of setting technology limits is an important first step. Putting her phone aside will also help her compartmentalize time so that she can get her work done more thoroughly and then have free time afterward. Technological boundaries may lead to major pushback—especially now, when kids rely on technology for most forms of socializing—but this temporary misery is undoubtedly worth it in the long run.
And emphasize that short-term pleasure equals long-term pain. Empathize with children who do not want to do something that’s hard. Then remind them that the immediate instinct to procrastinate and play video games will make life miserable later. While they may resist and grumble, helping establish rules will ultimately prevent suffering tonight, tomorrow, and next week. Kids thrive in the comfort, reliability, and safety of a structured, focused work environment. It’s never easy, but on evenings when you want to tear your hair out because your child won’t sit down to work, reinforce the message that short-term gratification will only get in the way of long-term goals.
Finally, explain the relevance of the assignment. If kids don’t understand why they’re doing the work, they’re more likely to be frustrated. For example, your child might ask, “Why do I need to know algebra? I’ll never use it when I’m older.” You can tell the truth: “You probably won’t need to know about variables in everyday life, but learning algebra will give you a framework for understanding how to break down and solve complex tasks down the road.”
Learning to work independently, without a teacher’s direct counsel, is key to building academic and personal autonomy. So when your child is overwhelmed, help her figure out why, and then model strategies that foster independence, confidence, and well-being.
This piece is adapted from Freireich and Platzer’s new book, Taking the Stress out of Homework . Every Tuesday, they answer education-related questions . Have one? Email them at [email protected].
About the Authors

Tips and tools for helping kids with their homework (but not doing it for them!)
Today’s post answers reader questions on the topic of helping kids with their homework . You can read previous answers to readers’ questions here.
It must be the time of year for it because recently many readers have asked questions on how to help kids with their homework. With only two kids in school now (year 8 and year 10) I really don’t do a lot of helping with homework. I actually don’t do anything at all with the year 10 child other than answer questions if he has any and remind him occasionally to monotask – not try and listen to podcasts etc, while doing homework! With the year 8 child it isn’t so much as helping with the homework but helping him be better organised with how he approaches his homework and study.
Helping secondary students with their organisational skills
The key to helping with homework is making sure they are the ones doing the work and that they have some systems or processes in place so they can keep up to date with it. A process I have put in place for the year 8 child is a very quick weekend homework planning session. This takes place on Friday afternoons when he gets home from school and before he heads on to the PS4 to play with friends. He needs to write up a plan of what he needs to do on the weekend, checking his diary for upcoming commitments.
The plan isn’t overly prescriptive but he will write out what key activities he wants to complete each day. He usually has Friday nights free from homework and then will work out how to fit his homework around his sporting and social commitments. So the plan will look something like this:
Saturday after football
- Practice for the Spanish listening test
- Math questions – 16a – 16g
- Science practice test
Sunday before football
- Make flash cards for Japanese
- English grammar exercise
- Maths end of topic questions
I get him to take me over the plan and there are usually a few suggestions that I make to him like:
- Work on your quotes collection for the English novel
- Create study notes for recently completed units
- Practice language subjects
At this stage, he currently just looks at his diary and writes down what is due but will often forget to look a couple of weeks in advance to see when unit tests etc are. There are times across the weekend when I will direct him back to his plan if I think he isn’t sticking to it and ticking off the activities as he needs to.
Homework help tips for when you have multiple kids
This was a very popular topic readers wanted me to address and I knew at some point I had written a newsletter about it many years ago, so I hunted it down because it seems some time ago when all five kids were in school! This will hopefully help those of you with younger kids or multiple kids.
I wrote this back in 2015 when to some extent all of the five kids had homework. It ranged from:
- Essays, assignments, study etc for the year 11 and year 8 children
- Worksheets and projects for the year 6 child
- Spelling and maths work for the year 3 child
- Nightly reading for the year 1 child
On any given night some or all of the kids could request assistance with their homework. My general approach to helping the kids with their homework was:
- Homework is the child’s responsibility.
- Parents to assist with the process, not the content.
Finding the time to help with homework
Knowing how I am going to help them with their tasks was one thing, finding the time to do it could so be a completely different and more difficult story. I had a pretty planned approach to it, so as best as I can, I could help each child when they need it:
- I worked with the three younger kids before dinner or immediately after bath time if we have been out later at after-school activities.
- For the older two boys, they knew they could ask me questions at any time, but if they needed me to sit down with them and spend more than a few minutes on something, they needed to let me know and I would make sure I could help them once the younger three were in bed. The year 8 child was particularly good at this. He would often ask me in the middle of the week if I could allocate some time on the weekend to go through something with him or read over an essay.
- There were/are certain areas that their dad is much better equipped to help them with, so I would/will delegate homework support to dad as needed. The kids would/will then work out a time with their dad to sit down together and go through whatever homework they need help with.
