- Knowledge Base
- Get started
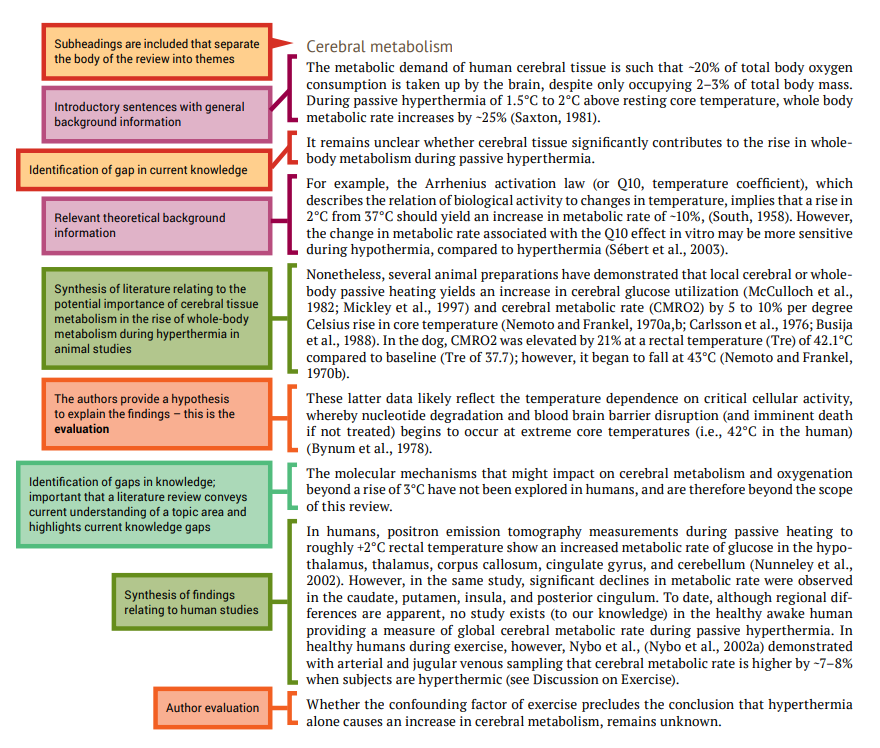
Top 20 Literature Review Examples
Struggling with writing a literature review? Our guide provides multiple examples of literature reviews across different fields to help you understand the structure and nuances of this crucial component of research.
If you’re new to academic writing, you may find the idea of writing a literature review daunting. A literature review is a critical component of most research papers, theses, and dissertations. It involves summarizing, analyzing, and synthesizing existing research to provide a foundation for your own work. To help you understand this process better, we've compiled multiple examples of literature reviews from different fields and contexts. This guide will not only show you what a literature review looks like but will also provide tips for writing your own.

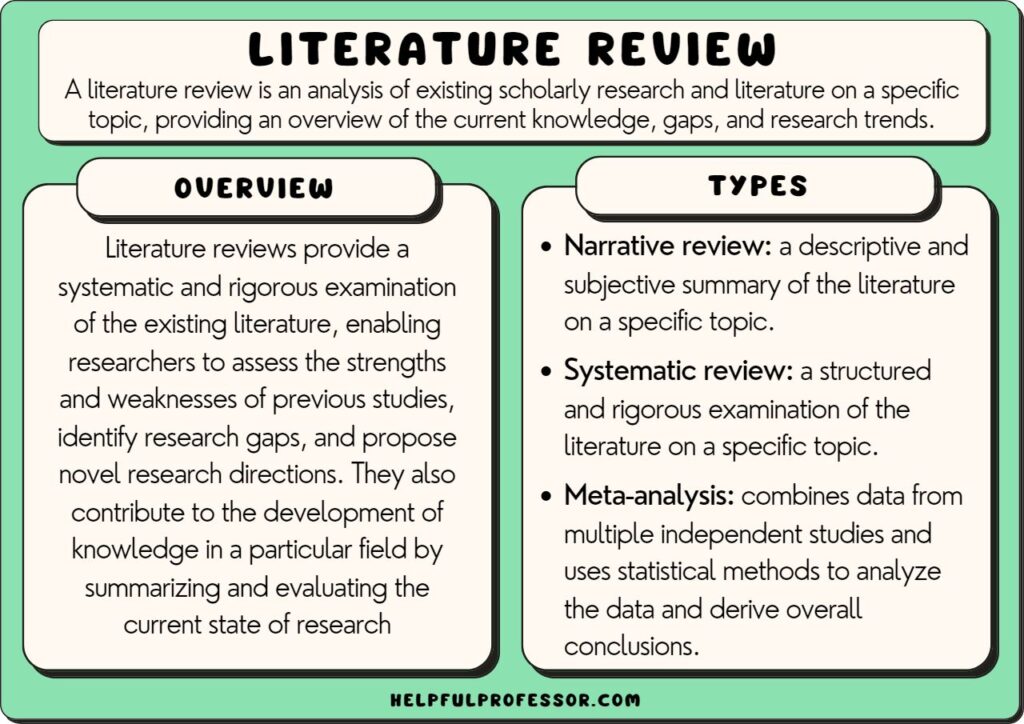
What Is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a comprehensive overview of the existing research on a particular topic. It typically surveys scholarly articles, books, and other credible sources to identify gaps, trends, and key arguments in the field. The purpose of a literature review is to demonstrate your understanding of the topic and to position your own research within the context of existing scholarship. Unlike a simple summary, a literature review provides critical analysis, demonstrates relationships between works, and often identifies areas for future research.

A good literature review not only synthesizes current research but also provides a critical framework that justifies the necessity of your research project. It’s about engaging deeply with the literature to show that you understand the complexities and nuances of your field. This engagement helps lay a solid foundation for your research objectives, creating a context that supports your hypothesis or research questions.
Why Are Literature Reviews Important?
Literature reviews are crucial because they provide context for your own research, showing where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. They help identify what has already been discovered, what questions remain unanswered, and how your research can contribute to the field. By synthesizing previous work, you lay the groundwork for the originality and significance of your own study.
Moreover, a literature review helps to establish credibility. It demonstrates that you are well-versed in the relevant literature and that you are capable of understanding and analyzing existing research critically. This is particularly important for convincing your audience—whether they are your professors, peers, or other researchers—of the validity and value of your work. A well-constructed literature review highlights your scholarly diligence and sets the stage for your contribution to the ongoing academic conversation.
Example 1: Literature Review in Psychology
Consider a literature review for a research paper on the impact of mindfulness on reducing anxiety. In this example, the author starts by summarizing foundational research on mindfulness practices, citing key studies that show how mindfulness reduces stress. Then, they move on to analyze recent findings that specifically target anxiety disorders. The author identifies a gap in the research: while there are numerous studies on general stress reduction, fewer studies focus on mindfulness and its impact on different types of anxiety. This literature review effectively highlights both well-established findings and areas where further research is needed.
The author also categorizes the literature into themes—mindfulness as a general wellness practice versus mindfulness targeted specifically at clinical anxiety. This thematic organization helps readers quickly understand the nuances between different applications of mindfulness. Furthermore, the author discusses methodological differences between studies, such as sample size and duration of mindfulness interventions, which adds depth to the analysis and provides a more rounded understanding of the current research landscape.
Example 2: Literature Review in Business Management
A literature review in business management might focus on leadership styles and their impact on employee productivity. The author begins by outlining different leadership theories such as transformational, transactional, and servant leadership. The review then examines existing studies that link these leadership styles to employee satisfaction and productivity metrics. A critical analysis is provided, suggesting that while transformational leadership is often associated with high productivity, there is still debate about its effectiveness across different cultural contexts. The author uses this debate as a basis for proposing their own research question, which seeks to explore the relationship between leadership styles and employee productivity in non-Western countries.
In addition, the author includes a subsection on leadership styles in the digital age, discussing how virtual teams and remote work environments challenge traditional leadership paradigms. This perspective helps highlight the evolving nature of leadership and adds an extra layer of relevance by connecting classical leadership theories to modern organizational challenges. The author also identifies inconsistencies in the literature, such as conflicting findings regarding which style is most effective in high-stress environments, thus setting up the importance of further research.
Example 3: Literature Review in Medicine
For a literature review in the field of medicine, let’s look at a study focused on the effectiveness of telemedicine in rural healthcare settings. The author summarizes existing literature on telemedicine, including studies that highlight its benefits—such as increased access to healthcare and cost efficiency. The review also presents findings that discuss the challenges of telemedicine, such as technology barriers and privacy concerns. The author synthesizes these perspectives to demonstrate that while telemedicine offers promise for rural healthcare, further studies are needed to understand its long-term impact on patient outcomes. This literature review is structured to identify both the strengths and challenges in current research, setting the stage for further exploration.
Additionally, the author discusses the role of policy and government initiatives in supporting telemedicine, providing context on how regulations affect the adoption and efficacy of telemedicine practices. By incorporating this broader socio-political context, the author adds depth to the analysis, emphasizing that the success of telemedicine is not just about technology but also about institutional and regulatory frameworks. The literature review ends with a section on future research directions, suggesting that longitudinal studies are necessary to assess patient outcomes over extended periods, which is a critical gap identified in the current body of research.
Example 4: Literature Review in Education
In an education-based literature review, the focus might be on the impact of technology in the classroom. The author starts by covering historical perspectives on educational technology, then moves on to discuss the evolution of tools like smartboards, learning management systems, and tablets. A significant part of the review involves analyzing the effectiveness of these technologies on student learning outcomes. The author contrasts studies that show positive results with those that point out limitations, such as reduced social interaction and technology dependence. By presenting both sides, the author provides a balanced view, ultimately highlighting the need for more nuanced research into the types of technology that contribute most effectively to different learning environments.
The author also categorizes the literature by age groups—examining the impact of technology in early childhood education, primary school, and higher education. This breakdown allows for a more targeted analysis, as the impact of technology can vary significantly depending on the developmental stage of the students. The author also integrates perspectives from educators, students, and parents, providing a comprehensive look at how different stakeholders view educational technology, thereby enriching the analysis and pointing out areas for further inquiry.
Example 5: Literature Review in Environmental Science
A literature review in environmental science might explore the impact of climate change on coastal ecosystems. The author begins by summarizing foundational studies on climate change, highlighting the major effects on sea levels and temperature changes. Then, they analyze specific studies focusing on coastal regions, pointing out the increased frequency of extreme weather events and their consequences on marine biodiversity. The author categorizes the studies into subtopics such as coral reef degradation, changes in fish populations, and the socio-economic impacts on coastal communities. The literature review emphasizes the importance of both mitigation and adaptation strategies and calls for more research into localized solutions to climate impacts.
Example 6: Literature Review in Sociology
In sociology, a literature review might examine the relationship between social media use and mental health among teenagers. The author starts by summarizing studies that explore different aspects of social media, including both its positive impacts (e.g., social connectedness) and negative outcomes (e.g., anxiety and depression). The review synthesizes findings by categorizing studies into those that focus on frequency of use, type of content consumed, and peer interactions. The author critically discusses conflicting results—some studies show positive social outcomes, while others link heavy social media use to increased feelings of loneliness. By highlighting these inconsistencies, the author sets up a strong case for their research question, which seeks to clarify under what conditions social media has a positive or negative impact.
Example 7: Literature Review in Political Science
A literature review in political science could focus on the effectiveness of international sanctions. The author starts by discussing the historical context of sanctions, reviewing examples from major international conflicts. The literature is then organized by theme, such as economic sanctions, diplomatic sanctions, and their impact on civilian populations. The author identifies the challenges of measuring the effectiveness of sanctions due to political biases and varying methodologies. The review points out that while sanctions can pressure governments, they often have unintended consequences for ordinary citizens, leading to a discussion on the ethical implications. The author uses this to propose further research into alternative diplomatic tools.
Example 8: Literature Review in Public Health
In public health, a literature review might examine the effectiveness of vaccination campaigns in increasing immunization rates in underserved populations. The author begins by summarizing foundational public health theories related to immunization and community health. They then present studies on specific vaccination campaigns, noting differences in approaches such as door-to-door outreach versus community center initiatives. The review also considers barriers like vaccine misinformation, accessibility issues, and socio-cultural resistance. The author identifies successful strategies, such as involving local community leaders, and suggests areas for further research, including the role of digital platforms in spreading accurate health information.
Example 9: Literature Review in Economics
A literature review in economics might explore the concept of universal basic income (UBI) and its potential impact on poverty alleviation. The author starts by summarizing theoretical frameworks behind UBI, including Keynesian and libertarian perspectives. Then, they evaluate empirical studies from different countries that have piloted UBI programs, such as Finland and Kenya. The review highlights the positive outcomes, such as reduced financial stress and increased entrepreneurship, but also addresses concerns about inflation and work disincentives. The author identifies a gap in the literature regarding the long-term socio-economic effects of UBI and suggests that further longitudinal studies are needed.
Example 10: Literature Review in Engineering
In an engineering context, a literature review might focus on advancements in renewable energy storage solutions. The author reviews various technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries, hydrogen fuel cells, and thermal storage. Each section provides an overview of the technology, its current applications, and challenges. The author also compares the efficiency and scalability of each solution, pointing out the trade-offs in terms of cost, safety, and environmental impact. By highlighting the need for improved energy storage to support renewable power grids, the author makes a case for future research into hybrid storage systems that combine the strengths of multiple technologies.
Example 11: Literature Review in Anthropology
A literature review in anthropology might investigate the cultural implications of globalization on indigenous communities. The author begins by reviewing early theories of globalization and their predicted effects on cultural identity. Then, they present specific case studies from various regions, such as the Amazon and Southeast Asia, to illustrate the real-world impact on traditional practices and languages. The review highlights both the resilience of certain communities and the challenges they face, such as loss of land and cultural commodification. The author concludes by calling for more participatory research methods that involve indigenous voices directly.
Example 12: Literature Review in Linguistics
In a linguistics literature review, the focus might be on language acquisition in bilingual children. The author summarizes foundational research in language development theories, such as Chomsky's theory of innate grammar versus behaviorist models. They then present recent studies that examine how bilingual children navigate multiple languages at home and in school settings. The author highlights differences in cognitive development, social factors, and the effects of simultaneous versus sequential bilingualism. This review points out gaps in the research, particularly the need for longitudinal studies to understand long-term academic outcomes for bilingual children.
Example 13: Literature Review in Environmental Policy
A literature review in environmental policy could focus on carbon pricing mechanisms as a tool for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The author begins by reviewing economic theories related to carbon taxes and cap-and-trade systems. They then analyze real-world examples, such as carbon pricing initiatives in the European Union and British Columbia. The review discusses both successes and challenges, including economic impacts on industries and the effectiveness in reducing emissions. The author suggests that future research should explore hybrid models that combine regulatory and market-based approaches to improve policy outcomes.
Example 14: Literature Review in Computer Science
In computer science, a literature review might explore the evolution of machine learning algorithms for natural language processing (NLP). The author starts by summarizing the development of early NLP models, such as rule-based systems, and transitions into modern deep learning approaches. The review categorizes algorithms into supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning methods, analyzing their respective advantages and limitations. The author also addresses ethical concerns regarding biases in language models and calls for more research into fair and transparent AI development practices.
Example 15: Literature Review in Urban Studies
A literature review in urban studies might explore the phenomenon of urban gentrification and its impact on local communities. The author begins by providing a historical overview of gentrification and reviewing early theoretical frameworks, such as rent gap theory. Then, they present case studies from cities like New York, London, and Berlin to highlight the social and economic effects on displaced residents. The author contrasts perspectives that see gentrification as a driver of economic revitalization with those that view it as a source of inequality. The review concludes by identifying a need for more community-centered research to understand the long-term social implications of urban redevelopment.
Example 16: Literature Review in Philosophy
A literature review in philosophy could focus on ethical theories related to artificial intelligence. The author begins by outlining classical ethical frameworks, such as utilitarianism, deontology, and virtue ethics, and discusses how these theories apply to AI. The review then examines contemporary debates, such as the moral implications of autonomous decision-making and the responsibilities of AI developers. By exploring both philosophical arguments and practical considerations, the author highlights gaps in current ethical guidelines and calls for interdisciplinary research to address the unique challenges posed by AI.
Example 17: Literature Review in Criminal Justice
A literature review in criminal justice could focus on the effectiveness of rehabilitation programs for reducing recidivism among offenders. The author begins by presenting an overview of different rehabilitation strategies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), vocational training, and restorative justice programs. The review categorizes studies by the type of offender, such as juvenile versus adult, and discusses the varying success rates. The author identifies a gap in longitudinal studies examining the long-term success of rehabilitation, proposing future research to explore how these programs impact offenders years after release.
Example 18: Literature Review in Nutrition Science
A literature review in nutrition science might examine the role of plant-based diets in preventing chronic diseases. The author starts by summarizing foundational research on the health benefits of plant-based eating, such as reduced risks of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. The review then discusses recent studies comparing plant-based diets to omnivorous diets in terms of nutrient intake and overall health outcomes. The author highlights methodological variations, such as differences in dietary definitions, and suggests further research into the role of supplementation in plant-based diets to ensure nutritional adequacy.
Example 19: Literature Review in Marketing
A literature review in marketing might explore the impact of influencer endorsements on consumer purchasing behavior. The author begins by reviewing early studies on celebrity endorsements and their influence on brand perception. The review then transitions to modern social media influencers, comparing their effectiveness to that of traditional celebrities. The author categorizes studies based on different factors, such as the type of product, audience demographics, and platform used. The review points out a gap in the literature related to the ethical implications of influencer marketing, suggesting further research into transparency and consumer trust.
Example 20: Literature Review in History
In a history-based literature review, the focus could be on the causes of the Industrial Revolution. The author starts by reviewing various theories, including economic, technological, and cultural explanations. The literature is organized by different schools of thought, such as Marxist interpretations, which emphasize economic factors, versus cultural historians who focus on shifts in societal values. The author also presents case studies from different countries, comparing how the Industrial Revolution unfolded in Britain, France, and Germany. This comparative analysis reveals inconsistencies in existing theories and suggests a need for a more integrated approach to understanding the multiple causes of this transformative period.
Tips for Writing Your Own Literature Review
- Define Your Scope : Clearly define the scope of your literature review. What are you trying to cover, and what are the boundaries of your topic? Be specific to avoid overwhelming yourself with too much material.
- Organize by Theme : Instead of summarizing each source chronologically, group your literature by themes or trends. This helps to create a more cohesive narrative and makes it easier for readers to follow your argument.