General homework help tips
I have found that some things worked better than others for our kids, here are some tips that have been successful for us:
- Play to their strengths – some kids are more creative, some kids are more comfortable with technology. I don’t fight this. If they have an assignment that can be either a poster or a PowerPoint presentation, get them to think about what they like doing best and assist them with creating a plan selecting their preferred medium.
- Read their moods – sometimes the year 1 child would be just too tired towards the end of the week to do his reading after dinner. It was much quicker and more enjoyable to do it the next morning before school. He was/is an early riser so we had plenty of time. I communicated the change and let him go to bed knowing it will still be done (he worried about it!).
- Eliminate distractions – in a house with 5 kids, there could/can be a lot going on. That is the main reason I helped the older kids once the younger ones were in bed, then there were fewer interruptions and generally less noise in the house. When working with any of the kids I make sure there is no TV or music on and that my mobile phone is away from me (as are any devices they don’t need for the homework task).
- Always allow more time – it almost always takes longer than I would think the task would take. If I assumed it will only take me 15 minutes and I ended up spending 45 minutes, I could start watching the clock a little, thinking about all the other things that I needed to do. By allowing more time than I think it could possibly take, I could end up being pleasantly surprised and maybe get off to bed a little earlier.
I have written previous posts on the blog on some specific areas of helping kids with their homework that you may find helpful also:
- Homework help – managing it with multiple kids
- Homework tips for parents
- Managing homework materials
Templates and resources to help the kids with their homework
My approach to homework is that I assist with the process, not the content. To that end over the years, I have created a number of templates and resources for the kids to use.
These resources allow them to plan and structure their work and some guide them through the process they need to undertake to complete them. I have listed below the ones the kids have found most helpful.
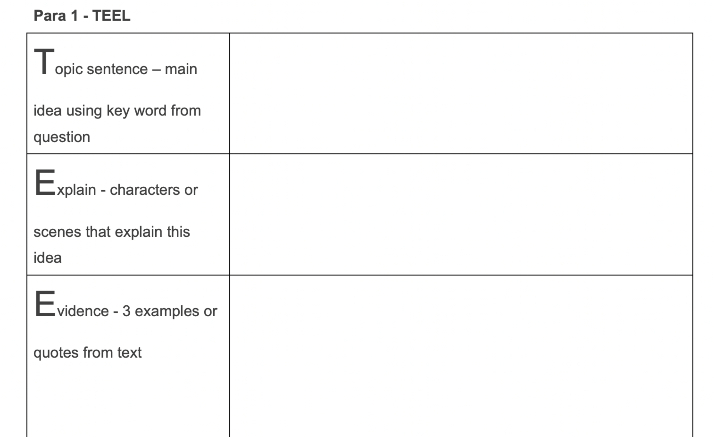
TEEL Essay Structure – this is aimed at secondary school students. The TEEL Essay Structure is a basic framework for students to use to ensure they cover the key components in their English essays.
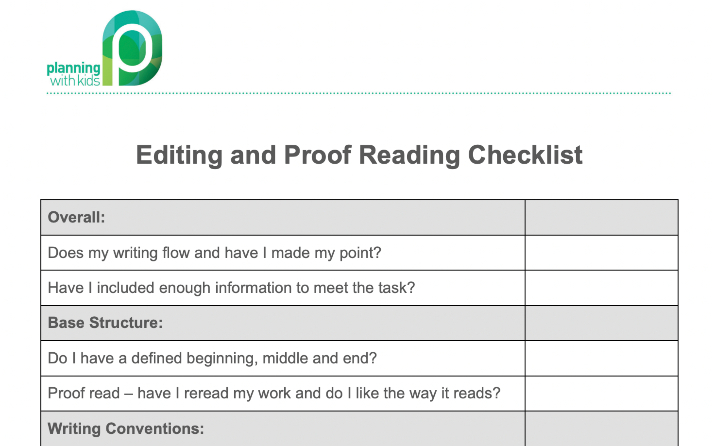
Proof Reading and Editing Checklist For Kids – Aimed at upper primary school children. The template helps take kids through a step-by-step approach to proofreading their work.

Creative Writing Proforma – aimed at mid to upper primary school children. The purpose of this proforma is to teach the child about planning out stories/essays.

How To Write A Biography – This is aimed at upper primary school students. It provides a framework for children to plan out a basic biography.
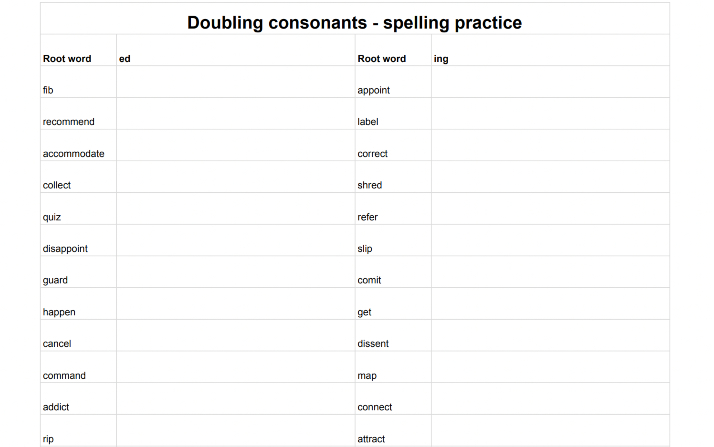
Spelling rules: doubling consonants – some rules and tips to help your child with when they need to double consonants.