- Synthesize, Don’t Summarize : Go beyond simply summarizing the studies—synthesize them by comparing, contrasting, and connecting different sources. Show how the research interacts, where it agrees, and where it diverges.
- Highlight Gaps : Identify areas where more research is needed. This shows your understanding of the field and justifies your own research. Pointing out gaps also demonstrates that your research has a unique contribution to make.
- Use Credible Sources : Always use reputable academic sources, such as peer-reviewed journal articles, books by experts in the field, and official reports. Credible sources strengthen your argument and add validity to your review.
- Be Critical, Not Just Descriptive : A good literature review involves critical analysis. Question methodologies, identify biases, and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. This critical approach will make your review more engaging and informative.
- Keep It Organized : Use headings and subheadings to keep your literature review well-structured. A well-organized review is easier to follow and helps emphasize the relationships between different pieces of literature.
- Take Notes and Summarize Key Points : During the research phase, make detailed notes and summarize the key findings of each source. This will make it easier to identify connections and gaps in the literature when you start writing.
- Use Direct Quotes Sparingly : While quoting sources can be effective, use direct quotes sparingly. Instead, paraphrase the content and provide your interpretation or analysis. This will make your literature review more original and will better showcase your understanding of the material.
- Incorporate Contrasting Perspectives : Including differing viewpoints makes your literature review more comprehensive. When appropriate, address contrasting theories or studies that challenge your own perspective. Analyzing these opposing views will add depth to your review and demonstrate critical thinking.
- Establish Relationships Between Studies : Highlight connections between studies by showing how one piece of research builds on or refines another. This helps create a storyline for your literature review and illustrates the development of knowledge within your topic.
- Limit Scope Creep : It's easy to get sidetracked while researching. Stay focused on your specific research questions and avoid expanding your scope too broadly. Limiting scope creep ensures that your literature review remains concise and coherent.
- Summarize Each Section : At the end of each major section, provide a brief summary that ties together the points you’ve discussed. This will help to reinforce the main themes and make it easier for readers to follow your overall argument.
- Use Visual Aids Where Applicable : If possible, include tables, charts, or concept maps to organize and summarize key findings visually. This can make your literature review more engaging and help convey complex relationships more clearly.
- Revise and Edit Thoroughly : Writing a literature review is an iterative process. After your first draft, revisit your review to refine the flow, strengthen connections, and improve clarity. Pay attention to consistency in your writing style and ensure that each section logically builds on the previous one.
Final Thoughts
A well-written literature review is more than just a summary of existing work—it’s a critical analysis that provides context for your research and helps position it within the broader academic landscape. By examining these examples and understanding how they are structured, you can gain valuable insights into how to write a literature review that is both informative and engaging. Remember, the key is to create a narrative that ties together different pieces of research while demonstrating your unique contribution to the topic.
Whether you are writing a literature review in psychology, business, medicine, or education, these examples should give you a solid foundation. The more practice you get in analyzing and synthesizing existing research, the better equipped you will be to produce high-quality academic work. Always aim for depth, critical engagement, and clarity, as these elements will make your literature review a strong backbone for your research.
Sourcely weekly newsletters
Cut through the AI noise with a focus on Students! Subscribe for 3 Student AI tools every week to accelerate your academic career.
Join Sourcely weekly newsletters
Ready to get started.
Start today and explore all features with up to 300 characters included. No commitment needed — experience the full potential risk-free!
Check out our other products
Discover cutting-edge research with arXivPulse: Your AI-powered gateway to scientific papers
Don't stress about deadlines. Write better with Yomu and simplify your academic life.
Welcome to Sourcely! Our AI-powered source finding tool is built by students for students, and this approach allows us to create a tool that truly understands the needs of the academic community. Our student perspective also enables us to stay up-to-date with the latest research and trends, and our collaborative approach ensures that our tool is continually improving and evolving.
- Refund Policy
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Friends of Sourcely
- ArXiv Pulse
- Semantic Reader
- AI Tools Inc
- AI Tools Boot Camp for Researchers
© 2024 Sourcely
15 Literature Review Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal . They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Ideally, once you have completed your literature review, you will be able to identify how your research project can build upon and extend existing knowledge in your area of study.
Generally, for my undergraduate research students, I recommend a narrative review, where themes can be generated in order for the students to develop sufficient understanding of the topic so they can build upon the themes using unique methods or novel research questions.
If you’re in the process of writing a literature review, I have developed a literature review template for you to use – it’s a huge time-saver and walks you through how to write a literature review step-by-step:
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review.
Literature Review Examples
For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics.
1. Narrative Review Examples
Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
It often includes both qualitative and quantitative studies and may cover a wide range of years.
The narrative review’s purpose is to identify commonalities, gaps, and contradictions in the literature .
I recommend to my students that they should gather their studies together, take notes on each study, then try to group them by themes that form the basis for the review (see my step-by-step instructions at the end of the article).
Example Study
Title: Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations
Citation: Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.12686
Overview: This narrative review analyzed themes emerging from 69 articles about communication in healthcare contexts. Five key themes were found in the literature: poor communication can lead to various negative outcomes, discontinuity of care, compromise of patient safety, patient dissatisfaction, and inefficient use of resources. After presenting the key themes, the authors recommend that practitioners need to approach healthcare communication in a more structured way, such as by ensuring there is a clear understanding of who is in charge of ensuring effective communication in clinical settings.
Other Examples
- Burnout in United States Healthcare Professionals: A Narrative Review (Reith, 2018) – read here
- Examining the Presence, Consequences, and Reduction of Implicit Bias in Health Care: A Narrative Review (Zestcott, Blair & Stone, 2016) – read here
- A Narrative Review of School-Based Physical Activity for Enhancing Cognition and Learning (Mavilidi et al., 2018) – read here
- A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents (Dyrbye & Shanafelt, 2015) – read here
2. Systematic Review Examples
This type of literature review is more structured and rigorous than a narrative review. It involves a detailed and comprehensive plan and search strategy derived from a set of specified research questions.
The key way you’d know a systematic review compared to a narrative review is in the methodology: the systematic review will likely have a very clear criteria for how the studies were collected, and clear explanations of exclusion/inclusion criteria.
The goal is to gather the maximum amount of valid literature on the topic, filter out invalid or low-quality reviews, and minimize bias. Ideally, this will provide more reliable findings, leading to higher-quality conclusions and recommendations for further research.
You may note from the examples below that the ‘method’ sections in systematic reviews tend to be much more explicit, often noting rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria and exact keywords used in searches.
Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review
Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422441730122X
Overview: This systematic review included 72 studies of food naturalness to explore trends in the literature about its importance for consumers. Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. Studies were included if they examined consumers’ preference for food naturalness and contained empirical data. The authors found that the literature lacks clarity about how naturalness is defined and measured, but also found that food consumption is significantly influenced by perceived naturalness of goods.
- A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018 (Martin, Sun & Westine, 2020) – read here
- Where Is Current Research on Blockchain Technology? (Yli-Huumo et al., 2016) – read here
- Universities—industry collaboration: A systematic review (Ankrah & Al-Tabbaa, 2015) – read here
- Internet of Things Applications: A Systematic Review (Asghari, Rahmani & Javadi, 2019) – read here
3. Meta-analysis
This is a type of systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine and summarize the results of several studies.
Due to its robust methodology, a meta-analysis is often considered the ‘gold standard’ of secondary research , as it provides a more precise estimate of a treatment effect than any individual study contributing to the pooled analysis.
Furthermore, by aggregating data from a range of studies, a meta-analysis can identify patterns, disagreements, or other interesting relationships that may have been hidden in individual studies.
This helps to enhance the generalizability of findings, making the conclusions drawn from a meta-analysis particularly powerful and informative for policy and practice.
Title: Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Meta-Meta-Analysis
Citation: Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Source: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060386
O verview: This study examines the relationship between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Researchers conducted a systematic search of meta-analyses and reviewed several databases, collecting 100 primary studies and five meta-analyses to analyze the connection between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. They find that the literature compellingly demonstrates that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels significantly influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) – read here
- How Much Does Education Improve Intelligence? A Meta-Analysis (Ritchie & Tucker-Drob, 2018) – read here
- A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling (Geiger et al., 2019) – read here
- Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits (Patterson, Chung & Swan, 2014) – read here
Other Types of Reviews
- Scoping Review: This type of review is used to map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects in their own right, or as a precursor to a systematic review.
- Rapid Review: This type of review accelerates the systematic review process in order to produce information in a timely manner. This is achieved by simplifying or omitting stages of the systematic review process.
- Integrative Review: This review method is more inclusive than others, allowing for the simultaneous inclusion of experimental and non-experimental research. The goal is to more comprehensively understand a particular phenomenon.
- Critical Review: This is similar to a narrative review but requires a robust understanding of both the subject and the existing literature. In a critical review, the reviewer not only summarizes the existing literature, but also evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. This is common in the social sciences and humanities .
- State-of-the-Art Review: This considers the current level of advancement in a field or topic and makes recommendations for future research directions. This type of review is common in technological and scientific fields but can be applied to any discipline.
How to Write a Narrative Review (Tips for Undergrad Students)
Most undergraduate students conducting a capstone research project will be writing narrative reviews. Below is a five-step process for conducting a simple review of the literature for your project.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use scholarly databases related to your field of study, provided by your university library, along with appropriate search terms to identify key scholarly articles that have been published on your topic.
- Evaluate and Select Sources: Filter the source list by selecting studies that are directly relevant and of sufficient quality, considering factors like credibility , objectivity, accuracy, and validity.
- Analyze and Synthesize: Review each source and summarize the main arguments in one paragraph (or more, for postgrad). Keep these summaries in a table.
- Identify Themes: With all studies summarized, group studies that share common themes, such as studies that have similar findings or methodologies.
- Write the Review: Write your review based upon the themes or subtopics you have identified. Give a thorough overview of each theme, integrating source data, and conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge then suggestions for future research based upon your evaluation of what is lacking in the literature.
Literature reviews don’t have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong degree of comprehension of academic studies. But it can be feasibly done through following a structured approach to data collection and analysis. With my undergraduate research students (who tend to conduct small-scale qualitative studies ), I encourage them to conduct a narrative literature review whereby they can identify key themes in the literature. Within each theme, students can critique key studies and their strengths and limitations , in order to get a lay of the land and come to a point where they can identify ways to contribute new insights to the existing academic conversation on their topic.
Ankrah, S., & Omar, A. T. (2015). Universities–industry collaboration: A systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 31(3), 387-408.
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A. M., & Javadi, H. H. S. (2019). Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Computer Networks , 148 , 241-261.
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical education , 50 (1), 132-149.
Geiger, J. L., Steg, L., Van Der Werff, E., & Ünal, A. B. (2019). A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. Journal of environmental psychology , 64 , 78-97.
Martin, F., Sun, T., & Westine, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018. Computers & education , 159 , 104009.
Mavilidi, M. F., Ruiter, M., Schmidt, M., Okely, A. D., Loyens, S., Chandler, P., & Paas, F. (2018). A narrative review of school-based physical activity for enhancing cognition and learning: The importance of relevancy and integration. Frontiers in psychology , 2079.
Patterson, G. T., Chung, I. W., & Swan, P. W. (2014). Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits: A meta-analysis. Journal of experimental criminology , 10 , 487-513.
Reith, T. P. (2018). Burnout in United States healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Cureus , 10 (12).
Ritchie, S. J., & Tucker-Drob, E. M. (2018). How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological science , 29 (8), 1358-1369.
Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 3087.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., & Smolander, K. (2016). Where is current research on blockchain technology?—a systematic review. PloS one , 11 (10), e0163477.
Zestcott, C. A., Blair, I. V., & Stone, J. (2016). Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 19 (4), 528-542

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Free Social Skills Worksheets
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7 Writing a Literature Review
Hundreds of original investigation research articles on health science topics are published each year. It is becoming harder and harder to keep on top of all new findings in a topic area and – more importantly – to work out how they all fit together to determine our current understanding of a topic. This is where literature reviews come in.
In this chapter, we explain what a literature review is and outline the stages involved in writing one. We also provide practical tips on how to communicate the results of a review of current literature on a topic in the format of a literature review.
7.1 What is a literature review?

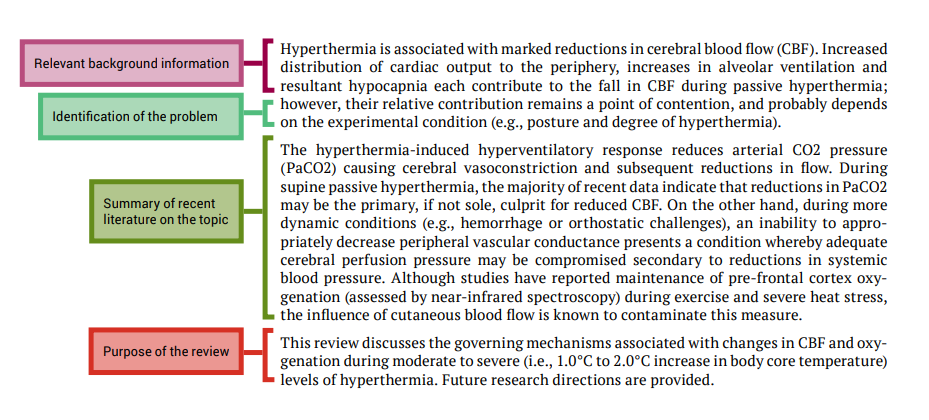
Literature reviews provide a synthesis and evaluation of the existing literature on a particular topic with the aim of gaining a new, deeper understanding of the topic.
Published literature reviews are typically written by scientists who are experts in that particular area of science. Usually, they will be widely published as authors of their own original work, making them highly qualified to author a literature review.
However, literature reviews are still subject to peer review before being published. Literature reviews provide an important bridge between the expert scientific community and many other communities, such as science journalists, teachers, and medical and allied health professionals. When the most up-to-date knowledge reaches such audiences, it is more likely that this information will find its way to the general public. When this happens, – the ultimate good of science can be realised.
A literature review is structured differently from an original research article. It is developed based on themes, rather than stages of the scientific method.
In the article Ten simple rules for writing a literature review , Marco Pautasso explains the importance of literature reviews:
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications. For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively. Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests. Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read. For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way (Pautasso, 2013, para. 1).
An example of a literature review is shown in Figure 7.1.
Video 7.1: What is a literature review? [2 mins, 11 secs]
Watch this video created by Steely Library at Northern Kentucky Library called ‘ What is a literature review? Note: Closed captions are available by clicking on the CC button below.
Examples of published literature reviews
- Strength training alone, exercise therapy alone, and exercise therapy with passive manual mobilisation each reduce pain and disability in people with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review
- Traveler’s diarrhea: a clinical review
- Cultural concepts of distress and psychiatric disorders: literature review and research recommendations for global mental health epidemiology
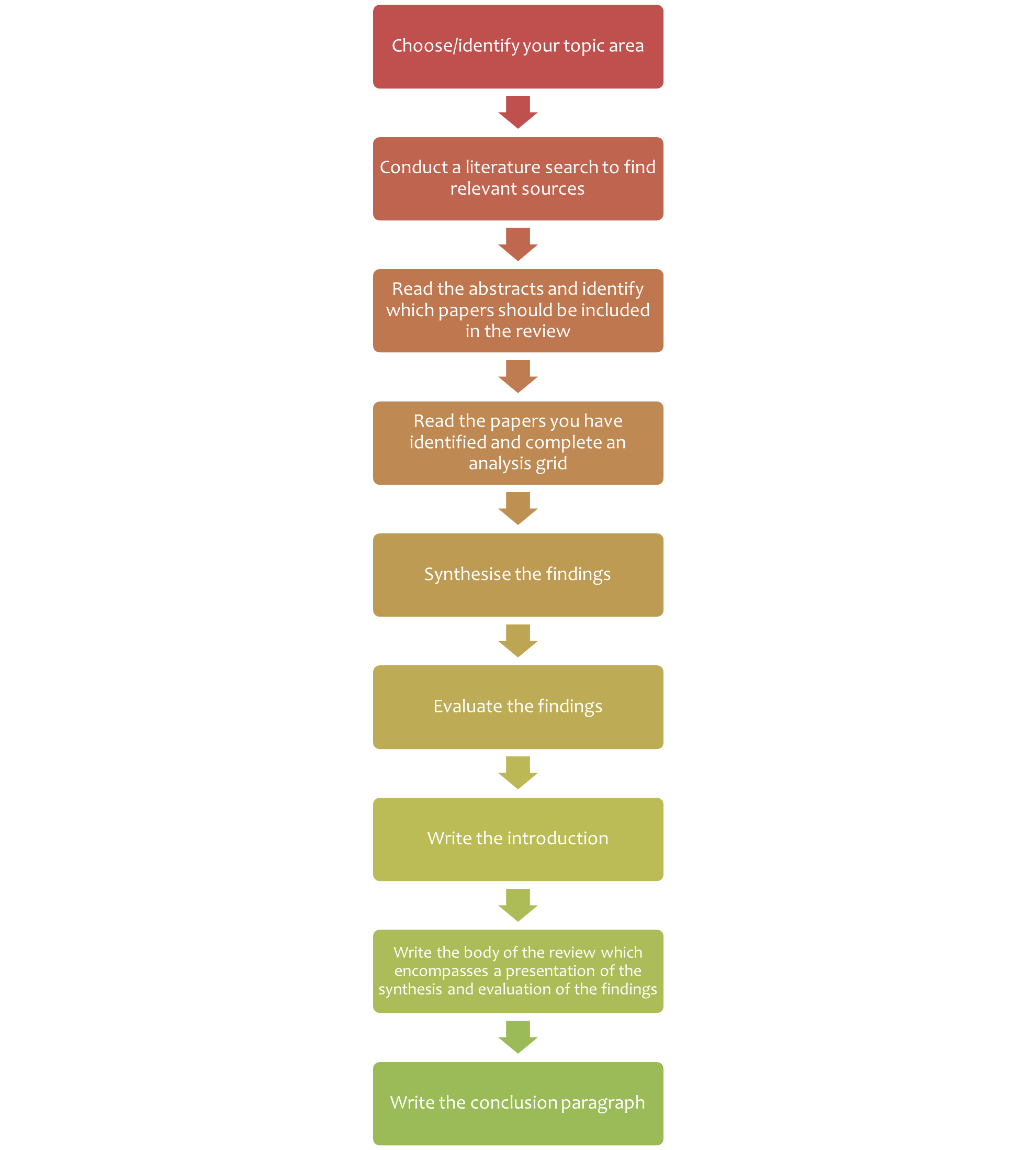
7.2 Steps of writing a literature review
Writing a literature review is a very challenging task. Figure 7.2 summarises the steps of writing a literature review. Depending on why you are writing your literature review, you may be given a topic area, or may choose a topic that particularly interests you or is related to a research project that you wish to undertake.