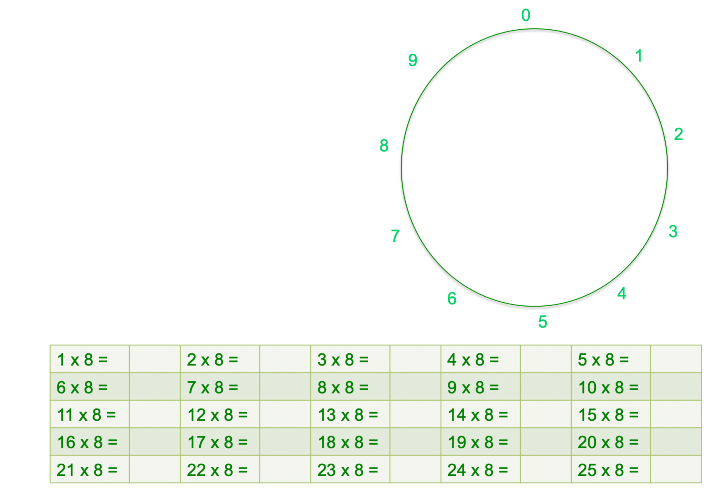
8 Times Tables – this activity teaches kids a simple trick to help them easily recall their 8 Times Tables.
Multiplication Grid – This is aimed at mid-primary school kids. A simple colouring-in activity that can help kids practice their timetables.
Do you have some tips and tools for helping kids with their homework to share? Please feel free to leave links below!
Home / Expert Articles / Child Behavior Problems / School & Homework
The Homework Battle: How to Get Children to Do Homework
By debbie pincus, ms lmhc.

Parents often feel it’s their job to get their kids to do well in school. Naturally, you might get anxious about this responsibility as a parent. You might also get nervous about your kids succeeding in life—and homework often becomes the focus of that concern.
But when parents feel it’s their responsibility to get their kids to achieve, they now need something from their children—they need them to do their homework and be a success. I believe this need puts you in a powerless position as a parent because your child doesn’t have to give you what you want.
The battle about homework becomes a battle over control. Your child starts fighting to have more control over the choices in their life, while you feel that your job as a parent is to be in control of things. So you both fight harder, and it turns into a war in your home.
Over the years, I’ve talked to many parents who are in the trenches with their kids, and I’ve seen firsthand that there are many creative ways kids rebel when it comes to schoolwork. Your child might forget to do their homework, do their homework but not hand it in, do it sloppily or carelessly, or not study properly for their test. These are just a few ways that kids try to hold onto the little control they have.
When this starts happening, parents feel more and more out of control, so they punish, nag, threaten, and argue. Some parents stop trying altogether to get their children to do homework. Or, and this is common, parents will over-function for their kids by doing the work for them.
Now the battle is in full swing: reactivity is heightened as anxiety is elevated—and homework gets lost in the shuffle. The hard truth for parents is that you cannot make your children do anything, let alone homework. But what you can do is to set limits, respect their individual choices, and help motivate them to motivate themselves.
You might be thinking to yourself, “You don’t know my child. I can’t motivate him to do anything.” Many parents tell me that their children are not motivated to do their work. I believe that children are motivated—they just may not be motivated the way you’d like them to be. Keep reading for some concrete tips to help you guide them in their work without having to nag, threaten, or fight with them.

Also, keep in mind that if you carry more of the worry, fear, disappointments, and concern than your child does about their work, ask yourself, “What’s wrong with this picture, and how did this happen?” Remember, as long as you carry their concerns, they don’t have to.
Stop the Nightly Fights
The way you can stop fighting with your kids over homework every night is to stop fighting with them tonight. Disengage from the dance. Choose some different steps or decide not to dance at all. Let homework stay where it belongs—between the teacher and the student. Stay focused on your job, which is to help your child do their job. Don’t do it for them.
If you feel frustrated, take a break from helping your child with homework. Your blood pressure on the rise is a no-win for everyone. Take five or ten minutes to calm down, and let your child do the same if you feel a storm brewing.
Create Structure Around Homework Time
Set limits around homework time. Here are a few possibilities that I’ve found to be effective with families:
- Homework is done at the same time each night.
- Homework is done in a public area of your house.
- If grades are failing or falling, take away screen time so your child can focus and have more time to concentrate on their work.
- Make it the rule that weekend activities don’t happen until work is completed. Homework comes first. As James Lehman says, “The weekend doesn’t begin until homework is done.”
Let Your Child Make Their Own Choices
I recommend that your child be free to make their own choices within the parameters you set around schoolwork. You need to back off a bit as a parent. Otherwise, you won’t be helping them with their responsibilities.