Chapter 6 provides instructions on finding scientific literature that would form the basis for your literature review.
Once you have your topic and have accessed the literature, the next stages (analysis, synthesis and evaluation) are challenging. Next, we look at these important cognitive skills student scientists will need to develop and employ to successfully write a literature review, and provide some guidance for navigating these stages.
Analysis, synthesis and evaluation
Analysis, synthesis and evaluation are three essential skills required by scientists and you will need to develop these skills if you are to write a good literature review ( Figure 7.3 ). These important cognitive skills are discussed in more detail in Chapter 9.
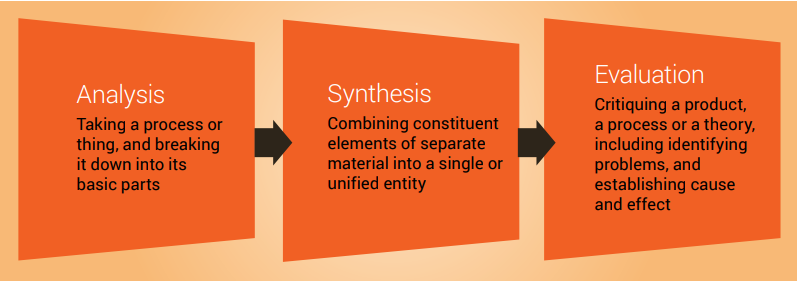
The first step in writing a literature review is to analyse the original investigation research papers that you have gathered related to your topic.
Analysis requires examining the papers methodically and in detail, so you can understand and interpret aspects of the study described in each research article.
An analysis grid is a simple tool you can use to help with the careful examination and breakdown of each paper. This tool will allow you to create a concise summary of each research paper; see Table 7.1 for an example of an analysis grid. When filling in the grid, the aim is to draw out key aspects of each research paper. Use a different row for each paper, and a different column for each aspect of the paper ( Tables 7.2 and 7.3 show how completed analysis grid may look).
Before completing your own grid, look at these examples and note the types of information that have been included, as well as the level of detail. Completing an analysis grid with a sufficient level of detail will help you to complete the synthesis and evaluation stages effectively. This grid will allow you to more easily observe similarities and differences across the findings of the research papers and to identify possible explanations (e.g., differences in methodologies employed) for observed differences between the findings of different research papers.
Table 7.1: Example of an analysis grid
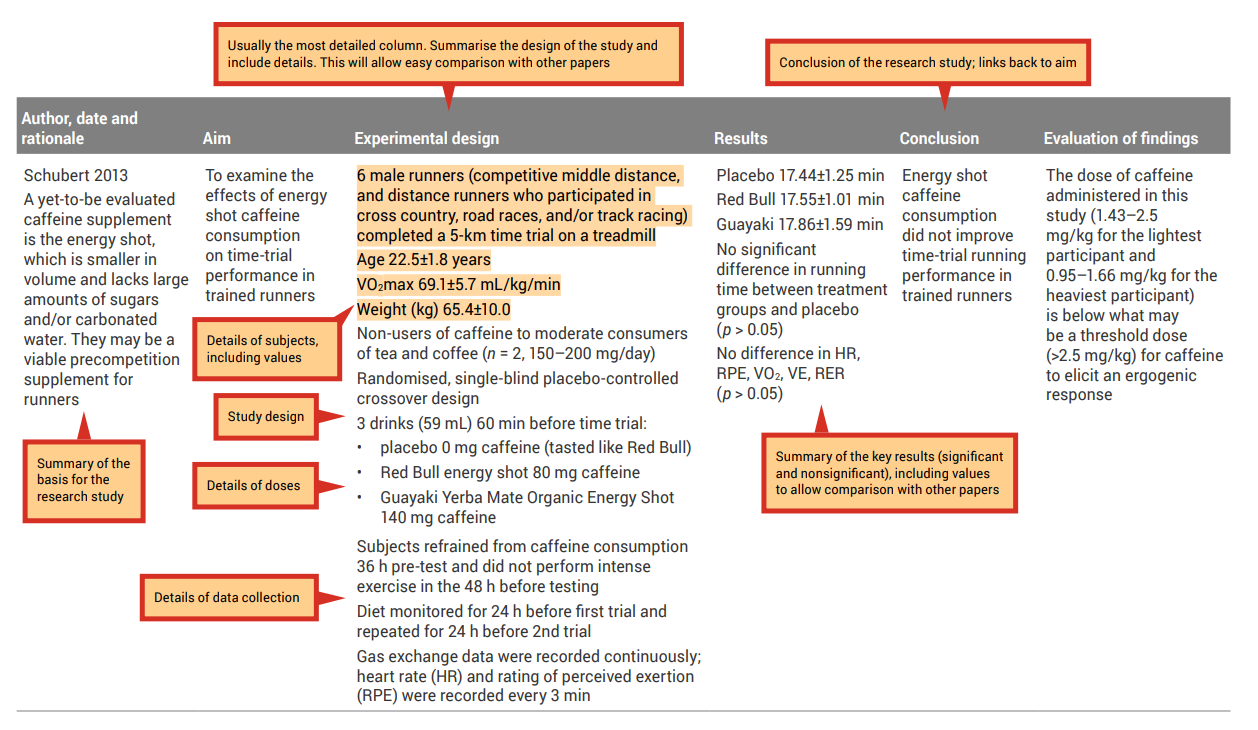
Table 7.3: Sample filled-in analysis grid for research article by Ping and colleagues
Source: Ping, WC, Keong, CC & Bandyopadhyay, A 2010, ‘Effects of acute supplementation of caffeine on cardiorespiratory responses during endurance running in a hot and humid climate’, Indian Journal of Medical Research, vol. 132, pp. 36–41. Used under a CC-BY-NC-SA licence.
Step two of writing a literature review is synthesis.
Synthesis describes combining separate components or elements to form a connected whole.
You will use the results of your analysis to find themes to build your literature review around. Each of the themes identified will become a subheading within the body of your literature review.
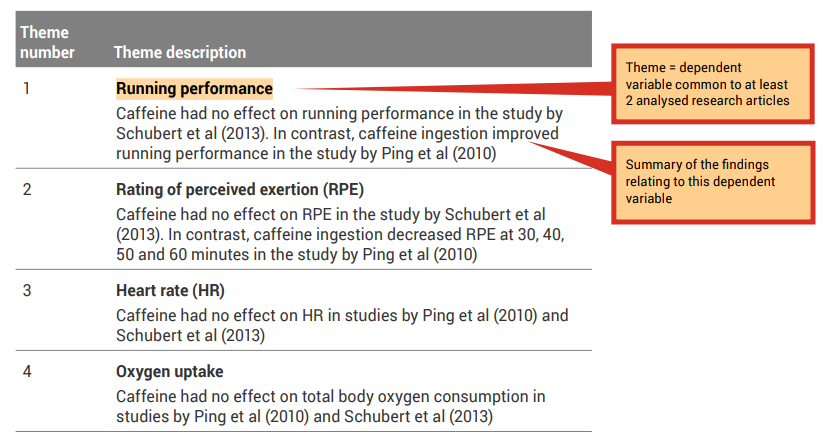
A good place to start when identifying themes is with the dependent variables (results/findings) that were investigated in the research studies.
Because all of the research articles you are incorporating into your literature review are related to your topic, it is likely that they have similar study designs and have measured similar dependent variables. Review the ‘Results’ column of your analysis grid. You may like to collate the common themes in a synthesis grid (see, for example Table 7.4 ).
Step three of writing a literature review is evaluation, which can only be done after carefully analysing your research papers and synthesising the common themes (findings).
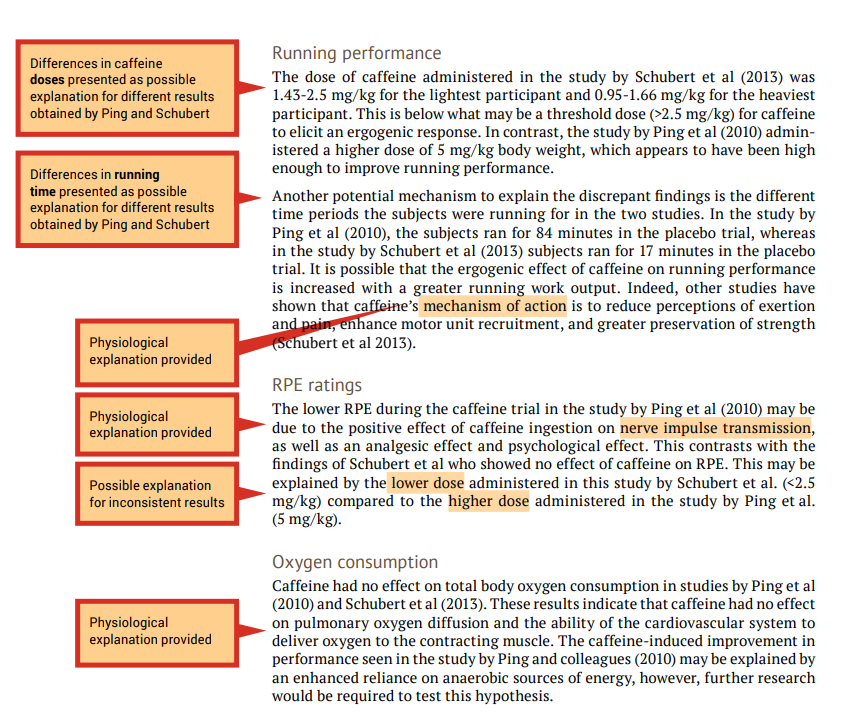
During the evaluation stage, you are making judgements on the themes presented in the research articles that you have read. This includes providing physiological explanations for the findings. It may be useful to refer to the discussion section of published original investigation research papers, or another literature review, where the authors may mention tested or hypothetical physiological mechanisms that may explain their findings.