If you take too much control over the situation, it will backfire on you by turning into a power struggle. And believe me, you don’t want a power struggle over homework. I’ve seen many kids purposely do poorly just to show their parents who’s in charge. I’ve also seen children who complied to ease their parents’ anxiety, but these same kids never learned to think and make choices for themselves.
Let Your Child Own the Consequences of Their Choices
I’m a big believer in natural consequences when it comes to schoolwork. Within the structure you set up, your child has some choices. They can choose to do their homework or not. And they can choose to do it well and with effort or not. The natural consequences will come from their choices—if they don’t choose to do their work, their grades will drop.
When that happens, you can ask them some honest questions:
“Are you satisfied with how things are going?”
“What do you want to do about your grade situation?”
“How can I be helpful to you?”
Be careful not to be snarky or judgmental. Just ask the question honestly. Show honest concern and try not to show disappointment.
Intervene Without Taking Control
The expectation is that homework is done to the best of your child’s ability. When they stop making an effort, and you see their grades drop, that’s when you invite yourself in. You can say:
“It’s my job to help you do your job better. I’m going to help you set up a plan to help yourself, and I will check in to make sure you’re following it.”
Set up a plan with your child’s input to get them back on their feet. For example, the new rules might be that homework must be done in a public place in your home until they get their grades back up. You and your child might meet with the teacher to discuss disciplinary actions should their grades continue to drop.
In other words, you will help your child get back on track by putting a concrete plan in place. And when you see this change, you can step back out of it. But before that, your child is going to sit in a public space and you’re going to monitor their work.
You’re also checking in more. Depending on your child’s age, you’re making sure that things are checked off before they go out. You’re adding a half-hour of review time for their subjects every day. And then, each day after school, they’re checking with their teacher or going for some extra help.
Remember, this plan is not a punishment—it’s a practical way of helping your child to do their best.
“I Don’t Care about Bad Grades!”
Many parents will say that their kids just don’t care about their grades. My guess is that somewhere inside, they do care. “I don’t care” also becomes part of a power struggle.
In other words, your child is saying, “I’m not going to care because you can’t make me. You don’t own my life.” And they’re right. The truth is, you can’t make them care. Instead, focus on what helps their behavior improve. And focus more on their actions and less on their attitude because it’s the actions that matter the most.
Motivation Comes From Ownership
It’s important to understand that caring and motivation come from ownership. You can help your child be motivated by allowing them to own their life more.
So let them own their disappointment over their grades. Don’t feel it more than they do. Let them choose what they will do or not do about their homework and face the consequences of those choices. Now they will begin to feel ownership, which may lead to caring.
Let them figure out what motivates them, not have them motivated by fear of you. Help guide them, but don’t prevent them from feeling the real-life consequences of bad choices. Think of it this way: it’s better for your child to learn from those consequences at age ten by failing their grade and having to go to summer school than for them to learn at age 25 by losing their job.
When Your Child Has a Learning Disability
I want to note that it’s very important that you check to see that there are no other learning issues around your child’s refusal to do homework. If they’re having difficulty doing the work or are performing below grade-level expectations, they should be tested to rule out any learning disabilities or other concerns.
If there is a learning disability, your child may need more help. For example, some kids need a little more guidance; you may need to sit near your child and help a little more. You can still put structures into place depending on who your child is.

But be careful. Many times, kids with learning disabilities get way too much help and develop what psychologists call learned helplessness . Be sure you’re not over-functioning for your learning disabled child by doing their work for them or filling in answers when they’re capable of thinking through them themselves.
The Difference Between Guidance and Over-Functioning
Your child needs guidance from you, but understand that guidance does not mean doing their spelling homework for them. Rather, it’s helping them review their words. When you cross the line into over-functioning, you take on your child’s work and put their responsibilities on your shoulders. So you want to guide them by helping them edit their book report themselves or helping them take the time to review before a test. Those can be good ways of guiding your child, but anything more than that is taking too much ownership of their work.
If your child asks for help, you can coach them. Suggest that they speak with their teacher on how to be a good student and teach them those communication skills. In other words, show them how to help themselves. So you should not back off altogether—it’s that middle ground that you’re looking for. That’s why I think it’s essential to set up a structure. And within that structure, you expect your child to do what they have to do to be a good student.
Focus on Your Own Goals
When you start over-focusing on your child’s work, pause and think about your own goals and what do you need to get done to achieve those goals. Model your own persistence and perseverance to your child.
Believe In Your Child
I also tell parents to start believing in their children. Don’t keep looking at your child as a fragile creature who can’t do the work. I think we often come to the table with fear and doubt—we think if we don’t help our kids, they’re just not going to do it.
But as much as you say, “I’m just trying to help you,” what your child hears is, “You’re a failure; I don’t believe you can do it on your own.”
Instead, your message should be, “I know you can do it. And I believe in you enough to let you make your own choices and deal with the consequences.”
Related content: What Can I Do When My Child Refuses to Go to School? “My Child Refuses to Do Homework” — How to Stop the Nightly Struggle Over Schoolwork
For more information on the concept of learned helplessness in psychology and behavior, we recommend the following articles:
Psychology Today: Learned Helplessness
VeryWell Mind: What Is Learned Helplessness and Why Does it Happen?
About Debbie Pincus, MS LMHC
For more than 25 years, Debbie has offered compassionate and effective therapy and coaching, helping individuals, couples and parents to heal themselves and their relationships. Debbie is the creator of the Calm Parent AM & PM™ program and is also the author of numerous books for young people on interpersonal relations.
You must log in to leave a comment. Don't have an account? Create one for free!
Frank My daughter Nina just turned 8 (Feb 11). She does not like to do homework one bit. Her teacher gives her homework every day except Friday. She loves Fridays because she doesn't like homework. She always hides her homework under her bed, refuses to do her homework, and in the More morning she tells her teacher "I lost it last night and can't find it!". She feels homework is a waste of time, yes, we all feel that way, but poor Nina needs to learn that homework is important to help you stay smart. She needs to start doing homework. How can I make her 2nd-grade brain know that homework is actually good? Is there a way to make her love, love, LOVE homework? Let me know.
Rebecca Wolfenden, Parent Coach We appreciate you writing in to Empowering Parents and sharing your story. Because we are a website aimed at helping people become more effective parents, we are limited in the advice and suggestions we can give to those outside of a direct parenting role. In addition to the tips in More the article above, it may be helpful to look into local resources to help you develop a plan for addressing these particular issues with your cousins, such as their doctor or their teachers. We wish you the best going forward. Take care.
Rebecca Wolfenden, Parent Coach I hear you. Homework can be a challenging, frustrating time in many families even under the best of circumstances, so you are not alone. When kids struggle with a subject, it can be even more difficult to get assignments completed. Although you didn’t indicate that your daughter More has ADHD, you might find some helpful tips in Why School is Hard for Kids with ADHD—and How You Can Help . Author Anna Stewart outlines techniques that can be useful to help make homework more interesting for kids with a variety of learning challenges in this article. You might also consider checking in with your daughter’s teacher, as s/he might have some additional ideas for engaging your daughter in her homework. Please be sure to write back and let us know how things are going for you and your family. Take care.
So, after reading this I get to say…GREAT…You really do not know my child. We have done 100% of everything listed in this article. In the end, my son has utterly declared “I DON’T CARE, AND I DON’T NEED SCHOOL”. We have attempted a “reward” system as well, and that doesn’t work. He cares about 3 or 4 things. Nintendo DS, Lego, K’Nex, TV…all of those he has lost over the past year. Now he reads, ALL the time. Fine, but that doesn’t get his homework done. It also doesn’t get anything else he needs to do done. We’ve done “task boards”, we’ve done “Reward Systems”, we’ve done the “What is on your list to complete”. EVERYTHING is met with either a full fledged meltdown (think 2 year old…on the floor, kicking and screaming and crying). His IMMEDIATE response to ANYTHING that may interrupt him is “NO” or worse. If something doesn’t go his way directly he throws a fit INSTANTLY, even if the response is “Give me a second” it’s NOW OR I’M DESTROYING SOMETHING. He’s been suspended multiple times for his anger issues, and he’s only 10. Unfortuantely we have no family history as he was adopted from Russia. His “formal” diagnosis are ADHD and Anxiety. I’m thinking there is something much more going on. BTW: He did have an IQ test and that put him at 145 for Spacial and Geometric items, with a 136 for written and language. His composite was 139, which puts him in the genius category, but he’s failing across the board…because he refuses to do the work.
Interesting article and comments. Our son (6th grade) was early diagnosed as ADHD and for the first 3 years of elementary school several of his teachers suggested he might require special education. But then the school counseling staff did a workup and determined that his IQ is 161 and from that point forward his classroom antics were largely tolerated as “eccentric”. He has now moved to middle school (6th grade) and while his classroom participation seems to be satisfactory to all teachers, he has refused to do approximately 65% of his homework so far this school year. We have tried talking with him, reasoning with him, removing screen time, offering cash payments (which he lectures us as being unethical “bribes”), offering trips, offering hobbies and sporting events, and just about anything we can think of. Our other children have all been through the “talented and gifted” programs, but he simply refuses to participate in day-to-day school work. His fall report card was pretty much solid “F” or “O” grades. He may be bored out of his mind, or he may have some other issues. Unfortunately, home schooling is not an option, and neither is one of the $40,000 per year local private schools which may or may not be in a better position to deal with his approach to school. Do “learning centers” work for kids like this? Paying somebody else to force him to do his homework seems like a coward’s solution but I am nearly at the end of my rope! Thanks..