When the findings of the investigations related to a particular theme are inconsistent (e.g., one study shows that caffeine effects performance and another study shows that caffeine had no effect on performance) you should attempt to provide explanations of why the results differ, including physiological explanations. A good place to start is by comparing the methodologies to determine if there are any differences that may explain the differences in the findings (see the ‘Experimental design’ column of your analysis grid). An example of evaluation is shown in the examples that follow in this section, under ‘Running performance’ and ‘RPE ratings’.
When the findings of the papers related to a particular theme are consistent (e.g., caffeine had no effect on oxygen uptake in both studies) an evaluation should include an explanation of why the results are similar. Once again, include physiological explanations. It is still a good idea to compare methodologies as a background to the evaluation. An example of evaluation is shown in the following under ‘Oxygen consumption’.
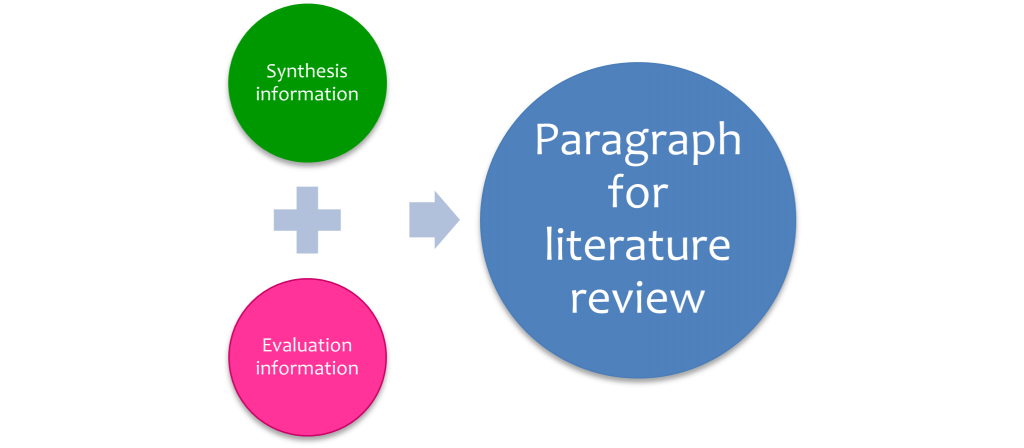
7.3 Writing your literature review
Once you have completed the analysis, and synthesis grids and written your evaluation of the research papers , you can combine synthesis and evaluation information to create a paragraph for a literature review ( Figure 7.4 ).
The following paragraphs are an example of combining the outcome of the synthesis and evaluation stages to produce a paragraph for a literature review.
Note that this is an example using only two papers – most literature reviews would be presenting information on many more papers than this ( (e.g., 106 papers in the review article by Bain and colleagues discussed later in this chapter). However, the same principle applies regardless of the number of papers reviewed.

The next part of this chapter looks at the each section of a literature review and explains how to write them by referring to a review article that was published in Frontiers in Physiology and shown in Figure 7.1. Each section from the published article is annotated to highlight important features of the format of the review article, and identifies the synthesis and evaluation information.
In the examination of each review article section we will point out examples of how the authors have presented certain information and where they display application of important cognitive processes; we will use the colour code shown below:

This should be one paragraph that accurately reflects the contents of the review article.
Introduction
The introduction should establish the context and importance of the review

Body of literature review
The reference section provides a list of the references that you cited in the body of your review article. The format will depend on the journal of publication as each journal has their own specific referencing format.
It is important to accurately cite references in research papers to acknowledge your sources and ensure credit is appropriately given to authors of work you have referred to. An accurate and comprehensive reference list also shows your readers that you are well-read in your topic area and are aware of the key papers that provide the context to your research.
It is important to keep track of your resources and to reference them consistently in the format required by the publication in which your work will appear. Most scientists will use reference management software to store details of all of the journal articles (and other sources) they use while writing their review article. This software also automates the process of adding in-text references and creating a reference list. In the review article by Bain et al. (2014) used as an example in this chapter, the reference list contains 106 items, so you can imagine how much help referencing software would be. Chapter 5 shows you how to use EndNote, one example of reference management software.
Click the drop down below to review the terms learned from this chapter.
Copyright note:
- The quotation from Pautasso, M 2013, ‘Ten simple rules for writing a literature review’, PLoS Computational Biology is use under a CC-BY licence.
- Content from the annotated article and tables are based on Schubert, MM, Astorino, TA & Azevedo, JJL 2013, ‘The effects of caffeinated ‘energy shots’ on time trial performance’, Nutrients, vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 2062–2075 (used under a CC-BY 3.0 licence ) and P ing, WC, Keong , CC & Bandyopadhyay, A 2010, ‘Effects of acute supplementation of caffeine on cardiorespiratory responses during endurance running in a hot and humid climate’, Indian Journal of Medical Research, vol. 132, pp. 36–41 (used under a CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 licence ).
Bain, A.R., Morrison, S.A., & Ainslie, P.N. (2014). Cerebral oxygenation and hyperthermia. Frontiers in Physiology, 5 , 92.
Pautasso, M. (2013). Ten simple rules for writing a literature review. PLoS Computational Biology, 9 (7), e1003149.
How To Do Science Copyright © 2022 by University of Southern Queensland is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Science Literature Review Example: A Comprehensive Guide
A literature review is a crucial component of scientific research, serving as a foundation for understanding the current state of knowledge in a particular field. It involves analyzing, synthesizing, and critically evaluating existing research to identify gaps, trends, and potential areas for further investigation.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of conducting a science literature review, providing examples and insights to help you master this essential skill.
What You'll Learn
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a systematic survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing researchers to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. The primary purposes of a literature review include:
- Demonstrating your knowledge of the research topic
- Identifying the most relevant and significant studies in your field
- Establishing a theoretical framework for your research
- Identifying contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the literature
- Providing a context for your research within the existing body of knowledge
Example: In a study on the effects of climate change on coral reefs, a literature review might begin with:
“This literature review examines the current state of knowledge regarding the impacts of climate change on coral reef ecosystems. It synthesizes findings from peer-reviewed articles published between 2000 and 2023, focusing on three main areas: ocean acidification, rising sea temperatures, and extreme weather events. By analyzing these studies, we aim to identify trends, gaps, and potential areas for future research in coral reef conservation.”
Types of Literature Reviews
There are several types of literature reviews, each serving a specific purpose in scientific research:
1. Narrative Review
A narrative review provides a comprehensive overview of a topic, synthesizing the available literature to tell a story about the current state of knowledge. It is often used to introduce a research topic or provide background information.
Example: “The Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance: A Narrative Review” might cover the history of antibiotic discovery, mechanisms of resistance, and current challenges in combating resistant bacteria.
2. Systematic Review
A systematic review follows a rigorous, predefined protocol to identify, select, and critically appraise relevant research. It often includes a meta-analysis of quantitative data from multiple studies.
Example: “The Efficacy of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis” would outline specific inclusion criteria, search strategies, and statistical methods used to analyze the combined results of multiple clinical trials.
3. Meta-Analysis
A meta-analysis is a statistical approach to combining the results of multiple studies, providing a quantitative summary of the evidence.
Example: “The Impact of Exercise on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: A Meta-Analysis” would use statistical techniques to synthesize data from various studies, calculating an overall effect size for the relationship between exercise and cognitive performance.
4. Scoping Review
A scoping review aims to map the key concepts, types of evidence, and gaps in research related to a specific area. It is often used to determine the feasibility of a full systematic review.
Example: “Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: A Scoping Review” might explore the breadth of AI applications across different medical specialties, identifying areas where more research is needed.
Steps to Conduct a Literature Review
1. define your research question.
The first step in conducting a literature review is to clearly define your research question or topic. This will guide your search for relevant literature and help you focus your review.
Example: Research Question: “How does microplastic pollution affect marine ecosystems?”

2. Develop a Search Strategy
Create a comprehensive search strategy to identify relevant literature. This includes:
- Choosing appropriate databases (e.g., PubMed, Web of Science, Google Scholar)
- Selecting keywords and search terms
- Defining inclusion and exclusion criteria
Example Search Strategy: Databases: Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar Keywords: microplastic*, marine ecosystem*, ocean*, pollution, impact*, effect* Inclusion Criteria: Peer-reviewed articles published between 2010-2023, English language Exclusion Criteria: Studies focused solely on freshwater ecosystems, conference abstracts
3. Conduct the Literature Search
Execute your search strategy across the chosen databases. Keep a detailed record of your search process, including the databases searched, search terms used, and the number of results obtained.