RebeccaW_ParentalSupport 12yokosuka Many parents struggle with staying calm when their child is acting out and screaming, so you are not alone. It tends to be effective to set up a structured time for kids to do their homework and study, and they can earn a privilege if they comply and meet More their responsibilities. What this might look like for your daughter is that if she studies, she can earn her phone that day. If she refuses, and chooses to argue or scream at you instead, then she doesn’t earn her phone that day and has another chance the next day. You can read more about this in https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/end-the-nightly-homework-struggle-5-homework-strategies-that-work-for-kids/. If you are also looking for resources to help you stay calm, I encourage you to check out our articles, blogs, and other resources on https://www.empoweringparents.com/article-categories/parenting-strategies-techniques/calm-parenting/. Please let us know if you have any additional questions. Take care.
Scott carcione
I’m sorry to hear about the challenges you are experiencing with your
son.I also hear the different
approaches you and your ex are taking toward parenting your son.While it would be ideal if you were able to
find common ground, and present a consistent, united response to your son’s
choices, in the end, you can only https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/parenting-after-divorce-9-ways-to-parent-on-your-own-terms/.At
this point, it might be useful to meet with the school to discuss how you can
work together to hold your son accountable for his actions, such as receiving a
poor grade if he refuses to do his work.Janet Lehman discusses this more in https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/when-your-child-has-problems-at-school-6-tips-for-parents/.Take care.
It can be so challenging when your child is acting out at school, yet does
not act that way at home.One strategy I
recommend is talking with your son at home about his behavior at school.During this conversation, I encourage you to
address his choices, and come up with a specific plan for what he can do differently
to follow the rules.I also recommend
working with his teachers, and discussing how you can assist them in helping
your son to follow the rules.You might
find additional useful tips in our article, https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/acting-out-in-school-when-your-child-is-the-class-troublemaker/.Please be sure to write back and let us know
how things are going for you and your son.Take care.
I hear you.It can be so challenging
when your young child is having outbursts like this.A lot of young children tend to act out and
have tantrums when they are experiencing a big transition, such as starting a
new school or adjusting to having a younger sibling, so you are not alone.Something that can be helpful is to set up
clear structure and expectations around homework, as Janet Lehman points out in
https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/my-child-refuses-to-do-homework-heres-how-to-stop-the-struggle/.I also encourage you to set aside some time
for you to have https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/attention-seeking-behavior-in-young-children-dos-and-donts-for-parents/ with your daughter as well.Please be sure to write back and let us know
how things are going for you and your family.Take care.
JoJoSuma I am having the exact same problem with my 9 year old son. His grades are quickly falling and I have no idea why or where to begin with helping him turn things around. When he applies himself he receives score of 80% or higher, and when he doesn't it clearly shows and he receives failing scores. He, too, says that he doesn't do or want to do the work because it is boring, or that he "Forgot" or "lost it". He has started to become a disruption to the class and at this rate I am afraid that he will have to repeat 5th grade. I am also a single parent so my frustration is at an all time high. You are not alone and I wish you and your family the best.
Thank you so much for these tips RebeccaW_ParentalSupport because I SERIOUSLY had nowhere to turn and no clue where to begin. I have cried many nights feeling like I was losing control. I will try your tips and see where things go from here.
It’s not uncommon
for kids to avoid doing homework, chores or other similar tasks. After
all, homework can be boring or difficult, and most people (both kids and adults
alike) tend to prefer activities which are enjoyable or fun. This does
not mean that you cannot address this with your daughter, though.
Something which can be helpful for many families is to set up a structured
homework time, and to require that your daughter complete her homework in order
to earn a privilege later on that evening. You can read about this, and
other tips, in https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/end-the-nightly-homework-struggle-5-homework-strategies-that-work-for-kids/.
Please be sure to write back and let us know how things are going for you and
your daughter. Take care.
Thestruggleisreal I'm just now signing up for these articles, I'm struggling with my 12 year and school work, she just doesn't want to do it, she has no care I'm world to do, she is driving me crazy over not doing, I hate to see her More fail, but I don't know what to do
FamilyMan888
I can hear how much your
daughter’s education means to you, and the additional difficulties you are
facing as a result of her learning disabilities. You make a great point
that you cannot force her to do her work, or get additional help, and I also
understand your concern that getting her teachers to “make” her do these things
at school might create more conflict there as well. As James Lehman
points out in his article, https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/stop-the-blame-game-how-to-teach-your-child-to-stop-making-excuses-and-start-taking-responsibility/, lowering your expectations for your daughter due to her
diagnosis is probably not going to be effective either. Instead, what you
might try is involving her in the https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/the-surprising-reason-for-bad-child-behavior-i-cant-solve-problems/, and asking her what she thinks she needs, and what she will do
differently, to meet classroom expectations. Please be sure to write back
and let us know how things are going for you and your family. Take care.
tvllpit Very effective to kids age of 5, 7, and 11 years old. Thank you for sharing your idea.
Thank you for
your question. You are correct that we recommend setting up a structured
time for kids to do homework, yet not getting into a power struggle with them
if they refuse to do their work during that time. It could be useful to
talk with your 11 year old about what makes it difficult to follow through with
doing homework at that time, and perhaps experimenting with doing homework at
another time to see if that works more effectively. In the end, though,
if your child is simply refusing to do the work, then we recommend giving a
consequence and avoiding a power struggle. Megan Devine details this
process more in her article, https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/end-the-nightly-homework-struggle-5-homework-strategies-that-work-for-kids/.
Please let us know if you have any additional questions. Take care.
jovi916 I'm a mother to a 10 year old 5th grader. Since 3rd grade I've been struggling with homework. That first year, I thought it was just lack of consistency since my children go between mine and dad's house. I tried setting some sort of system up with More the teacher to get back on track, but the teacher said it was the child's responsibility to get the hw done. This year has been esp. Difficult. He stopped doing hw, got an F, so I got on him. He stared turning half done work, but same grades so I still got on him. Grades went up, I loosened up, then he stopped with in school work. Now it's back to not turning anything in, even big projects and presentations. He had never really been allowed to watch tv, but now it's a definite no, I took his Legos away, took him out of sports. Nothing is working. He's basically sitting at the table every night, and all weekend long in order to get caught up with missing assignments. I'm worried, and next year he'll be in middle school. I try setting an example by studying in front of him. My daughter just does her homework and gets good grades. Idk what to do.
I can hear your concern. Academic achievement is important
to most parents and when your children seem to be struggling to complete their
work and get good grades, it can be distressing. Ultimately, your childrens’
school work and grades are their responsibility. You shouldn’t have to quit
your own studies in order to help them improve theirs. The above article gives
some great tips for helping motivate your children to complete their homework.
We do have a couple other articles you may also find useful: https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/10-ways-to-motivate-your-child-to-do-better-in-school/ & https://www.empoweringparents.com/article/sinking-fast-at-school-how-to-help-your-child-stay-afloat/. We appreciate you
writing in and hope you find the information useful. Take care.
RNM I have the exact same issues with my 8 year old. It makes me feel like I'm doing something wrong. He's a smart kid, he just doesn't seem to care to do his homework let alone if he gets a bad grade as a result. He hates reading, but does More very well in spelling and science. Homework is an issue nightly and the teacher pulled me aside today to tell me again how much he talks in class and that now he isn't writing down his assignments and is missing 3 assignments this week. SMH, I don't know what to do anymore other than to coach him (some more) and take away basketball if he doesn't do his homework.
What? "Let homework stay where it belongs—between the teacher and the student. Refuse to get pulled in by the school.." I do not see the logic or benefit of this advice. Homework, by definition, is the responsibility of the student and parent (NOT the teacher). The teacher does not live at the student's home or run the house.
In my opinion, the lack of parental involvement with academics often causes the low student performance evident across the U.S. I do not agree with advocating for even LESS parental involvement.
I completely agree with you. Parental, or adult, engagement at home can be a deal-maker/breaker when it comes to student performance. I subscribe to theories that differ from the author's.
First, if an adult is involved with the child and his activities, then the child will commonly react with "hey, somebody cares about me" leading to an increased sense of self-worth. A sense of caring about one's-self leads to caring about grades and other socially acceptable behaviors (Maslow).
Secondly, I am a FIRM believer in the techniques of behavior modification through positive reinforcement (Karen Pryor). It's up to an invested adult to determine what motivates the student and use those motivators to shape and reinforce desirable behavior such as daily homework completion. A classroom teacher has too many students and too little time to apply this theory.
Letting a child sink or swim by himself is a bad idea. Children have only one childhood; there are no do-overs.
And yes, children are work.
Many experience similar feelings of being at fault when
their child fails, so, you’re not alone. Truth of the matter is, allowing your
child to experience natural consequences of their actions by allowing them to
fail gives them the opportunity to look at themselves and change their
behavior. We have a couple articles I think you may find helpful: When You Should Let Your Child Fail: The Benefits of Natural Consequences & 5 Natural Consequences You Should Let Your Child Face . Good luck to you and
your family moving forward. Take care.
hao hao It is so true, we can't control our children's home. It is their responsibility. But they don't care it. What can we do it?
indusreepradeep
How great it is that you want to help your brother be more
productive with his homework. He’s lucky to have a sibling who cares about him
and wants him to be successful. Because we are a website aimed at helping
parents develop better ways of managing acting out behavior, we are limited in
the advice we can offer you as his sibling. There is a website that may be able
to offer you some suggestions. http://www.yourlifeyourvoice.org/
is a website aimed at helping teens and young adults figure out ways of dealing
with challenges they may be facing in their lives. They offer several ways of
getting support, such as by e-mail or text, through an online forum and chat,
and also a call in helpline. You can check out what they have to offer at http://www.yourlifeyourvoice.org/. Good luck
to you and your family moving forward. Take care.
Kathleenann indusreepradeep
Thank you so much for your humble support....