Example: “The initial search in Web of Science using the keywords ‘microplastic* AND marine ecosystem*’ yielded 782 results. After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 245 articles were selected for further review.”
4. Screen and Select Relevant Studies
Review the titles and abstracts of the search results to identify studies that meet your inclusion criteria. For those that seem relevant, obtain and review the full text to determine if they should be included in your review.
Example: “Of the 245 articles identified, 87 were selected for full-text review based on their relevance to the research question. After thorough examination, 52 studies were included in the final literature review.”
5. Analyze and Synthesize the Literature
Critically evaluate the selected studies, considering factors such as research design, methodology, sample size, and findings. Look for patterns, themes, and contradictions across the literature.
Example: “Analysis of the 52 included studies revealed three main themes: (1) the physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms, (2) the chemical effects of microplastic-associated pollutants, and (3) the potential for microplastics to act as vectors for invasive species and pathogens.”
6. Organize Your Findings
Structure your literature review in a logical manner, typically moving from general to specific information. You might organize your review chronologically, thematically, or methodologically, depending on your research question and the nature of the literature.
Example Organization (Thematic):
- Introduction to microplastic pollution in marine ecosystems
- Physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms
- Chemical effects of microplastic-associated pollutants
- Microplastics as vectors for invasive species and pathogens
- Gaps in current knowledge and future research directions
7. Write the Review
Begin writing your literature review, synthesizing the information you’ve gathered. Be sure to:
- Provide a clear introduction and conclusion
- Use appropriate citations and references
- Maintain a critical and analytical perspective throughout
- Highlight gaps in the literature and areas for future research
Example Introduction: “This literature review examines the current state of knowledge regarding the impacts of microplastic pollution on marine ecosystems. Over the past decade, microplastics have emerged as a significant environmental concern, with potential far-reaching consequences for marine life and ocean health. This review synthesizes findings from 52 peer-reviewed studies published between 2010 and 2023, focusing on three main areas: physical impacts on marine organisms, chemical effects of associated pollutants, and the role of microplastics as vectors for invasive species and pathogens. By analyzing these studies, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview of the current understanding of microplastic pollution in marine ecosystems and identify critical areas for future research.”
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Literature Reviews
1. lack of critical analysis.
A common pitfall is simply summarizing studies without providing critical analysis. Avoid this by evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of each study and considering how they contribute to the overall understanding of your topic.
Example of Critical Analysis: “While Smith et al. (2020) reported a significant correlation between microplastic ingestion and reduced growth rates in blue mussels, their small sample size (n=30) limits the generalizability of these findings. In contrast, Jones and Lee (2022) conducted a more robust study with a larger sample size (n=500) across multiple species, providing stronger evidence for the broader impacts of microplastic ingestion on bivalve growth.”
2. Overreliance on Secondary Sources
Relying too heavily on review articles or textbooks instead of primary research can lead to a superficial understanding of the topic. Always aim to read and cite original research papers.
Example: Instead of citing a review article that mentions a study, locate and read the original research paper. This allows you to critically evaluate the methodology and findings firsthand.
3. Ignoring Contradictory Evidence
Failing to address studies that contradict your main argument can weaken your review. Acknowledge conflicting findings and discuss possible reasons for these discrepancies.
Example: “While the majority of studies reviewed found negative impacts of microplastics on marine organisms, Zhang et al. (2021) reported no significant effects on the growth or reproduction of certain zooplankton species. This contradictory finding highlights the complexity of microplastic impacts and the need for species-specific investigations.”
4. Poor Organization
A disorganized literature review can be confusing and difficult to follow. Ensure your review has a clear structure and logical flow.
Example of Good Organization:
- Introduction: State the purpose and scope of the review
- Background: Provide context on microplastic pollution
- Methodology: Explain how studies were selected and analyzed
- Main Body: Organize findings into themes or categories a. Physical impacts on marine organisms b. Chemical effects of associated pollutants c. Microplastics as vectors for invasive species and pathogens
- Discussion: Synthesize findings, identify gaps, and suggest future research directions
- Conclusion: Summarize key points and broader implications
5. Outdated Sources
Relying on outdated sources can lead to an inaccurate representation of the current state of knowledge. Ensure you include recent studies alongside seminal works in the field.
Example: “While Carson’s (1962) seminal work ‘Silent Spring’ laid the foundation for understanding marine pollution, recent studies by Johnson et al. (2022) and Liu and Chen (2023) provide crucial updates on the specific impacts of microplastics on marine food webs.”
Related article;
8 Tips for Writing a Scientific Literature Review Article
Literature Review Generator
Tips for Writing an Effective Literature Review
1. start with a clear focus.
Begin your literature review with a well-defined research question or objective. This will guide your search and help you maintain relevance throughout the review.
Example: Research Objective: “To synthesize current knowledge on the impacts of microplastic pollution on marine ecosystems and identify key areas for future research.”
2. Use a Systematic Approach
Develop a clear methodology for searching, selecting, and analyzing literature. This enhances the reproducibility and credibility of your review.
Example: “We conducted a systematic search of Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar using predefined keywords and inclusion criteria. The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) framework was used to ensure a comprehensive and transparent review process.”
3. Maintain a Critical Perspective
Critically evaluate the strengths and limitations of each study you include. Consider factors such as methodology, sample size, and potential biases.
Example: “While Brown et al. (2019) provided valuable insights into microplastic ingestion by marine mammals, their reliance on stranded animals may have introduced selection bias, potentially overestimating the prevalence of microplastic ingestion in healthy populations.”
4. Synthesize Information
Don’t just summarize individual studies; look for patterns, themes, and relationships across the literature. Identify areas of consensus and controversy.
Example: “Synthesis of the reviewed studies reveals a growing consensus on the negative impacts of microplastics on marine organisms at the individual level. However, there remains considerable debate regarding the long-term consequences for population dynamics and ecosystem functioning.”
5. Identify Gaps and Future Directions
Highlight areas where further research is needed and suggest potential avenues for future studies.
Example: “While numerous studies have examined microplastic ingestion in marine organisms, there is a notable lack of research on the potential transfer of microplastics through marine food webs. Future studies should focus on trophic transfer and biomagnification of microplastics and associated pollutants.”
6. Use Clear and Concise Language
Write in a clear, scientific style. Avoid jargon where possible, and explain complex concepts when necessary.
Example: Instead of: “The bioaccumulation of anthropogenic polymeric detritus in marine biota is a burgeoning concern.” Write: “The buildup of human-made plastic particles in marine organisms is an increasing worry for scientists and policymakers.”
7. Proper Citation and Referencing
Ensure all sources are properly cited and referenced according to the required style guide (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
Example: In-text citation: (Smith et al., 2022) Reference list entry: Smith, J., Johnson, A., & Lee, M. (2022). Microplastic pollution in the Pacific Ocean: A comprehensive review. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 175, 113371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113371
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Post navigation
Previous post.
📕 Studying HQ
Typically replies within minutes
Hey! 👋 Need help with an assignment?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us

Literature Reviews
- General overview of Literature Reviews
- What should a Literature Review include?
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- Research - Getting Started
Online Resources
- CWU Learning Commons: Writing Resources
- Purdue OWL: Writing a Literature Review
Literature Reviews Examples
Social Sciences examples
- Psychology study In this example, the literature review can be found on pages 1086-1089, stopping at the section labeled "Aims and Hypotheses".
- Law and Justice study In this example, the literature review can be found on pages 431-449, stopping at the section labeled "Identifying and Evaluating the Impacts of the Prisoners' Rights Movement". This article uses a historical literature review approach.
- Anthropology study The literature review in this article runs from page 218 at the heading "Between Critique and Enchantment" and ends on page 221 before the heading "The Imagination as a Dimension of Reality".
Hard Science examples
- Physics article The literature review in this paper can be found in the Introduction section, ending at the section titled "Experimental procedure".
- Health Science article The literature review in this article is located at the beginning, before the Methods section.
Arts and Humanities examples
- Composition paper In this example, the literature review has its own dedicated section titled "Literature Review" on pages 2-3.
- Political geography paper The literature review in this paper is located in the introduction section.
Standalone Literature Review examples
- Project-based learning: A review of the literature
- Mental health and gender dysphoria: A review of the literature
- Academic engagement and commercialisation: A review of the literature on university–industry relations
- << Previous: What should a Literature Review include?
- Next: Research - Getting Started >>
- Last Updated: Sep 18, 2024 9:14 AM
- URL: https://libguides.lib.cwu.edu/LiteratureReviews
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
Note: These are sample literature reviews from a class that were given to us by an instructor when APA 6th edition was still in effect. These were excellent papers from her class, but it does not mean they are perfect or contain no errors. Thanks to the students who let us post!
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Oct 18, 2024 9:43 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview
- Privacy Policy

Home » Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents
A literature review is an essential part of research that surveys existing studies on a topic, providing a foundation and context for new research. It identifies gaps, highlights trends, and establishes a basis for the study’s research questions. This guide explains the types of literature reviews, offers a step-by-step writing guide, and includes examples to help you write a comprehensive and effective review.

Literature Review
A literature review synthesizes and evaluates previous research on a topic. It involves collecting relevant studies, analyzing their findings, and summarizing the knowledge gained. By conducting a literature review, researchers can establish their research within the broader academic conversation, showing how their study builds on or diverges from existing work.