It sounds like you have done a lot
of work to try to help your daughter achieve her educational goals, and it’s
normal to feel frustrated when she does not seem to be putting in the same
amount of effort. It can be useful to keep your focus on whether your
daughter is doing her work, and to keep that separate from whether she “cares”
about doing her work. Ultimately, it is up to your daughter to do her
work, regardless of how she appears to feel about it. To that end, we
recommend working with the various local supports you have in place, such as
her therapists and others on her IEP team, to talk about what could be useful
to motivate your daughter to do her school work. Because individuals with
autism can vary greatly with their abilities, it’s going to be more effective
to work closely with the professionals who are familiar with your daughter’s
strengths and level of functioning in order to develop a plan to address this
issue. Thank you so much for writing in; we wish you and your daughter
all the best as you continue to address her difficulties with school.
is there a blog for parents that went to Therapeutic boarding schooling for their adolescent?
Responses to questions posted on EmpoweringParents.com are not intended to replace qualified medical or mental health assessments. We cannot diagnose disorders or offer recommendations on which treatment plan is best for your family. Please seek the support of local resources as needed. If you need immediate assistance, or if you and your family are in crisis, please contact a qualified mental health provider in your area, or contact your statewide crisis hotline.
We value your opinions and encourage you to add your comments to this discussion. We ask that you refrain from discussing topics of a political or religious nature. Unfortunately, it's not possible for us to respond to every question posted on our website.
- 1. What to Do When Your Child or Teen is Suspended or Expelled From School
- 2. "My Child Refuses to Do Homework" — How to Stop the Nightly Struggle Over Schoolwork
- 3. Acting Out in School: When Your Child is the Class Troublemaker
- 4. Young Kids in School: Help for the Top 4 Behavior Problems
- 5. When Your Child Has Problems at School: 6 Tips for Parents
- 140,000+ Subscribers Subscribe
- 50,000+ Fans Follow
- 10,000+ Followers Follow
- 6,000+ Followers Follow
Disrespect... defiance... backtalk... lack of motivation...
Frustrated and exhausted by your child's behavior?
Get your FREE Personal Parenting Plan today.
Does your child exhibit angry outbursts , such as tantrums, lashing out, punching walls, and throwing things?
Would you like to learn about how to use consequences more effectively?
Backtalk... complaints... arguments... attitude... just plain ignoring you
Do you struggle with disrespect or verbal abuse from your child?
Has your child been diagnosed with oppositional defiant disorder (ODD)?
Or does your child exhibit a consistent and severe pattern of anger, irritability, arguing, defiance, and vindictiveness toward you or other authority figures?
Intimidation... aggression... physical abuse and violence ...
Are you concerned that your child may physically hurt you or others?
You must select at least one category to create your Personal Parenting Plan:
We're just about finished! Create a secure account with Empowering Parents to access your Personal Parenting Plan.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Helping your child with homework isn't the same as doing your child's homework. You can make suggestions, but your child must do the work for meaningful learning to take place. Have patience ...
Helping kids how to do homework can also mean modeling the behavior to them. This is a parenting hack that most parents fail to practice. It can be a good motivating factor for the kids if you do chores like budgeting or computing household expenses at the same time they do their assignments. This is one indirect way to teach kids how to do homework.
Many children who are not motivated by the enjoyment of doing homework are motivated by the high grade they hope to earn as a result of doing a quality job. Thus, the grade is an incentive, motivating the child to do homework with care and in a timely manner. For children who are not motivated by grades, parents will need to look for other rewards to help them get through their nightly chores.
Now that school is back in full swing, many households are dealing with how to handle homework. Helping your child be successful at homework is very important because it is a very critical part of children's academic success. Homework helps children in several ways, including: continues learning after the school day; teaches responsibility ...
Most kids struggle with homework from time to time. But kids who learn and think differently may struggle more than others. Understanding the homework challenges your child faces can help you reduce stress and avoid battles. Here are some common homework challenges and tips to help. The challenge: Rushing through homework
Don't Help Your Kids With Homework. Focus on prioritization and process, not the assignment itself. By Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer. Lucy Jones. March 2, 2021. Share. Save.
Where Parents Help Their Kids With Homework by Niall McCarthy data journalist at Statista. According to recent statistics, U.S. parents spend about 6.2 hours a week helping their kids with homework. This substantial investment of time underscores parents' critical role in their children's educational journey. Providing the right support ...
It must be the time of year for it because recently many readers have asked questions on how to help kids with their homework. With only two kids in school now (year 8 and year 10) I really don't do a lot of helping with homework. I actually don't do anything at all with the year 10 child other than answer questions if he has any and remind ...
Here's why kids resist doing homework and what you can do to help motivate them. Go. Our Programs Articles Behavior Charts FAQ. About Us Contact Us Join Our Mailing List (0) ... If you feel frustrated, take a break from helping your child with homework. Your blood pressure on the rise is a no-win for everyone. Take five or ten minutes to calm ...
Parents will not do homework for their children. This message lets children know that the parent role is to encourage and to help them get unstuck, while at the same time communicating that homework is designed to help children master skills that parents already attained. Helping Children at Home and School III | S2H11-1