Purposes of a Literature Review :
- Establish Context : Show the current state of research in the field.
- Identify Gaps : Highlight areas that need further investigation.
- Support Research Goals : Provide a foundation for research questions or hypotheses.
- Prevent Redundancy : Avoid duplicating existing studies by understanding what has already been done.
Types of Literature Reviews
1. narrative (traditional) literature review.
- Provides a comprehensive summary of the literature on a topic without a specific research question.
- Commonly used to establish context, it discusses broad themes and trends.
- Example : A narrative review on mental health might cover various treatment approaches and outcomes without a specific focus.
2. Systematic Literature Review
- Involves a structured, replicable process to collect, evaluate, and summarize relevant studies.
- Includes specific criteria for selecting studies and aims to answer a focused research question.
- Example : A systematic review on the effects of cognitive-behavioral therapy on anxiety would detail the selection process, inclusion criteria, and statistical findings.
3. Meta-Analysis
- A subtype of a systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine findings from multiple studies, providing quantitative insights.
- Example : A meta-analysis of studies on the impact of exercise on stress relief might provide an average effect size across all studies.
4. Theoretical Literature Review
- Focuses on evaluating theoretical frameworks, models, and key concepts rather than empirical data.
- Useful for exploring theories that guide research in specific fields.
- Example : Reviewing theories of motivation in education to understand which are most applicable to modern teaching practices.
5. Scoping Review
- Maps the breadth of literature on a broad topic without the rigor of a systematic review.
- Used to identify research gaps and potential areas for future study.
- Example : A scoping review of digital marketing practices in e-commerce might explore various strategies and technologies without evaluating outcomes.
6. Integrative Literature Review
- Integrates and synthesizes both qualitative and quantitative studies to provide a broad understanding of a topic.
- Useful for establishing new theoretical frameworks or identifying broad trends.
- Example : An integrative review on employee engagement could analyze surveys, interviews, and case studies to create a cohesive view of engagement factors.
Writing Guide for a Literature Review
Step 1: define your research scope and purpose.
Start by clarifying the purpose and scope of your literature review. Determine whether you are conducting a broad overview or focusing on specific questions or theories.
Example : “This literature review examines the relationship between social media use and mental health, focusing on how social media impacts self-esteem and anxiety.”
Step 2: Search for Relevant Literature
Use academic databases like PubMed, JSTOR, and Google Scholar to locate relevant articles. Define your search terms and criteria, and prioritize recent studies or key papers in the field.
- Keywords : Use specific keywords and phrases that are central to your topic.
- Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria : Define parameters for the studies you will include, such as publication date, sample size, or methodology.
Example : For a review on employee motivation, keywords might include “employee engagement,” “motivation in the workplace,” and “job satisfaction.”
Step 3: Organize and Summarize Key Themes
Read each study carefully and take notes on significant findings, methodologies, and limitations. Identify recurring themes, patterns, or controversies and organize the literature based on these insights.
Example : Themes in a review on remote work might include productivity, work-life balance, and mental health.
Step 4: Develop an Outline
Structure your literature review to maintain logical flow and readability. A typical outline includes:
- Introduction : Briefly introduce the topic, purpose, and scope of the review.
- Thematic Sections : Divide the review into sections based on themes or research approaches.
- Conclusion : Summarize findings, highlight research gaps, and suggest future research directions.
Example Outline for a Literature Review on Mental Health :
- Introduction
- Impact of Social Media on Self-Esteem
- Social Media’s Role in Anxiety and Depression
- Gaps in the Literature and Future Directions
Step 5: Analyze and Synthesize the Literature
Go beyond summarizing by comparing studies, analyzing their results, and synthesizing insights. Highlight consistencies, contradictions, or unique findings that contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Example : Discuss how different studies on cognitive-behavioral therapy report varying levels of effectiveness for depression, based on factors like sample size or intervention duration.
Step 6: Write the Literature Review
Following your outline, write each section of the literature review. Ensure that each paragraph flows logically and builds on previous sections. Use direct quotes sparingly and focus on paraphrasing findings to maintain your narrative.
- Introduction : Present an overview of the topic, importance, and objectives.
- Body : Detail each theme, comparing and contrasting findings.
- Conclusion : Summarize the main findings, acknowledge gaps, and suggest areas for further study.
Step 7: Cite Sources and Format Properly
Use consistent citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) and include a reference list of all sources. Proper referencing gives credit to authors and strengthens the credibility of your review.
Example of a Literature Review Excerpt
Title : Literature Review on the Effects of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health
Introduction Social media has become an integral part of adolescents’ lives, influencing their mental health and well-being. This literature review explores how social media affects self-esteem and anxiety among adolescents, summarizing studies conducted over the past decade.
Social Media and Self-Esteem Several studies have found that social media can have both positive and negative effects on adolescent self-esteem. For instance, Valkenburg and Peter (2019) observed that positive interactions on social media platforms boost self-esteem, while negative comments contribute to lower self-worth. Conversely, a study by Jackson (2020) indicated that adolescents who frequently compare themselves to others on social media report lower self-esteem overall.
Social Media and Anxiety Anxiety is another psychological issue linked to social media use. Research by Smith et al. (2018) suggests that excessive use of platforms like Instagram is associated with increased anxiety levels, particularly among girls. A meta-analysis by Johnson and Allen (2021) revealed a correlation between time spent on social media and higher levels of anxiety, although it acknowledged that causation could not be definitively established.
Conclusion The reviewed studies highlight both the positive and negative impacts of social media on adolescent mental health. However, gaps remain, particularly regarding longitudinal studies that track these effects over time. Future research should focus on examining the long-term psychological effects of social media use to guide effective interventions.
Tips for Writing an Effective Literature Review
- Be Objective : Avoid personal biases and represent the literature fairly.
- Stay Focused : Stick to the main research question and relevant studies.
- Use Clear Transitions : Ensure a logical flow between sections and ideas.
- Critique, Don’t Just Summarize : Analyze and evaluate studies to highlight strengths and weaknesses.
- Revise and Proofread : Ensure clarity, coherence, and consistency in writing style.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-Reliance on Direct Quotes : Paraphrase to keep your voice consistent.
- Lack of Structure : Use an outline to organize the literature review logically.
- Not Addressing Contradictory Findings : Acknowledge and discuss differing results.
- Ignoring Methodological Differences : Consider how study designs or sample sizes affect findings.
- Failure to Update Sources : Use the most recent and relevant studies to ensure your review is current.
A literature review is a critical component of research that establishes the foundation for your study. By understanding the types of literature reviews and following a structured writing guide, you can create a comprehensive, insightful review that supports your research goals. Whether conducting a systematic review, meta-analysis, or narrative review, a well-crafted literature review not only summarizes existing knowledge but also contributes to academic discourse by identifying research gaps and future directions.
- Booth, A., Sutton, A., & Papaioannou, D. (2016). Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Sage Publications.
- Creswell, J. W. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . Sage Publications.
- Hart, C. (2018). Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Research Imagination . Sage Publications.
- Machi, L. A., & McEvoy, B. T. (2016). The Literature Review: Six Steps to Success . Corwin Press.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...

Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing...

Critical Analysis – Types, Examples and Writing...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Nov 5, 2024 · Example 14: Literature Review in Computer Science In computer science, a literature review might explore the evolution of machine learning algorithms for natural language processing (NLP). The author starts by summarizing the development of early NLP models, such as rule-based systems, and transitions into modern deep learning approaches.
Dec 6, 2023 · For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics. 1. Narrative Review Examples. Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
A literature review is a compilation of current knowledge on a particular topic derived from the critical evaluation of different scholarly sources such as books, articles, and publications, which is then presented in an organized manner to relate to a specific research problem being investigated. It highlights the methods, relevant theories, and gaps in existing research on a particular ...
Dec 14, 2024 · Literature Review Examples: A Step-by-Step Guide for Researchers Transform your literature review writing with proven examples and strategies from successful researchers. Learn how to craft compelling reviews that make an impact, backed by real academic models across multiple disciplines.
The following paragraphs are an example of combining the outcome of the synthesis and evaluation stages to produce a paragraph for a literature review. Note that this is an example using only two papers – most literature reviews would be presenting information on many more papers than this ( (e.g., 106 papers in the review article by Bain and ...
Oct 15, 2024 · A literature review is a crucial component of scientific research, serving as a foundation for understanding the current state of knowledge in a particular field. It involves analyzing, synthesizing, and critically evaluating existing research to identify gaps, trends, and potential areas for further investigation.
May 3, 2024 · Scientific literature review examples showcase how to evaluate and synthesize existing research in a particular field. By analyzing expert opinions, methodologies, and findings, you can better understand a subject and identify gaps to explore.
Sep 18, 2024 · In this example, the literature review can be found on pages 1086-1089, stopping at the section labeled "Aims and Hypotheses". Law and Justice study In this example, the literature review can be found on pages 431-449, stopping at the section labeled "Identifying and Evaluating the Impacts of the Prisoners' Rights Movement".
Oct 18, 2024 · Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
Mar 26, 2024 · Start by clarifying the purpose and scope of your literature review. Determine whether you are conducting a broad overview or focusing on specific questions or theories. Example: “This literature review examines the relationship between social media use and mental health, focusing on how social media impacts self-esteem and anxiety.”